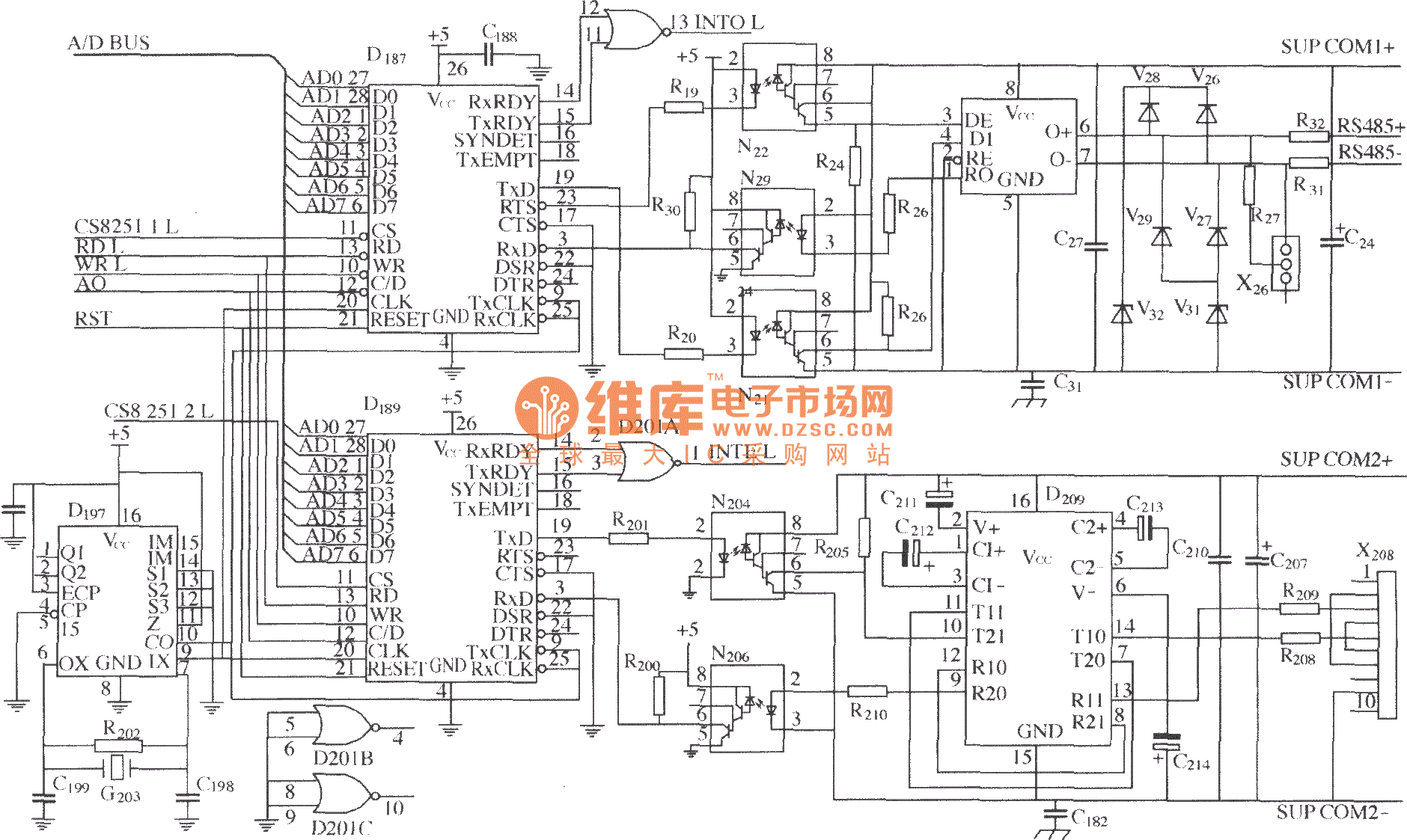
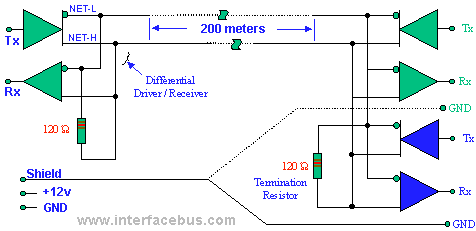
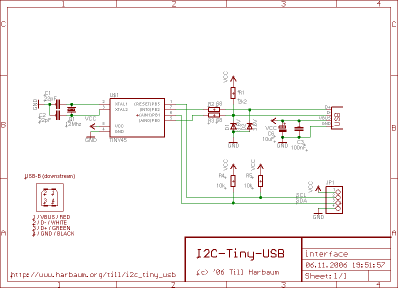
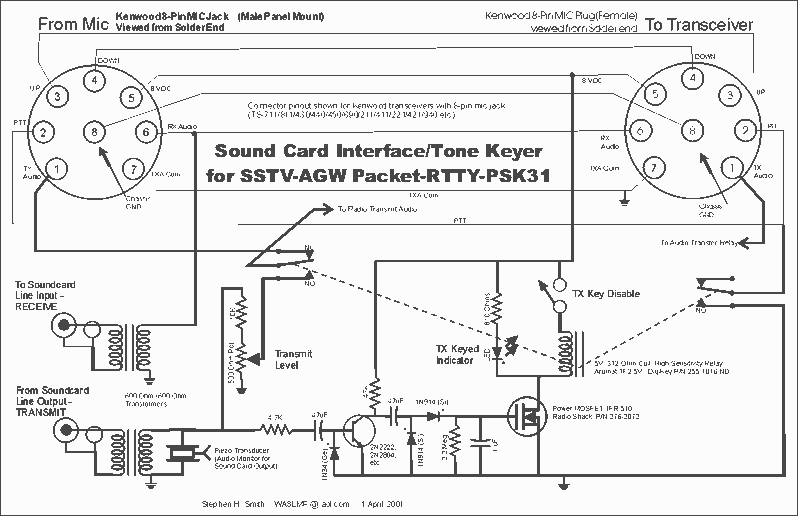
IrDA Interface
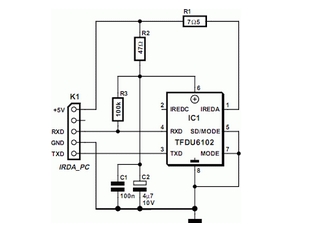
Many modern motherboards are equipped with an infrared data interface compliant with the IrDA standard, but this interface is not very often used.
The infrared data interface, adhering to the Infrared Data Association (IrDA) standard, provides a wireless communication method that allows devices to exchange data over short distances using infrared light. This technology is integrated into many contemporary motherboards, enabling functionalities such as file transfers, remote control operations, and other data exchanges without the need for physical connections.
The IrDA interface typically operates at data rates ranging from 9600 bps to 4 Mbps, depending on the specific implementation and distance between the communicating devices. The standard specifies various protocol layers, including the Physical Layer, Link Layer, and several Application Protocols, ensuring compatibility and interoperability among different devices.
The physical implementation of the IrDA interface on a motherboard usually consists of an infrared transceiver module that includes a light-emitting diode (LED) for transmitting data and a photodiode or phototransistor for receiving data. The transceiver is connected to the motherboard's communication ports, allowing the CPU to manage data transmission and reception through software drivers.
Despite its capabilities, the utilization of the IrDA interface has diminished in favor of more versatile wireless technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, which offer greater range and higher data rates. Nonetheless, the presence of the IrDA interface on modern motherboards serves as a reminder of the evolution of wireless communication technologies and their historical significance in enabling device interconnectivity.Many modern motherboards are equipped with an infrared data interface compliant with the IrDA standard, but this interface not very often used. However, i.. 🔗 External reference
