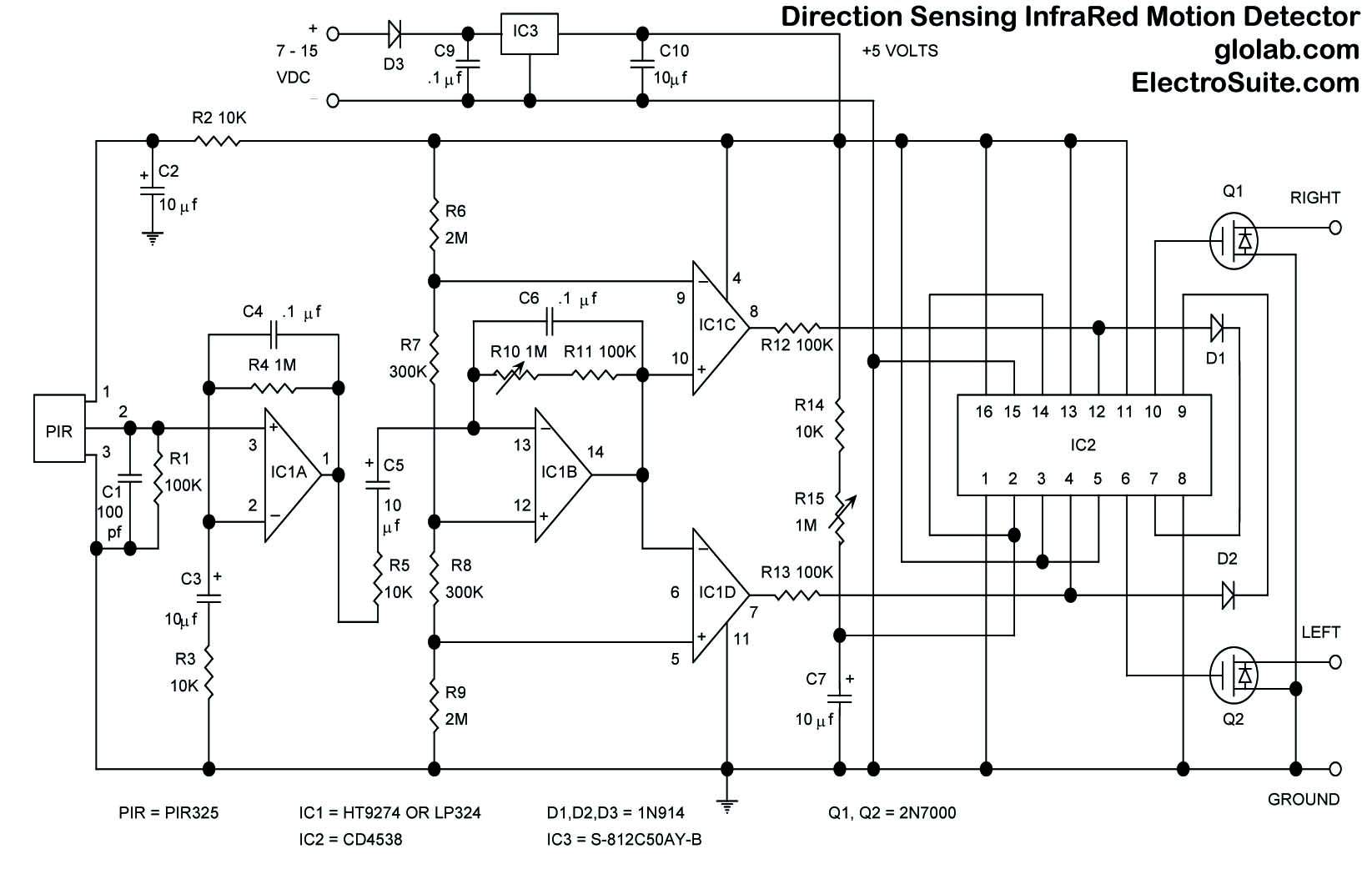
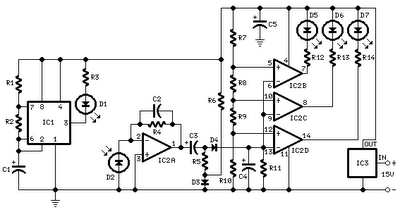
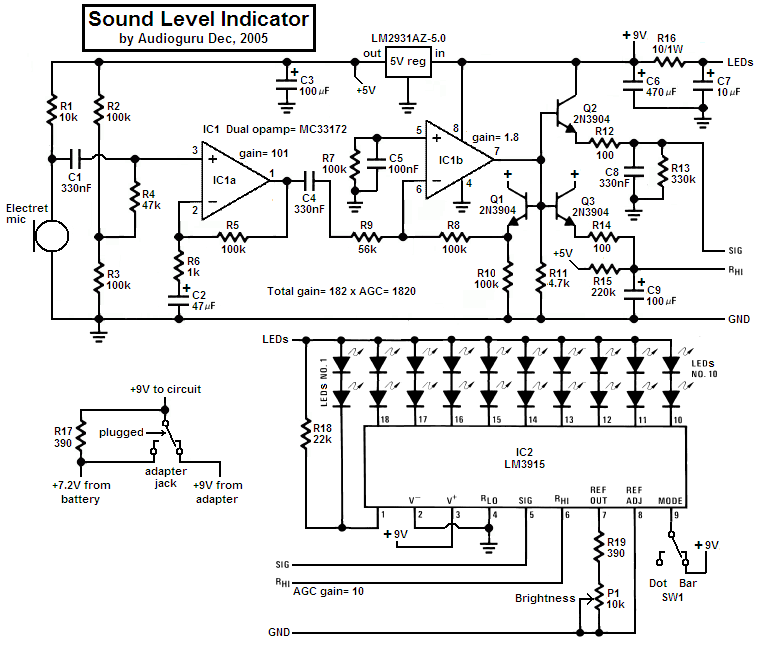
Level sensor for cryogenic fluids
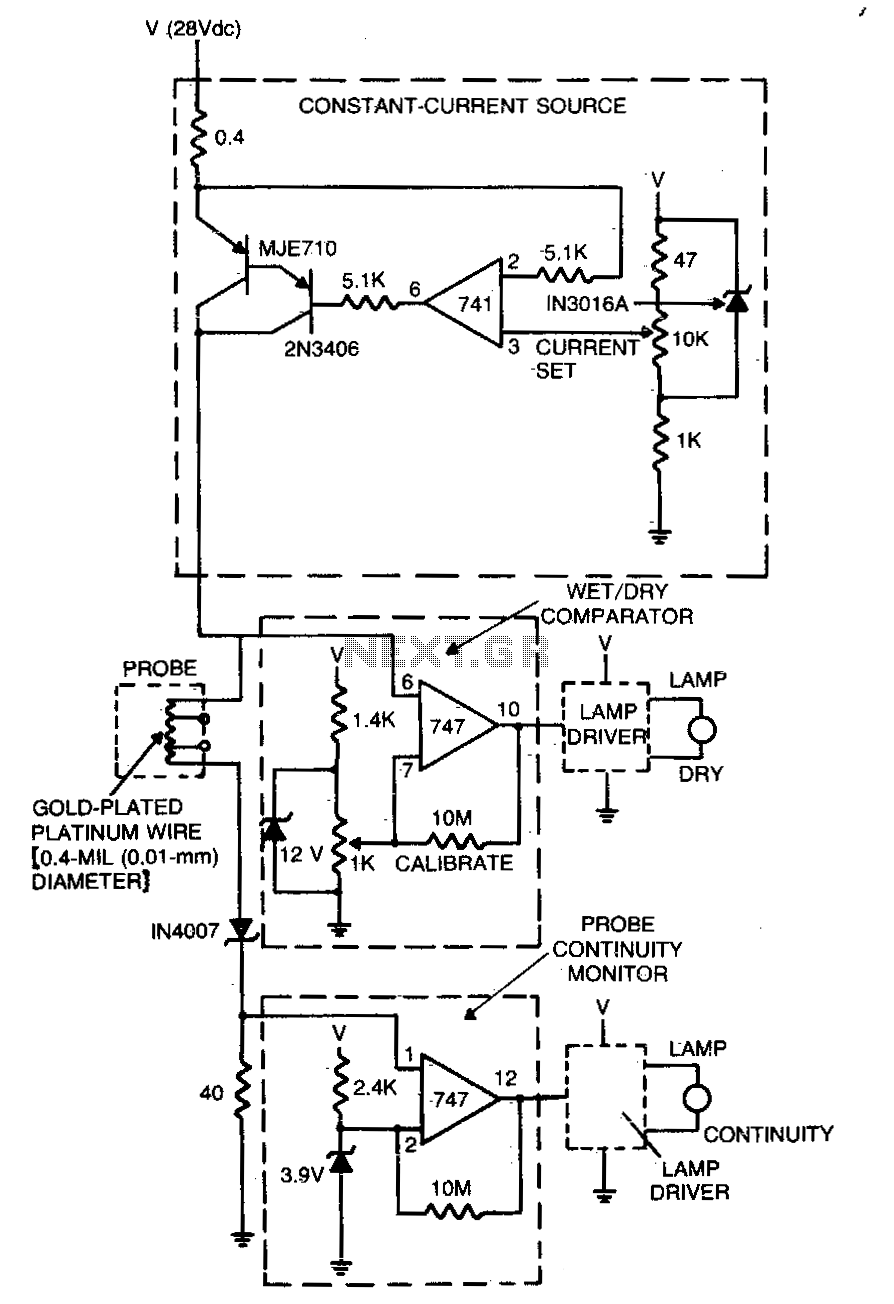
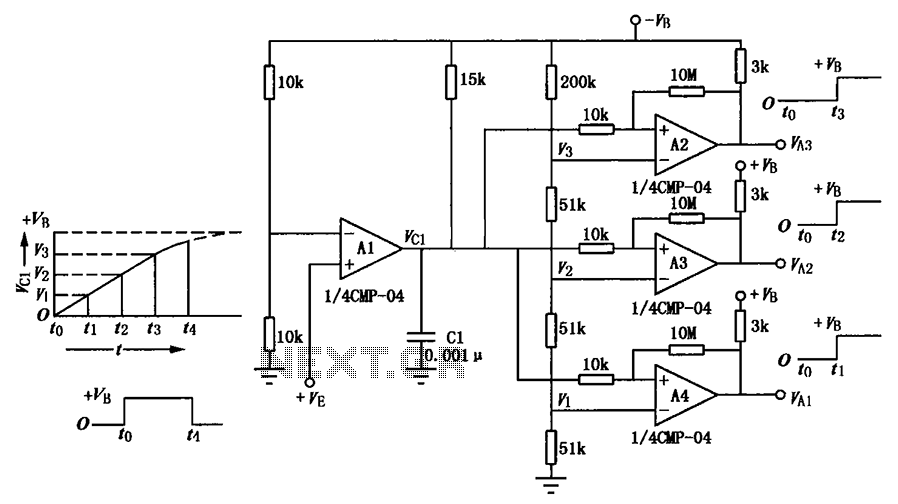
The sensor circuit is adaptable to different liquids and sensors. The constant-current source drives current through the sensing probe and a fixed resistor. The voltage-comparator circuits interpret the voltage drops to determine whether the probe is immersed in liquid and whether there is current in the probe.
The sensor circuit is designed to provide versatility for various liquid types and sensor configurations. At the core of the circuit is a constant-current source, which ensures a steady flow of current through the sensing probe. This current is crucial for accurate measurements and is maintained regardless of variations in the resistance of the probe or the characteristics of the liquid being tested. The fixed resistor in the circuit serves to establish a reference point for the voltage levels, allowing for precise voltage drop measurements across the sensing probe.
The output from the sensing probe is fed into voltage-comparator circuits, which play a pivotal role in interpreting the electrical signals generated during operation. These comparators analyze the voltage drops that occur when the probe is in contact with a liquid. When the probe is immersed, the voltage drop will change, indicating the presence of liquid. Additionally, the comparators can detect whether current is flowing through the probe, which is essential for confirming operational status and ensuring the reliability of the measurements.
