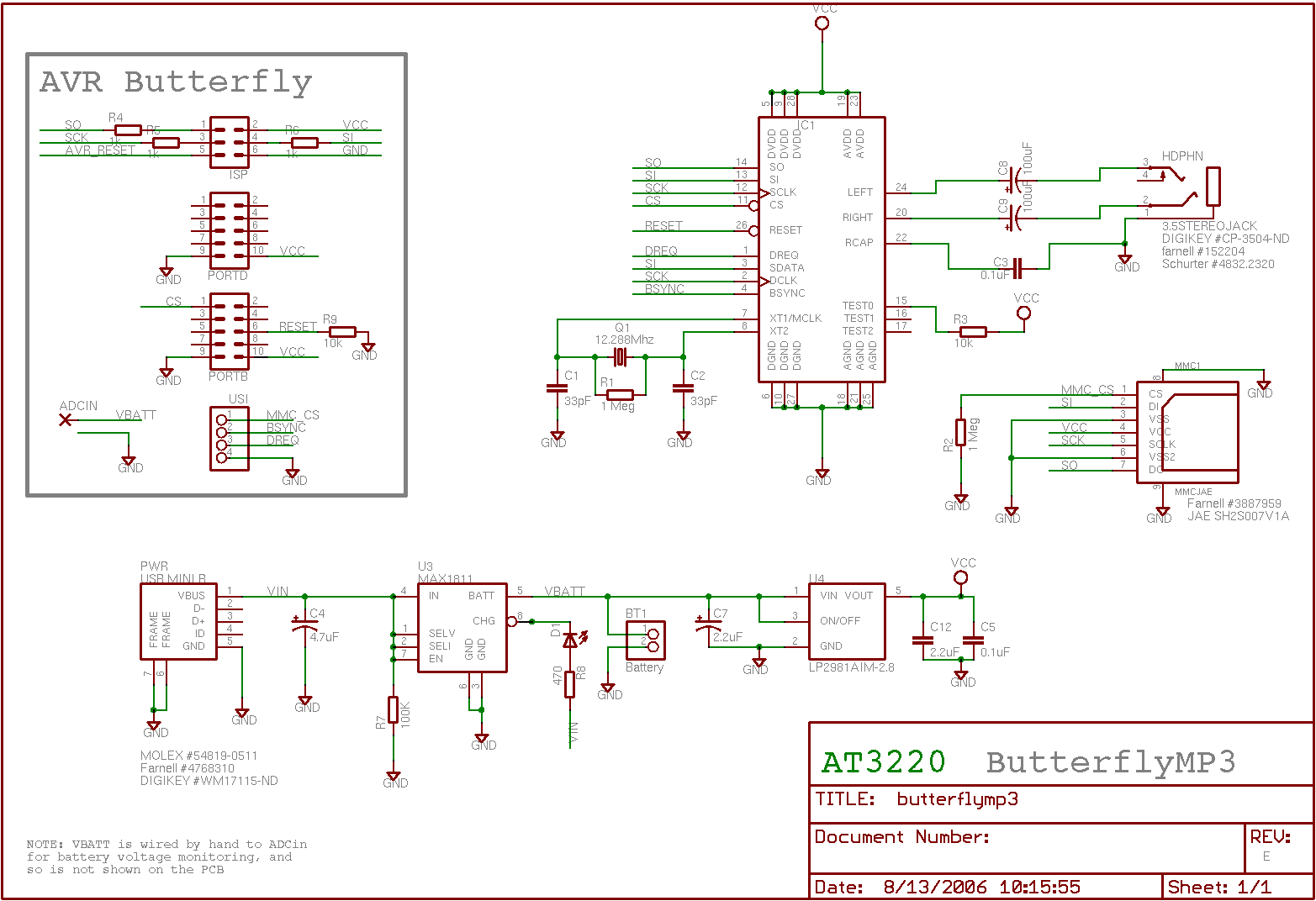
Led flasher IIV
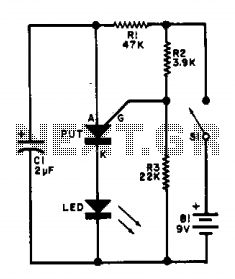
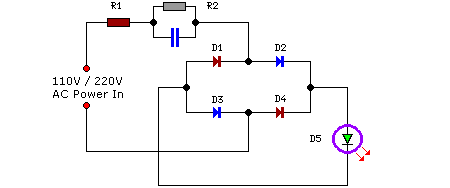
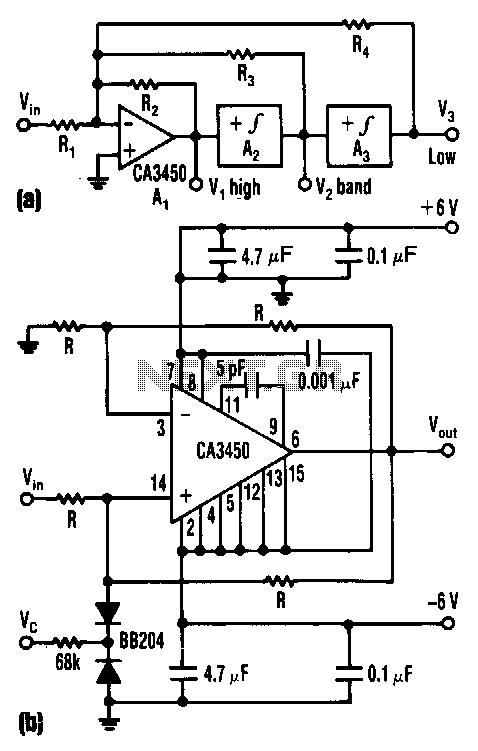
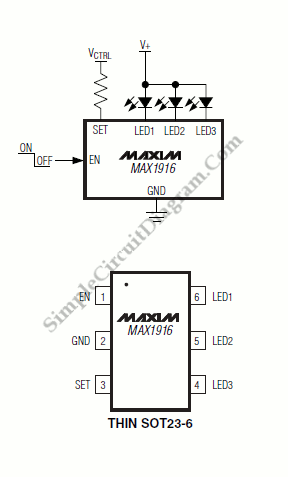
This flasher circuit functions as a relaxation oscillator, with capacitor C1 discharging periodically through the LED when the Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT) is activated. The flashing rate is approximately 100 times per minute, based on the specified component values.
The flasher circuit utilizes a relaxation oscillator configuration, which is characterized by the repeated charging and discharging of a capacitor to create a square wave output. In this design, the PUT acts as the switching element that controls the discharge of capacitor C1 through the LED, resulting in the LED flashing at a defined rate.
The circuit typically includes a resistor connected to the capacitor C1, which, along with the PUT, determines the timing characteristics of the oscillator. When the circuit is powered, C1 begins to charge through the resistor until it reaches a threshold voltage that triggers the PUT to conduct. Upon conduction, the stored charge in C1 is rapidly discharged through the LED, causing it to illuminate. As the capacitor discharges, the voltage across it drops, eventually turning off the PUT and allowing C1 to recharge, thus repeating the cycle.
The component values, including the resistance and capacitance, play a crucial role in defining the flashing rate. For a flashing rate of approximately 100 flashes per minute, appropriate resistor and capacitor values must be selected. The relationship between these components can be expressed through the time constant formula, which calculates the time it takes for the capacitor to charge or discharge to a certain percentage of the supply voltage.
