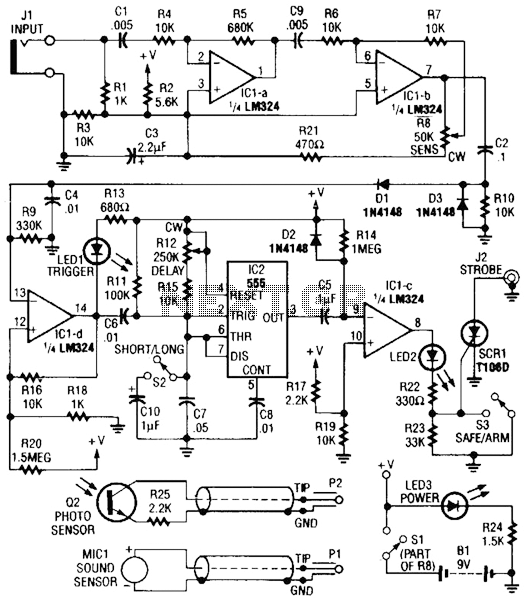
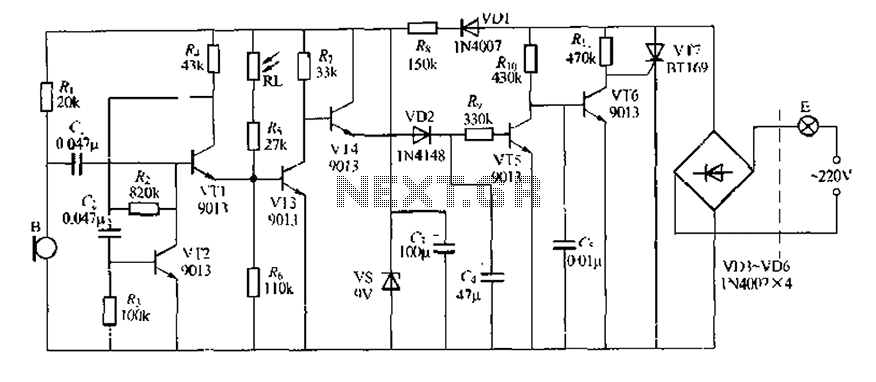
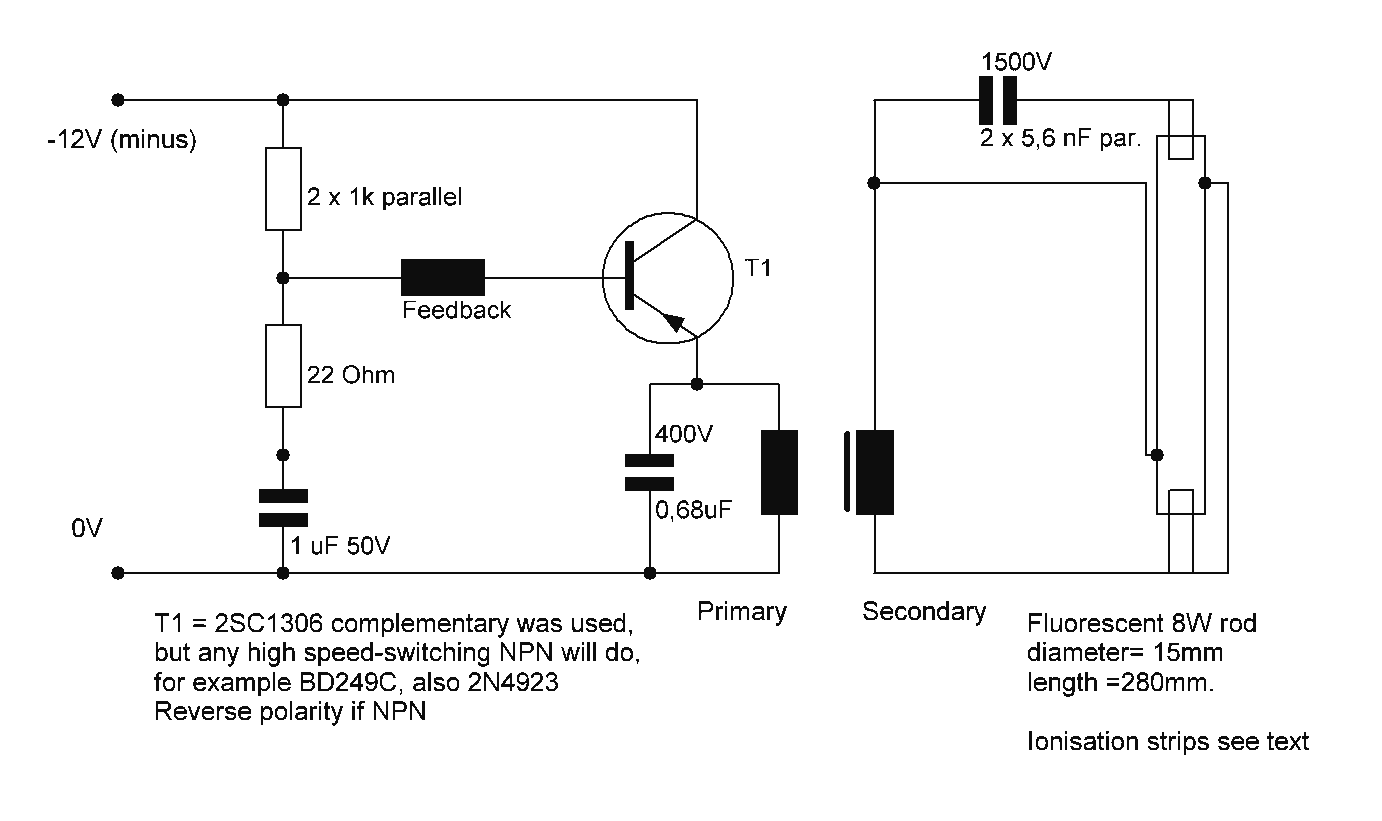
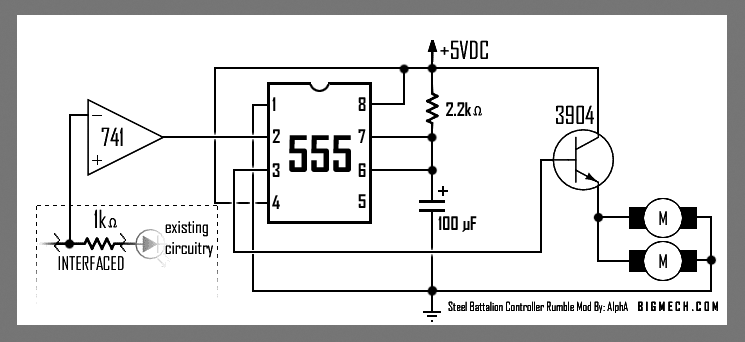
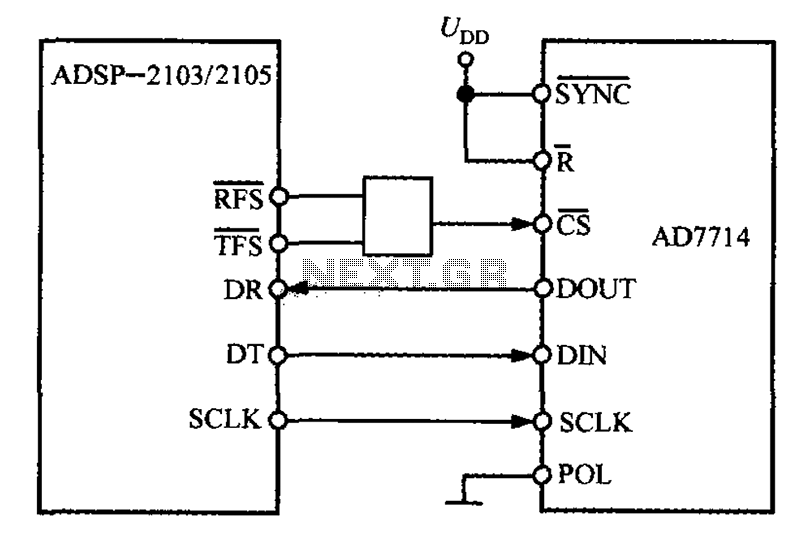
Direct Coupled Discrete Astable Multivibrator circuit
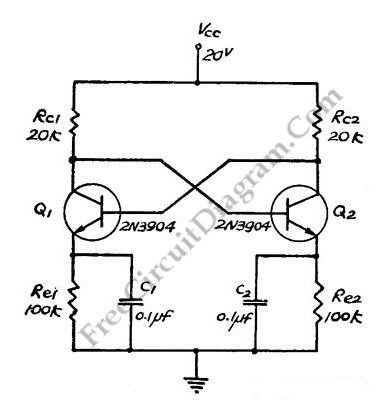
This flip-flop circuit functions as a free-running astable multivibrator, where the bases and collectors of both emitter-biased transistors are directly coupled. The switching action is facilitated by a capacitor in each emitter circuit, resulting in the generation of triangle waves at the emitters. As neither transistor can remain permanently off, free-running oscillations are produced. A single 0.1 µF capacitor can be used between the emitters in place of capacitors C1 and C2.
The described circuit operates as an astable multivibrator, utilizing two NPN transistors configured in a feedback loop. Each transistor's base is connected to the collector of the other, creating a regenerative feedback mechanism essential for continuous oscillation. The capacitors in the emitter circuits play a crucial role in determining the timing characteristics of the oscillation. Specifically, they charge and discharge, causing the transistors to switch states alternately.
In this configuration, the triangle wave output is generated due to the charging and discharging cycles of the capacitors, which control the timing of the transistor switching. The frequency of the oscillation can be adjusted by varying the capacitance of the capacitors or the resistances in the circuit. The use of a single 0.1 µF capacitor simplifies the design, reducing component count while maintaining the functionality of the circuit.
