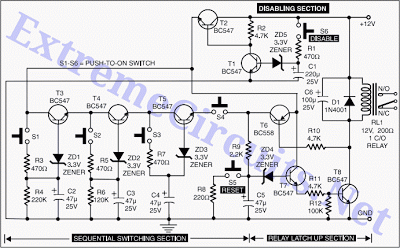
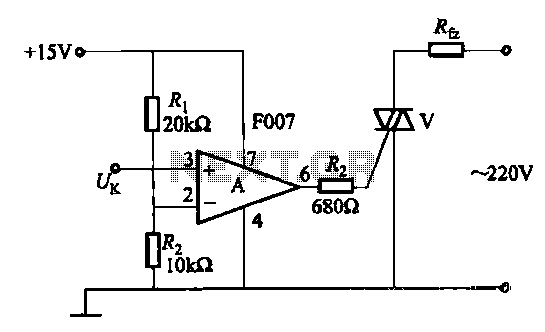
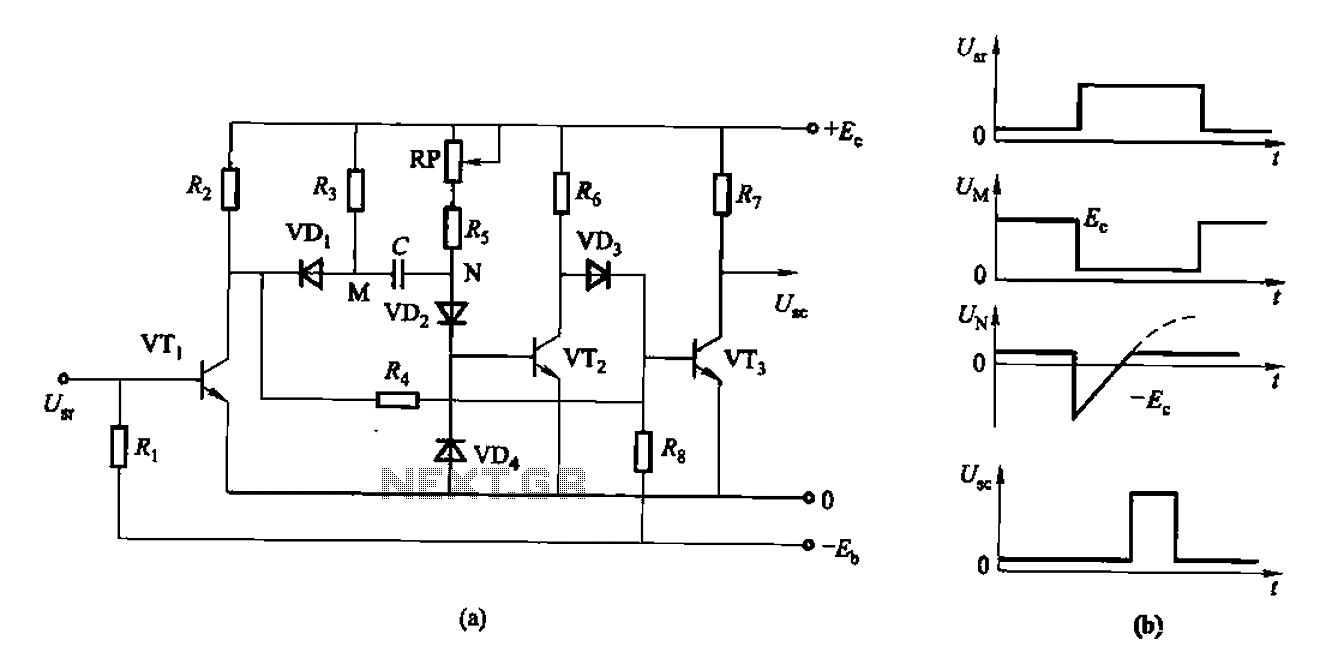
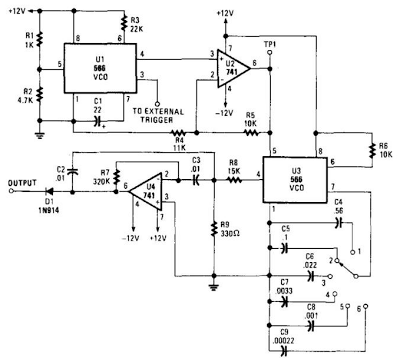
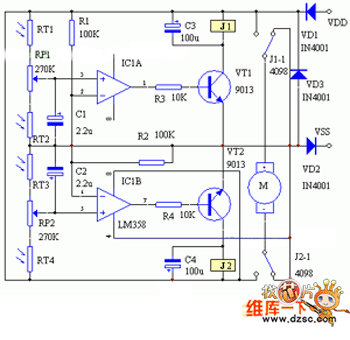
Multifunction adjustable universal time relay (NE555, CD4013) circuit
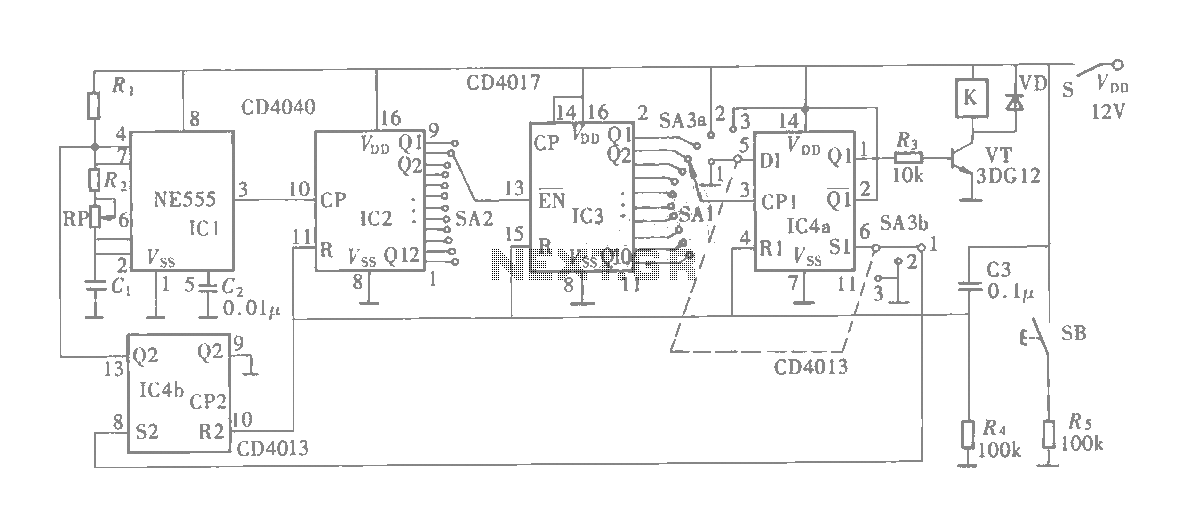
The multifunction circuit primarily refers to its capability to operate in three modes: "delayed pull," "time release," and "delayed cycle." The term "delay" indicates that the relay is energized after a predetermined time; however, the relay does not activate until the specified alarm time is reached. In contrast, the delayed release mode means that the relay activates immediately upon power-up, but it will only release after the timer reaches a preset duration. Both the delay and delayed release modes function as one-time operations, where the relay completes a work process, and the control section of the circuit stabilizes. The delay cycle mode allows the circuit to continuously operate as long as it is powered on, automatically cycling between the active state and a preset stop interval until the power switch is turned off or the operating state is changed. The circuit schematic is illustrated in the accompanying figure.
The multifunction circuit is designed to provide flexibility in control applications, utilizing a relay as the primary switching mechanism. In the delayed pull mode, the circuit incorporates a timer that begins counting once power is applied. The relay remains in an unenergized state until the timer reaches the predetermined alarm time, at which point the relay is activated, allowing current to flow through the connected load. This mode is particularly useful in applications where a delay is required before activating a device, such as in safety systems or time-sensitive operations.
Conversely, the delayed release mode operates by energizing the relay immediately upon power application. The relay remains engaged until the timer counts down to zero, at which point it deactivates, cutting off power to the load. This mode is beneficial for applications requiring an immediate activation followed by a controlled shutdown after a specific duration.
The delay cycle mode introduces a more dynamic operation, where the circuit alternates between on and off states based on user-defined intervals. Once powered, the relay will engage, and the timer will initiate a countdown. Upon reaching the preset stop time, the relay will disengage, and the cycle will repeat. This mode is advantageous for applications such as automated lighting systems, irrigation controls, or any system requiring periodic activation and deactivation.
The circuit design typically includes a microcontroller or timer IC to manage the timing functions accurately. Additional components may include resistors, capacitors, and diodes to ensure stable operation and protect against voltage spikes. A visual representation of the circuit can provide insight into the interconnections and component values necessary for achieving the desired operational modes.The multifunction circuit mainly refers to it can be "delayed pull", "time release", "delayed cycle" conversion three operating modes. The so-called delay means that the relay is energized after a preset power, the relay does not pull. Only when the preset alarm time, the relay was energized. Delay and delay the release pull the contrary, after turning on the preset relay when the timer reaches the preset time, the relay releases.
