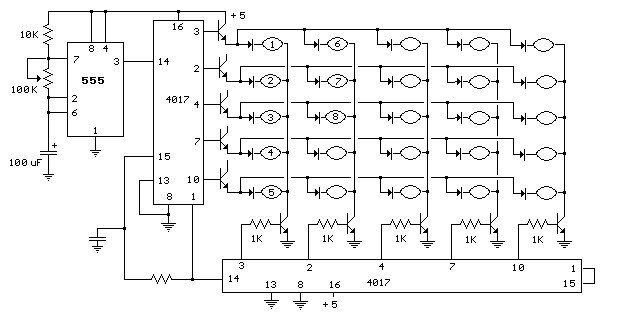
LEDs and Switches
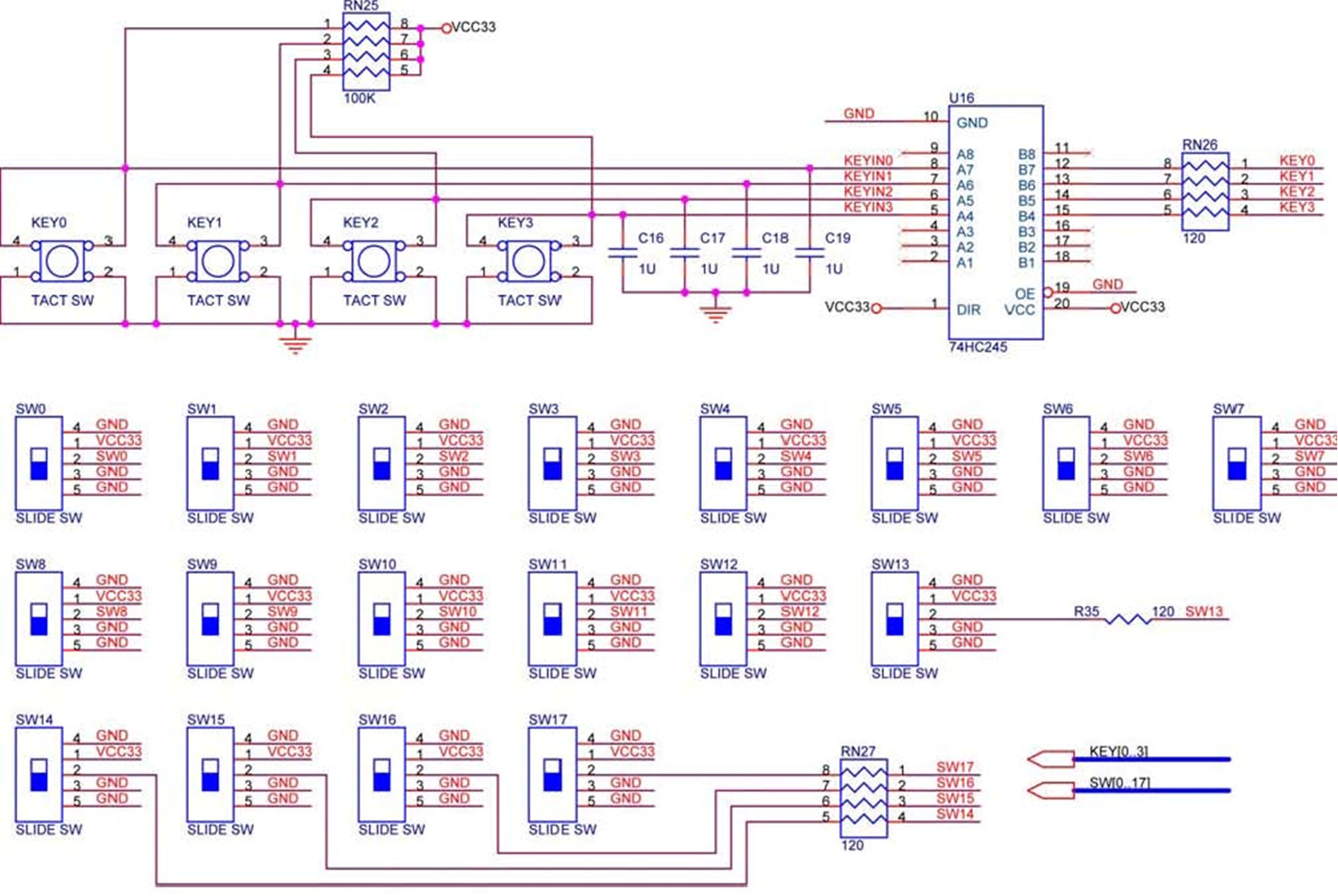
The DE2 board features four pushbutton switches, each of which is debounced using a Schmitt Trigger circuit, as shown in Figure 1. The outputs, labeled KEY0 to KEY3, from the Schmitt Trigger are directly connected to the Cyclone II FPGA. When not pressed, each switch outputs a high logic level of 3.3 volts, and when pressed, it outputs a low logic level of 0 volts. Due to the debouncing, these switches are suitable for use as clock or reset inputs in a circuit. Additionally, the DE2 board includes 18 toggle switches (sliders) that are not debounced and are designed for level-sensitive data inputs. Each toggle switch connects directly to a pin on the Cyclone II FPGA. In the DOWN position (closest to the edge of the board), a switch outputs a low logic level of 0 volts, while in the UP position, it outputs a high logic level of 3.3 volts. The board also contains 27 user-controllable LEDs: 18 red LEDs positioned above the toggle switches and eight green LEDs located above the pushbutton switches (with the ninth green LED centered among the 7-segment displays). Each LED is driven directly by a pin on the Cyclone II FPGA; setting the associated pin to a high logic level turns the LED on, while setting it to low turns it off. Schematic diagrams illustrating the pushbutton and toggle switches are shown in Figure 2, and the LED circuitry is depicted in Figure 3.
