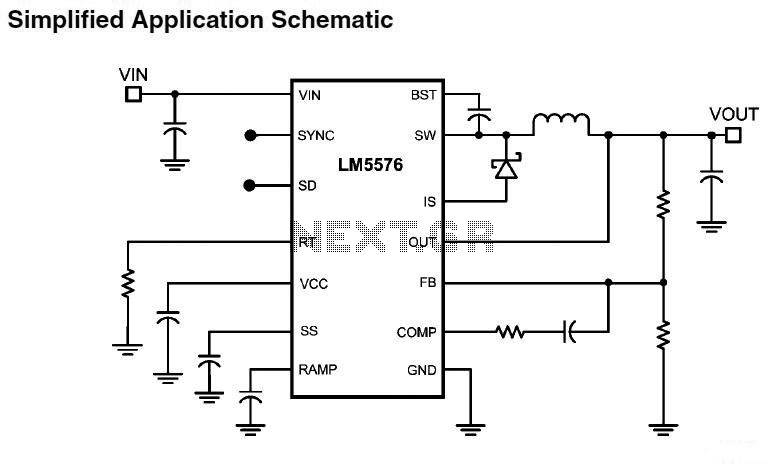
Keying oscillator circuit
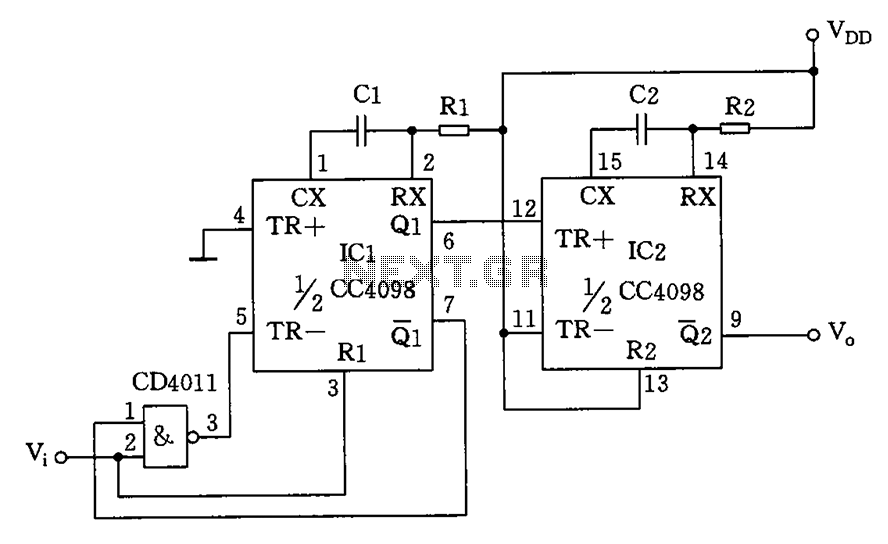
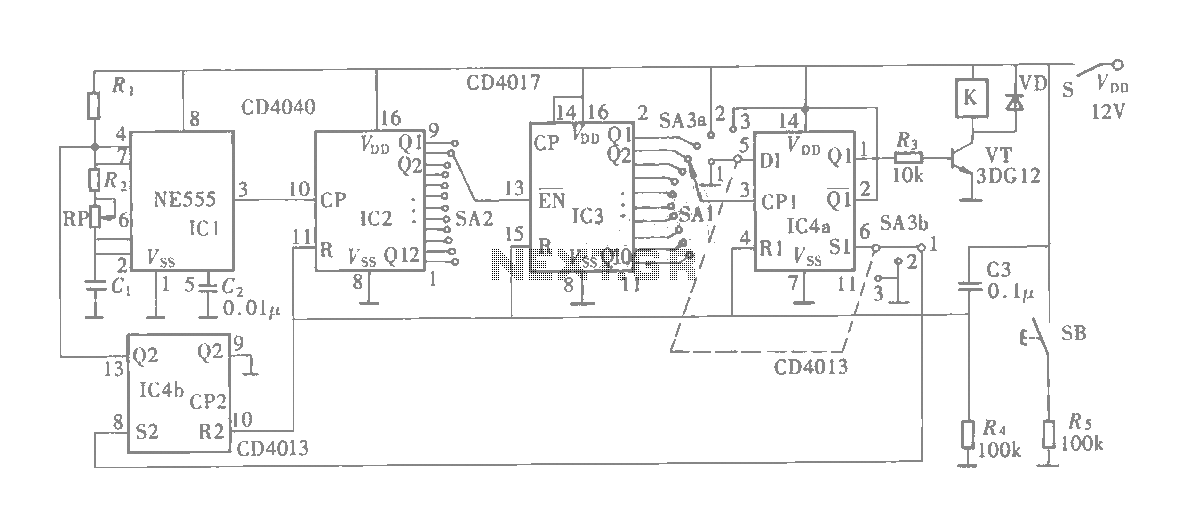
The circuit depicted features a double oscillator utilizing a monostable multivibrator CC4098 and a quad 2-input NAND gate CC4011, among other components. This circuit allows for adjustable frequency and duty cycle. It is primarily designed as a keying oscillator, functioning as a single-shot generator, suitable for producing low-frequency signals with less precision.
The described circuit employs the CC4098, a versatile monostable multivibrator, which is pivotal for generating a single output pulse in response to a triggering input. The duration of this pulse can be adjusted by varying the external resistor and capacitor values connected to the CC4098, thus allowing for customization of the output signal's timing characteristics. The CC4011 NAND gates are configured to create an oscillator circuit that can be tuned to the desired frequency range. By adjusting the feedback and timing components, the oscillation frequency can be modified, providing flexibility in the signal generation process.
The combination of the CC4098 and CC4011 enables the creation of a keying oscillator that can produce a low-frequency square wave signal. This signal is useful in various applications, such as driving other circuits, modulation, or as a timing reference. The circuit's ability to adjust both frequency and duty cycle makes it suitable for applications requiring different signal characteristics without the need for complex modifications.
In summary, this circuit design effectively integrates a monostable multivibrator and NAND gates to create a flexible low-frequency signal generator, emphasizing ease of use and adaptability for various electronic applications. Circuit as shown by the double oscillator is keyed monoflop CC4098, Quad 2-input NAND gate CC4011 and other composition. The circuit is the frequency and duty cycle adjustable keying oscillator constituted by a single-shot, mainly for less precision low-frequency signal generator.
The described circuit employs the CC4098, a versatile monostable multivibrator, which is pivotal for generating a single output pulse in response to a triggering input. The duration of this pulse can be adjusted by varying the external resistor and capacitor values connected to the CC4098, thus allowing for customization of the output signal's timing characteristics. The CC4011 NAND gates are configured to create an oscillator circuit that can be tuned to the desired frequency range. By adjusting the feedback and timing components, the oscillation frequency can be modified, providing flexibility in the signal generation process.
The combination of the CC4098 and CC4011 enables the creation of a keying oscillator that can produce a low-frequency square wave signal. This signal is useful in various applications, such as driving other circuits, modulation, or as a timing reference. The circuit's ability to adjust both frequency and duty cycle makes it suitable for applications requiring different signal characteristics without the need for complex modifications.
In summary, this circuit design effectively integrates a monostable multivibrator and NAND gates to create a flexible low-frequency signal generator, emphasizing ease of use and adaptability for various electronic applications. Circuit as shown by the double oscillator is keyed monoflop CC4098, Quad 2-input NAND gate CC4011 and other composition. The circuit is the frequency and duty cycle adjustable keying oscillator constituted by a single-shot, mainly for less precision low-frequency signal generator.