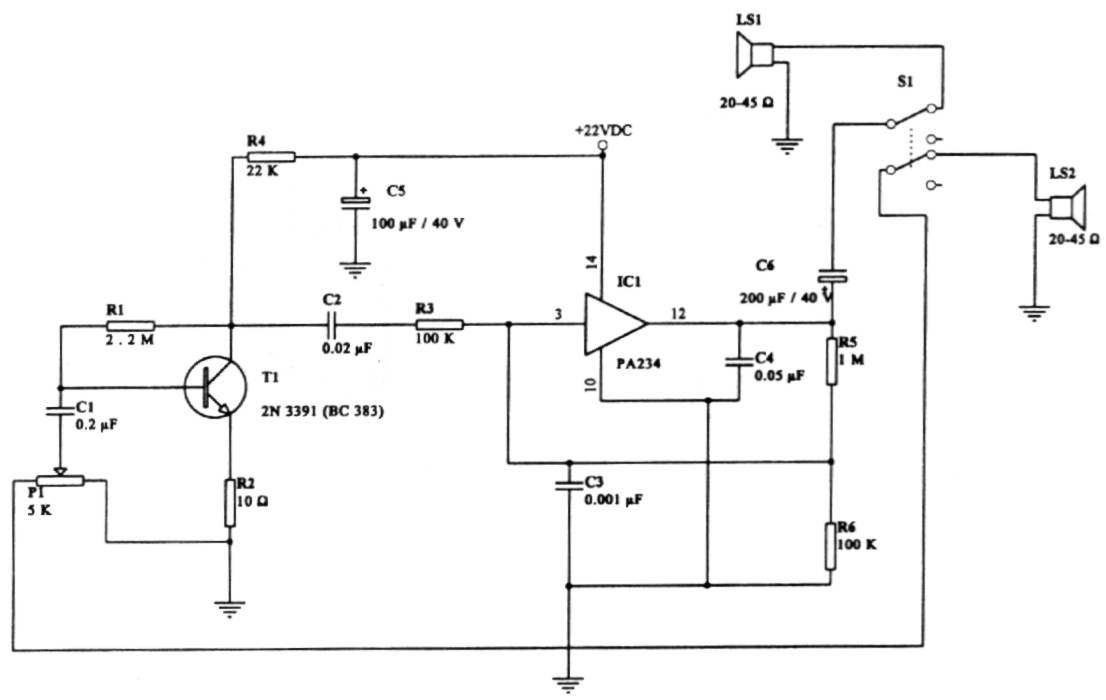
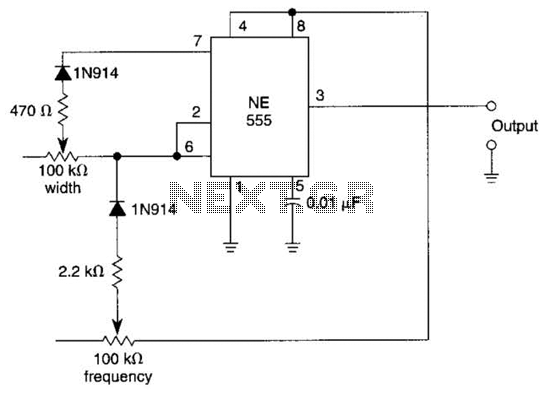
Level one thyristor-controlled circuit sink type b
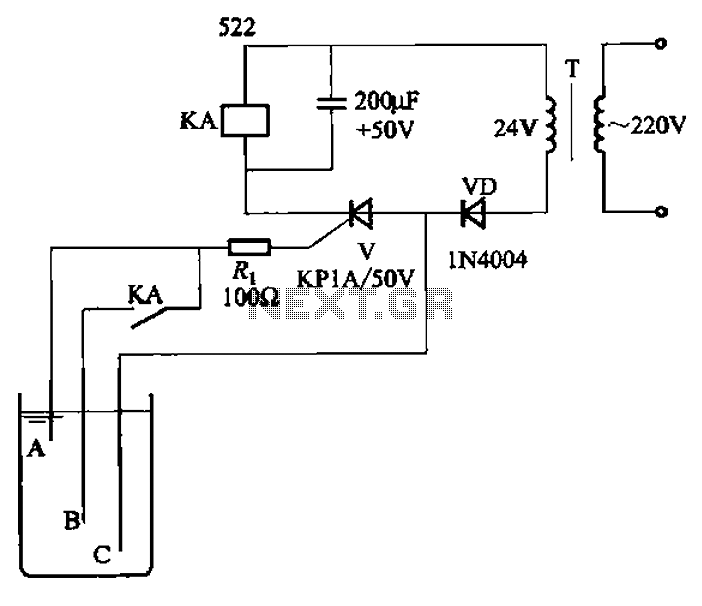
The circuit depicted in Figure 11-14 utilizes a unidirectional thyristor within liquid level automatic control systems. It incorporates electrodes that serve as sensing elements for detecting the level of water or other conductive liquids. The circuit features a current limiting resistor (Ri) designed to restrict the current flowing through the thyristor gate, preventing damage to the component.
The circuit operates by employing a thyristor, which is a semiconductor device that acts as a switch, allowing current to flow only when triggered by a gate signal. In this application, the thyristor is used to control the flow of current based on the liquid level detected by the electrodes. When the liquid level reaches a certain point, the electrodes become conductive, triggering the thyristor and allowing current to pass through.
The inclusion of a current limiting resistor (Ri) is critical for the protection of the thyristor. This resistor ensures that the gate current does not exceed the maximum ratings specified by the manufacturer, thus preventing thermal runaway and potential failure of the thyristor. The value of Ri must be carefully calculated based on the supply voltage and the required gate current for the thyristor to operate effectively.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various liquid level control systems, such as water tanks, chemical storage, and other applications where monitoring and controlling liquid levels is essential. The design can be expanded to include additional features, such as alarm systems or automatic pumps, to enhance the functionality of the liquid level control system. Overall, the integration of a thyristor and a current limiting resistor in this circuit provides an efficient and reliable solution for automatic liquid level control. Circuit shown in Figure 11-14. It uses a one-way thyristor, is poured into the liquid level automatic control circuits. Electrodes for detecting sensing element for water or ot her conductive liquid level control. Figure, Ri current limiting resistor to limit the flow of current through the thyristor gate, so as not to burn the tubes.
The circuit operates by employing a thyristor, which is a semiconductor device that acts as a switch, allowing current to flow only when triggered by a gate signal. In this application, the thyristor is used to control the flow of current based on the liquid level detected by the electrodes. When the liquid level reaches a certain point, the electrodes become conductive, triggering the thyristor and allowing current to pass through.
The inclusion of a current limiting resistor (Ri) is critical for the protection of the thyristor. This resistor ensures that the gate current does not exceed the maximum ratings specified by the manufacturer, thus preventing thermal runaway and potential failure of the thyristor. The value of Ri must be carefully calculated based on the supply voltage and the required gate current for the thyristor to operate effectively.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various liquid level control systems, such as water tanks, chemical storage, and other applications where monitoring and controlling liquid levels is essential. The design can be expanded to include additional features, such as alarm systems or automatic pumps, to enhance the functionality of the liquid level control system. Overall, the integration of a thyristor and a current limiting resistor in this circuit provides an efficient and reliable solution for automatic liquid level control. Circuit shown in Figure 11-14. It uses a one-way thyristor, is poured into the liquid level automatic control circuits. Electrodes for detecting sensing element for water or ot her conductive liquid level control. Figure, Ri current limiting resistor to limit the flow of current through the thyristor gate, so as not to burn the tubes.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713