The output can be taken from the emitters of the transistors, where the triangle wave can be utilized in various applications, such as waveform generation, signal modulation, or as a clock signal in digital circuits. Proper biasing of the transistors is essential to ensure they operate in the active region, allowing for stable oscillation without distortion in the output waveform. The circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice for generating oscillating signals in electronic applications.This flip-flop circuit is a free running/astable multivibrator one, with bases and collector of both emitter biased transistor are directly coupled to each other. Switching action is supported by means of capacitor in each emitter circuit. This configuration produce a triangle waves at emitters. Since neither transistor can remain permanently cut off, then a free running oscillation will be generated. We can use single 0. 1 uF capacitor between emitters in place of C1 and C2. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as an astable multivibrator, utilizing two NPN transistors configured in a feedback loop. Each transistor's base is connected to the collector of the other, creating a regenerative feedback mechanism essential for continuous oscillation. The capacitors in the emitter circuits play a crucial role in determining the timing characteristics of the oscillation. Specifically, they charge and discharge, causing the transistors to switch states alternately.
In this configuration, the triangle wave output is generated due to the charging and discharging cycles of the capacitors, which control the timing of the transistor switching. The frequency of the oscillation can be adjusted by varying the capacitance of the capacitors or the resistances in the circuit. The use of a single 0.1 µF capacitor simplifies the design, reducing component count while maintaining the functionality of the circuit.
The output can be taken from the emitters of the transistors, where the triangle wave can be utilized in various applications, such as waveform generation, signal modulation, or as a clock signal in digital circuits. Proper biasing of the transistors is essential to ensure they operate in the active region, allowing for stable oscillation without distortion in the output waveform. The circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice for generating oscillating signals in electronic applications.This flip-flop circuit is a free running/astable multivibrator one, with bases and collector of both emitter biased transistor are directly coupled to each other. Switching action is supported by means of capacitor in each emitter circuit. This configuration produce a triangle waves at emitters. Since neither transistor can remain permanently cut off, then a free running oscillation will be generated. We can use single 0. 1 uF capacitor between emitters in place of C1 and C2. 🔗 External reference