In summary, this flasher circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective application of a relaxation oscillator using a PUT, enabling a visually engaging LED flashing effect at a consistent rate determined by the chosen component values.This flasher circuit operates as a relaxation oscillator with Cl discharged periodically through the LED as the PUT switches on. The flashing rate is about 100/minute with the component values listed. 🔗 External reference
The flasher circuit utilizes a relaxation oscillator configuration, which is characterized by the repeated charging and discharging of a capacitor to create a square wave output. In this design, the PUT acts as the switching element that controls the discharge of capacitor C1 through the LED, resulting in the LED flashing at a defined rate.
The circuit typically includes a resistor connected to the capacitor C1, which, along with the PUT, determines the timing characteristics of the oscillator. When the circuit is powered, C1 begins to charge through the resistor until it reaches a threshold voltage that triggers the PUT to conduct. Upon conduction, the stored charge in C1 is rapidly discharged through the LED, causing it to illuminate. As the capacitor discharges, the voltage across it drops, eventually turning off the PUT and allowing C1 to recharge, thus repeating the cycle.
The component values, including the resistance and capacitance, play a crucial role in defining the flashing rate. For a flashing rate of approximately 100 flashes per minute, appropriate resistor and capacitor values must be selected. The relationship between these components can be expressed through the time constant formula, which calculates the time it takes for the capacitor to charge or discharge to a certain percentage of the supply voltage.
In summary, this flasher circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective application of a relaxation oscillator using a PUT, enabling a visually engaging LED flashing effect at a consistent rate determined by the chosen component values.This flasher circuit operates as a relaxation oscillator with Cl discharged periodically through the LED as the PUT switches on. The flashing rate is about 100/minute with the component values listed. 🔗 External reference