This circuit configuration is particularly advantageous in applications where liquid detection is critical, such as in industrial processes, environmental monitoring, and laboratory settings. The adaptability of the circuit allows for integration with various sensor types, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. By utilizing a constant-current source and voltage-comparator circuits, this sensor circuit achieves high sensitivity and accuracy, ensuring effective monitoring and detection of liquid levels and properties.The sensor circuit is adaptable to different liquids and sensors. The constant-current source drives current through the sensing probe and a fixed resistor The voltage-comparator circuits interpret the voltage drops to tell whether the probe is immersed in liquid and whether there is current in the probe. 🔗 External reference
The sensor circuit is designed to provide versatility for various liquid types and sensor configurations. At the core of the circuit is a constant-current source, which ensures a steady flow of current through the sensing probe. This current is crucial for accurate measurements and is maintained regardless of variations in the resistance of the probe or the characteristics of the liquid being tested. The fixed resistor in the circuit serves to establish a reference point for the voltage levels, allowing for precise voltage drop measurements across the sensing probe.
The output from the sensing probe is fed into voltage-comparator circuits, which play a pivotal role in interpreting the electrical signals generated during operation. These comparators analyze the voltage drops that occur when the probe is in contact with a liquid. When the probe is immersed, the voltage drop will change, indicating the presence of liquid. Additionally, the comparators can detect whether current is flowing through the probe, which is essential for confirming operational status and ensuring the reliability of the measurements.
This circuit configuration is particularly advantageous in applications where liquid detection is critical, such as in industrial processes, environmental monitoring, and laboratory settings. The adaptability of the circuit allows for integration with various sensor types, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. By utilizing a constant-current source and voltage-comparator circuits, this sensor circuit achieves high sensitivity and accuracy, ensuring effective monitoring and detection of liquid levels and properties.The sensor circuit is adaptable to different liquids and sensors. The constant-current source drives current through the sensing probe and a fixed resistor The voltage-comparator circuits interpret the voltage drops to tell whether the probe is immersed in liquid and whether there is current in the probe. 🔗 External reference