Delay the closing and delayed release of the two states operate as a one-time, when the relay to complete a work process, the control portion of the circuit into a stable state. Delay cycle work as long as the state is turned on, the circuit will be a good start and the preset stop time interval automatic cycle, never stop until the power switch off or switch the operating state.
Its circuit as shown in FIG.
The multifunction circuit is designed to provide flexibility in control applications, utilizing a relay as the primary switching mechanism. In the delayed pull mode, the circuit incorporates a timer that begins counting once power is applied. The relay remains in an unenergized state until the timer reaches the predetermined alarm time, at which point the relay is activated, allowing current to flow through the connected load. This mode is particularly useful in applications where a delay is required before activating a device, such as in safety systems or time-sensitive operations.
Conversely, the delayed release mode operates by energizing the relay immediately upon power application. The relay remains engaged until the timer counts down to zero, at which point it deactivates, cutting off power to the load. This mode is beneficial for applications requiring an immediate activation followed by a controlled shutdown after a specific duration.
The delay cycle mode introduces a more dynamic operation, where the circuit alternates between on and off states based on user-defined intervals. Once powered, the relay will engage, and the timer will initiate a countdown. Upon reaching the preset stop time, the relay will disengage, and the cycle will repeat. This mode is advantageous for applications such as automated lighting systems, irrigation controls, or any system requiring periodic activation and deactivation.
The circuit design typically includes a microcontroller or timer IC to manage the timing functions accurately. Additional components may include resistors, capacitors, and diodes to ensure stable operation and protect against voltage spikes. A visual representation of the circuit can provide insight into the interconnections and component values necessary for achieving the desired operational modes.The multifunction circuit mainly refers to it can be "delayed pull", "time release", "delayed cycle" conversion three operating modes. The so-called delay means that the relay is energized after a preset power, the relay does not pull. Only when the preset alarm time, the relay was energized. Delay and delay the release pull the contrary, after turning on the preset relay when the timer reaches the preset time, the relay releases.
Delay the closing and delayed release of the two states operate as a one-time, when the relay to complete a work process, the control portion of the circuit into a stable state. Delay cycle work as long as the state is turned on, the circuit will be a good start and the preset stop time interval automatic cycle, never stop until the power switch off or switch the operating state.
Its circuit as shown in FIG.