The infrared data interface, adhering to the Infrared Data Association (IrDA) standard, provides a wireless communication method that allows devices to exchange data over short distances using infrared light. This technology is integrated into many contemporary motherboards, enabling functionalities such as file transfers, remote control operations, and other data exchanges without the need for physical connections.
The IrDA interface typically operates at data rates ranging from 9600 bps to 4 Mbps, depending on the specific implementation and distance between the communicating devices. The standard specifies various protocol layers, including the Physical Layer, Link Layer, and several Application Protocols, ensuring compatibility and interoperability among different devices.
The physical implementation of the IrDA interface on a motherboard usually consists of an infrared transceiver module that includes a light-emitting diode (LED) for transmitting data and a photodiode or phototransistor for receiving data. The transceiver is connected to the motherboard's communication ports, allowing the CPU to manage data transmission and reception through software drivers.
Despite its capabilities, the utilization of the IrDA interface has diminished in favor of more versatile wireless technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, which offer greater range and higher data rates. Nonetheless, the presence of the IrDA interface on modern motherboards serves as a reminder of the evolution of wireless communication technologies and their historical significance in enabling device interconnectivity.Many modern motherboards are equipped with an infrared data interface compliant with the IrDA standard, but this interface not very often used. However, i.. 🔗 External reference