The DE2 board is designed to facilitate various input and output operations through its integrated components. The four debounced pushbutton switches utilize Schmitt Trigger circuits to provide stable and reliable transitions between logic levels, mitigating the effects of mechanical bounce that can occur during switch actuation. This feature enhances the performance of the switches when used for critical functions such as clock signals or reset inputs in digital circuits.
The connection of the switches to the Cyclone II FPGA allows for seamless integration into digital designs, enabling the FPGA to read the status of each switch accurately. The toggle switches, while lacking debouncing, serve as effective level-sensitive inputs, providing a straightforward method for users to interact with the FPGA. The clear logic level outputs from the toggle switches make them suitable for applications where continuous monitoring of the switch state is necessary.
The presence of 27 user-controllable LEDs offers visual feedback for the operation of the circuit. The arrangement of red and green LEDs allows for differentiated signaling, where red LEDs can indicate specific states or statuses of the toggle switches, while green LEDs can provide feedback from the pushbutton switches. The direct connection of the LEDs to the Cyclone II FPGA ensures that the control over these indicators is straightforward and flexible, allowing for dynamic updates based on the logic implemented within the FPGA.
Overall, the DE2 board's design, with its combination of debounced pushbutton switches, toggle switches, and user-controllable LEDs, provides a robust platform for developing and testing digital circuits, making it an invaluable resource for electronics engineers and hobbyists alike. The accompanying schematic diagrams further enhance understanding by visually representing the connections and functionalities of these components.The DE2 board provides four pushbutton switches. Each of these switches is debounced using a Schmitt Trigger circuit, as indicated in Figure 1. The four outputs called KEY0, . , KEY3 of the Schmitt Trigger device are connected directly to the Cyclone II FPGA. Each switch provides a high logic level (3. 3 volts) when it is not pressed, and provides a low logic level (0 volts) when depressed. Since the pushbutton switches are debounced, they are appropriate for use as clock or reset inputs in a circuit. There are also 18 toggle switches (sliders) on the DE2 board. These switches are not debounced, and are intended for use as level-sensitive data inputs to a circuit.
Each switch is connected directly to a pin on the Cyclone II FPGA. When a switch is in the DOWN position (closest to the edge of the board) it provides a low logic level (0 volts) to the FPGA, and when the switch is in the UP position it provides a high logic level (3. 3 volts). There are 27 user-controllable LEDs on the DE2 board. Eighteen red LEDs are situated above the 18 toggle switches, and eight green LEDs are found above the pushbutton switches (the 9th green LED is in the middle of the 7-segment displays).
Each LED is driven directly by a pin on the Cyclone II FPGA; driving its associated pin to a high logic level turns the LED on, and driving the pin low turns it off. A schematic diagram that shows the pushbutton and toggle switches is given in Figure 2. A schematic diagram that shows the LED circuitry appears in Figure 3. 🔗 External reference
The DE2 board is designed to facilitate various input and output operations through its integrated components. The four debounced pushbutton switches utilize Schmitt Trigger circuits to provide stable and reliable transitions between logic levels, mitigating the effects of mechanical bounce that can occur during switch actuation. This feature enhances the performance of the switches when used for critical functions such as clock signals or reset inputs in digital circuits.
The connection of the switches to the Cyclone II FPGA allows for seamless integration into digital designs, enabling the FPGA to read the status of each switch accurately. The toggle switches, while lacking debouncing, serve as effective level-sensitive inputs, providing a straightforward method for users to interact with the FPGA. The clear logic level outputs from the toggle switches make them suitable for applications where continuous monitoring of the switch state is necessary.
The presence of 27 user-controllable LEDs offers visual feedback for the operation of the circuit. The arrangement of red and green LEDs allows for differentiated signaling, where red LEDs can indicate specific states or statuses of the toggle switches, while green LEDs can provide feedback from the pushbutton switches. The direct connection of the LEDs to the Cyclone II FPGA ensures that the control over these indicators is straightforward and flexible, allowing for dynamic updates based on the logic implemented within the FPGA.
Overall, the DE2 board's design, with its combination of debounced pushbutton switches, toggle switches, and user-controllable LEDs, provides a robust platform for developing and testing digital circuits, making it an invaluable resource for electronics engineers and hobbyists alike. The accompanying schematic diagrams further enhance understanding by visually representing the connections and functionalities of these components.The DE2 board provides four pushbutton switches. Each of these switches is debounced using a Schmitt Trigger circuit, as indicated in Figure 1. The four outputs called KEY0, . , KEY3 of the Schmitt Trigger device are connected directly to the Cyclone II FPGA. Each switch provides a high logic level (3. 3 volts) when it is not pressed, and provides a low logic level (0 volts) when depressed. Since the pushbutton switches are debounced, they are appropriate for use as clock or reset inputs in a circuit. There are also 18 toggle switches (sliders) on the DE2 board. These switches are not debounced, and are intended for use as level-sensitive data inputs to a circuit.
Each switch is connected directly to a pin on the Cyclone II FPGA. When a switch is in the DOWN position (closest to the edge of the board) it provides a low logic level (0 volts) to the FPGA, and when the switch is in the UP position it provides a high logic level (3. 3 volts). There are 27 user-controllable LEDs on the DE2 board. Eighteen red LEDs are situated above the 18 toggle switches, and eight green LEDs are found above the pushbutton switches (the 9th green LED is in the middle of the 7-segment displays).
Each LED is driven directly by a pin on the Cyclone II FPGA; driving its associated pin to a high logic level turns the LED on, and driving the pin low turns it off. A schematic diagram that shows the pushbutton and toggle switches is given in Figure 2. A schematic diagram that shows the LED circuitry appears in Figure 3. 🔗 External reference