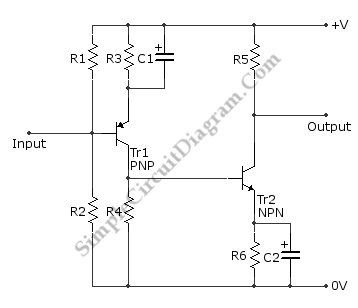
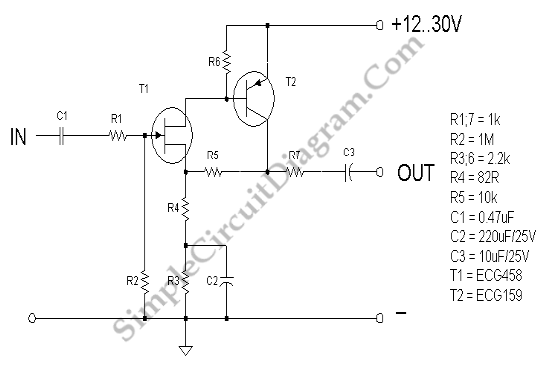
JFET AC Coupled Integrator
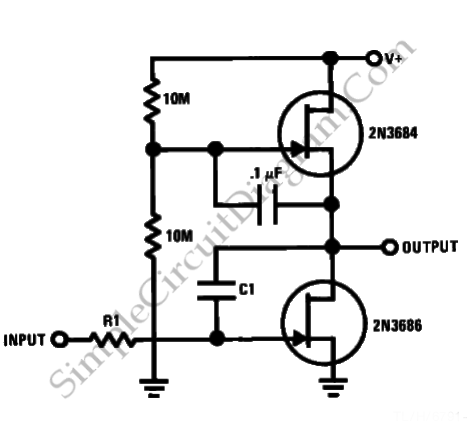
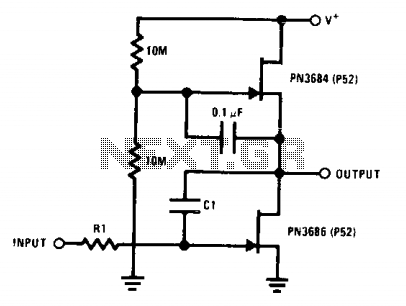
This is a JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit. This circuit is used to achieve very high voltage gain. To achieve very high voltage gain, this circuit uses...
The JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit is designed to provide significant voltage amplification while integrating input signals over time. The core component of this circuit is the Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), which is known for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics, making it ideal for sensitive applications.
The circuit typically consists of a JFET configured in an integrator topology, where the input signal is coupled through a capacitor to the gate of the JFET. This AC coupling allows the circuit to block any DC offset from the input signal, ensuring that only the AC components are processed. The capacitor also plays a critical role in defining the frequency response of the integrator, as it determines the time constant of the integration process.
The output of the JFET is taken from the drain, where a load resistor is connected. This resistor, in conjunction with the JFET's transconductance, sets the gain of the circuit. By adjusting the values of the load resistor and the input capacitor, the circuit can be tuned to achieve the desired voltage gain and frequency response.
Feedback can be implemented in the circuit to stabilize the gain and improve linearity. This is often done by connecting a resistor from the output back to the gate or source of the JFET. The use of feedback not only enhances the performance of the integrator but also helps in reducing distortion, making the circuit suitable for high-fidelity applications.
In summary, the JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit is a powerful tool for achieving high voltage gain while integrating input signals, making it valuable in various electronic applications, including signal processing and analog computation.This is JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit. This circuit is used to achieve very high voltage gain. To achieve very high voltage gain this circuit uses.. 🔗 External reference
The JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit is designed to provide significant voltage amplification while integrating input signals over time. The core component of this circuit is the Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), which is known for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics, making it ideal for sensitive applications.
The circuit typically consists of a JFET configured in an integrator topology, where the input signal is coupled through a capacitor to the gate of the JFET. This AC coupling allows the circuit to block any DC offset from the input signal, ensuring that only the AC components are processed. The capacitor also plays a critical role in defining the frequency response of the integrator, as it determines the time constant of the integration process.
The output of the JFET is taken from the drain, where a load resistor is connected. This resistor, in conjunction with the JFET's transconductance, sets the gain of the circuit. By adjusting the values of the load resistor and the input capacitor, the circuit can be tuned to achieve the desired voltage gain and frequency response.
Feedback can be implemented in the circuit to stabilize the gain and improve linearity. This is often done by connecting a resistor from the output back to the gate or source of the JFET. The use of feedback not only enhances the performance of the integrator but also helps in reducing distortion, making the circuit suitable for high-fidelity applications.
In summary, the JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit is a powerful tool for achieving high voltage gain while integrating input signals, making it valuable in various electronic applications, including signal processing and analog computation.This is JFET AC Coupled Integrator circuit. This circuit is used to achieve very high voltage gain. To achieve very high voltage gain this circuit uses.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713