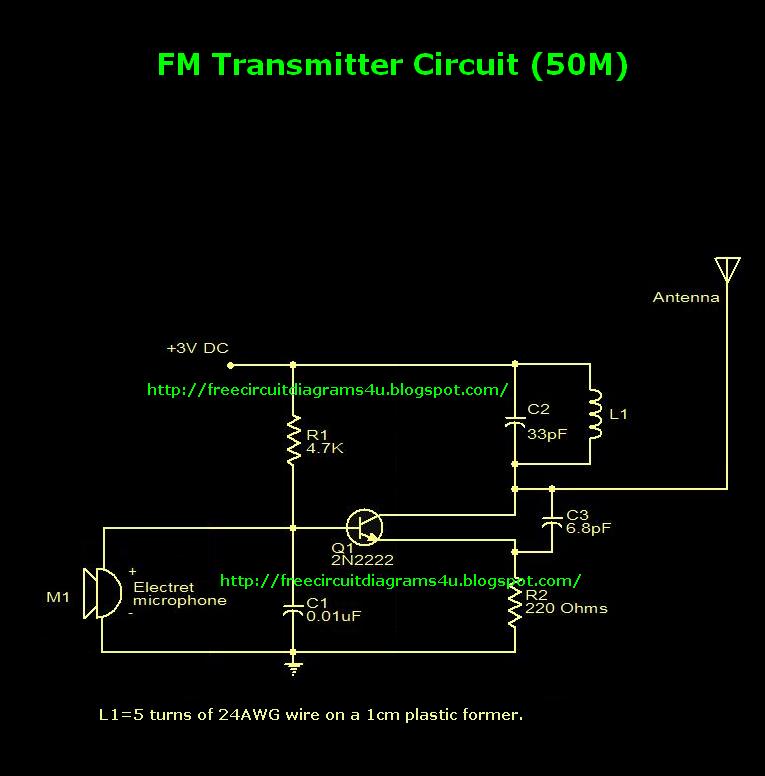
Ir Receiver Circuit
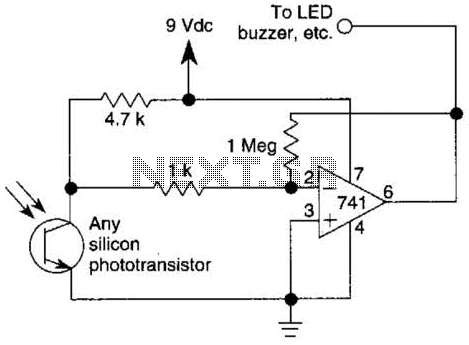
This circuit represents one of the simplest infrared (IR) receivers that can be constructed. The components are inexpensive, the layout is not critical, and a 9-V battery provides a long operational life.
The described IR receiver circuit typically consists of a few essential components: an infrared photodiode or phototransistor, a resistor, and an operational amplifier or a simple transistor for signal amplification. The photodiode detects infrared light emitted by a remote control or other IR source. When exposed to IR light, the photodiode generates a small current, which is then passed through a resistor to develop a voltage signal.
To enhance the sensitivity and range of the circuit, a transistor may be used as an amplifier. In this configuration, the photodiode is connected to the base of the transistor, which is powered by the 9-V battery. The collector of the transistor is connected to the load, which could be an LED or another output device.
The layout of the circuit is not critical, allowing for flexibility in design. However, it is important to keep the connections short to minimize noise and ensure reliable operation. The choice of components, particularly the photodiode or phototransistor, can affect the circuit's performance, including its response time and sensitivity to different wavelengths of infrared light.
Overall, this simple IR receiver circuit is an excellent project for beginners in electronics, providing a practical application of basic principles in photonics and signal amplification. The long-lasting 9-V battery ensures extended use, making it suitable for various applications such as remote control systems, wireless data transmission, and sensor networks. This circuit is just about the simplest IR receiver you can build. The parts are cheap, the layout is not critical, and a 9-V battery will last a long time.
The described IR receiver circuit typically consists of a few essential components: an infrared photodiode or phototransistor, a resistor, and an operational amplifier or a simple transistor for signal amplification. The photodiode detects infrared light emitted by a remote control or other IR source. When exposed to IR light, the photodiode generates a small current, which is then passed through a resistor to develop a voltage signal.
To enhance the sensitivity and range of the circuit, a transistor may be used as an amplifier. In this configuration, the photodiode is connected to the base of the transistor, which is powered by the 9-V battery. The collector of the transistor is connected to the load, which could be an LED or another output device.
The layout of the circuit is not critical, allowing for flexibility in design. However, it is important to keep the connections short to minimize noise and ensure reliable operation. The choice of components, particularly the photodiode or phototransistor, can affect the circuit's performance, including its response time and sensitivity to different wavelengths of infrared light.
Overall, this simple IR receiver circuit is an excellent project for beginners in electronics, providing a practical application of basic principles in photonics and signal amplification. The long-lasting 9-V battery ensures extended use, making it suitable for various applications such as remote control systems, wireless data transmission, and sensor networks. This circuit is just about the simplest IR receiver you can build. The parts are cheap, the layout is not critical, and a 9-V battery will last a long time.