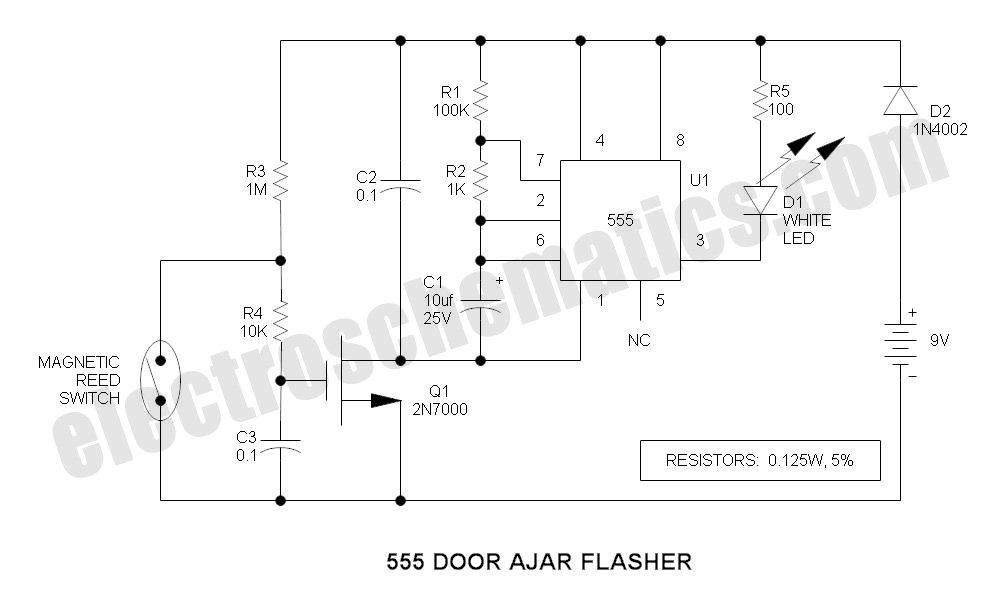
Led flasher
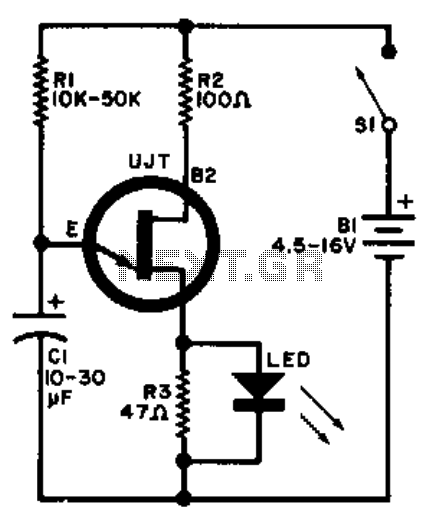
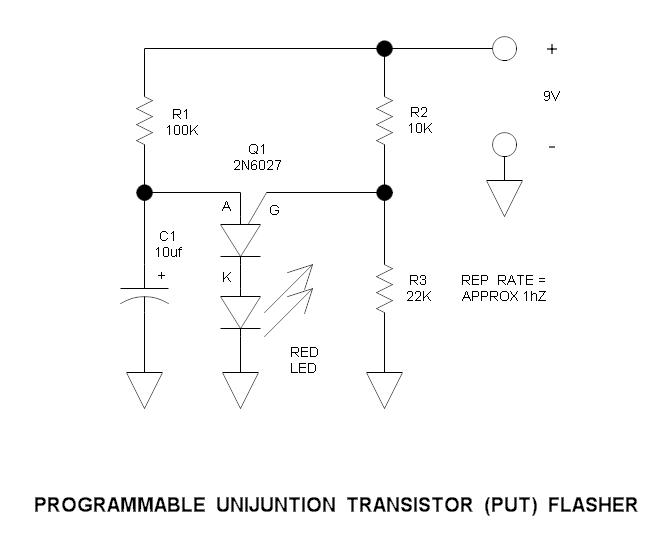
A relaxation oscillator is employed to flash an LED in the base circuit. The capacitor C1 is charged slowly through resistor R1 by the power source, and then it is discharged periodically through resistor R3 and the LED by the unijunction transistor (UJT). The flashing rate is determined by the supply voltage and the time constant of the R1-C1 combination. The UJT used in this circuit is the 2N4871.
The relaxation oscillator circuit operates by leveraging the charging and discharging characteristics of the capacitor C1. Initially, when power is supplied, C1 starts to charge through the resistor R1, which provides a gradual increase in voltage across the capacitor. Once the voltage across C1 reaches a certain threshold, the UJT (2N4871) is triggered into conduction. This conduction path allows C1 to discharge rapidly through resistor R3 and the LED, resulting in a brief flash of light emitted by the LED.
The time constant of the charging phase, dictated by the values of R1 and C1, plays a crucial role in determining the frequency of the LED flashes. A larger resistor R1 or a larger capacitor C1 will increase the time constant, leading to a slower charging rate and a lower flashing frequency. Conversely, reducing R1 or C1 will decrease the time constant, resulting in a faster flashing rate.
The UJT itself operates in a unique manner, characterized by its negative resistance region, which is essential for sustaining oscillations in the circuit. The 2N4871 UJT is specifically designed for such applications, providing reliable switching performance and stability in the oscillation frequency.
In summary, the relaxation oscillator circuit designed with the UJT 2N4871 effectively utilizes the charging and discharging of capacitor C1 to create a visually appealing LED flashing effect. The design parameters, including the values of R1, R3, and C1, can be adjusted to modify the flashing rate, allowing for customization based on specific application requirements.A relaxation oscillator is used to flash an LED in the base circuit. Cl is charged slowly through R1 by the power source, then discharged periodically through R3 and the LED by the UJT. Flashing rate is determined by the supply voltage and by Rl-Cl's time constant. UJT = 2N4871 🔗 External reference
The relaxation oscillator circuit operates by leveraging the charging and discharging characteristics of the capacitor C1. Initially, when power is supplied, C1 starts to charge through the resistor R1, which provides a gradual increase in voltage across the capacitor. Once the voltage across C1 reaches a certain threshold, the UJT (2N4871) is triggered into conduction. This conduction path allows C1 to discharge rapidly through resistor R3 and the LED, resulting in a brief flash of light emitted by the LED.
The time constant of the charging phase, dictated by the values of R1 and C1, plays a crucial role in determining the frequency of the LED flashes. A larger resistor R1 or a larger capacitor C1 will increase the time constant, leading to a slower charging rate and a lower flashing frequency. Conversely, reducing R1 or C1 will decrease the time constant, resulting in a faster flashing rate.
The UJT itself operates in a unique manner, characterized by its negative resistance region, which is essential for sustaining oscillations in the circuit. The 2N4871 UJT is specifically designed for such applications, providing reliable switching performance and stability in the oscillation frequency.
In summary, the relaxation oscillator circuit designed with the UJT 2N4871 effectively utilizes the charging and discharging of capacitor C1 to create a visually appealing LED flashing effect. The design parameters, including the values of R1, R3, and C1, can be adjusted to modify the flashing rate, allowing for customization based on specific application requirements.A relaxation oscillator is used to flash an LED in the base circuit. Cl is charged slowly through R1 by the power source, then discharged periodically through R3 and the LED by the UJT. Flashing rate is determined by the supply voltage and by Rl-Cl's time constant. UJT = 2N4871 🔗 External reference