led torch uses blocking
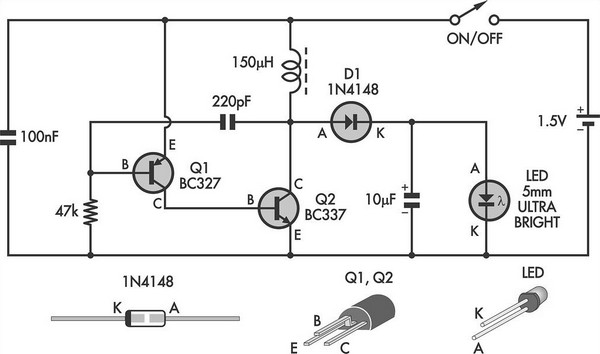
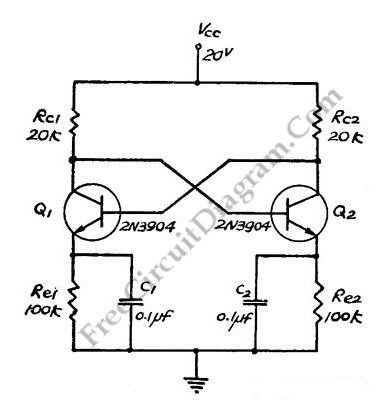
This simple LED torch is powered by a 2-transistor blocking oscillator that increases the voltage from a 1.5V cell. The design utilizes the natural current limiting characteristics of a 150 µH choke to prevent the white LED from being overdriven. Additionally, by replacing the white LED with a 9V zener diode, the circuit could serve as a 9V power supply, assuming the current draw remains within a reasonable range.
The circuit operates by employing a 2-transistor configuration that forms a blocking oscillator. When powered by a 1.5V cell, the circuit generates a high-frequency oscillation that drives the choke. The choke, with its inductive properties, stores energy during the 'on' phase and releases it during the 'off' phase, effectively stepping up the voltage to a level sufficient to illuminate the white LED. The inherent resistance of the choke limits the current flowing through the LED, thereby protecting it from excessive current that could lead to damage or reduced lifespan.
In the alternative configuration using a 9V zener diode, the circuit can be adapted to function as a voltage regulator. This setup is advantageous for powering low-current devices that require a stable 9V supply. The zener diode clamps the output voltage to 9V, ensuring that any variations in input voltage or load do not exceed this threshold, as long as the current drain is kept modest. This versatility makes the circuit suitable for various applications, from simple LED lighting to providing regulated power for small electronic devices.This simple LED torch is driven by a 2-transistor blocking oscillator which steps up the voltage from a 1. 5V cell. It relies on the inherent current limiting of the 150 µH choke to protect the white LED from over-drive.
With a 9V zener diode in place of the white LED, it could also provide a 9V supply provided the current drain is modest. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by employing a 2-transistor configuration that forms a blocking oscillator. When powered by a 1.5V cell, the circuit generates a high-frequency oscillation that drives the choke. The choke, with its inductive properties, stores energy during the 'on' phase and releases it during the 'off' phase, effectively stepping up the voltage to a level sufficient to illuminate the white LED. The inherent resistance of the choke limits the current flowing through the LED, thereby protecting it from excessive current that could lead to damage or reduced lifespan.
In the alternative configuration using a 9V zener diode, the circuit can be adapted to function as a voltage regulator. This setup is advantageous for powering low-current devices that require a stable 9V supply. The zener diode clamps the output voltage to 9V, ensuring that any variations in input voltage or load do not exceed this threshold, as long as the current drain is kept modest. This versatility makes the circuit suitable for various applications, from simple LED lighting to providing regulated power for small electronic devices.This simple LED torch is driven by a 2-transistor blocking oscillator which steps up the voltage from a 1. 5V cell. It relies on the inherent current limiting of the 150 µH choke to protect the white LED from over-drive.
With a 9V zener diode in place of the white LED, it could also provide a 9V supply provided the current drain is modest. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713