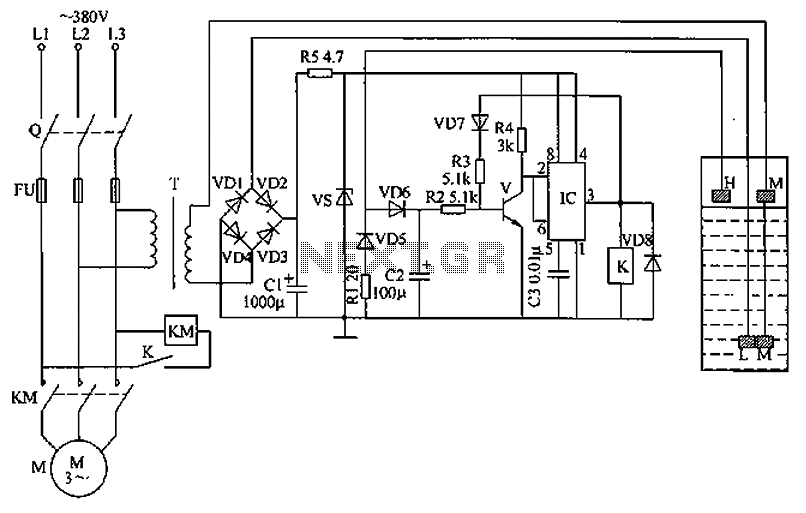
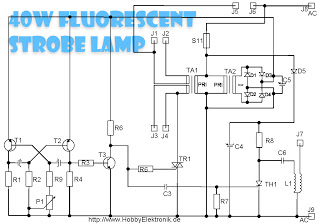
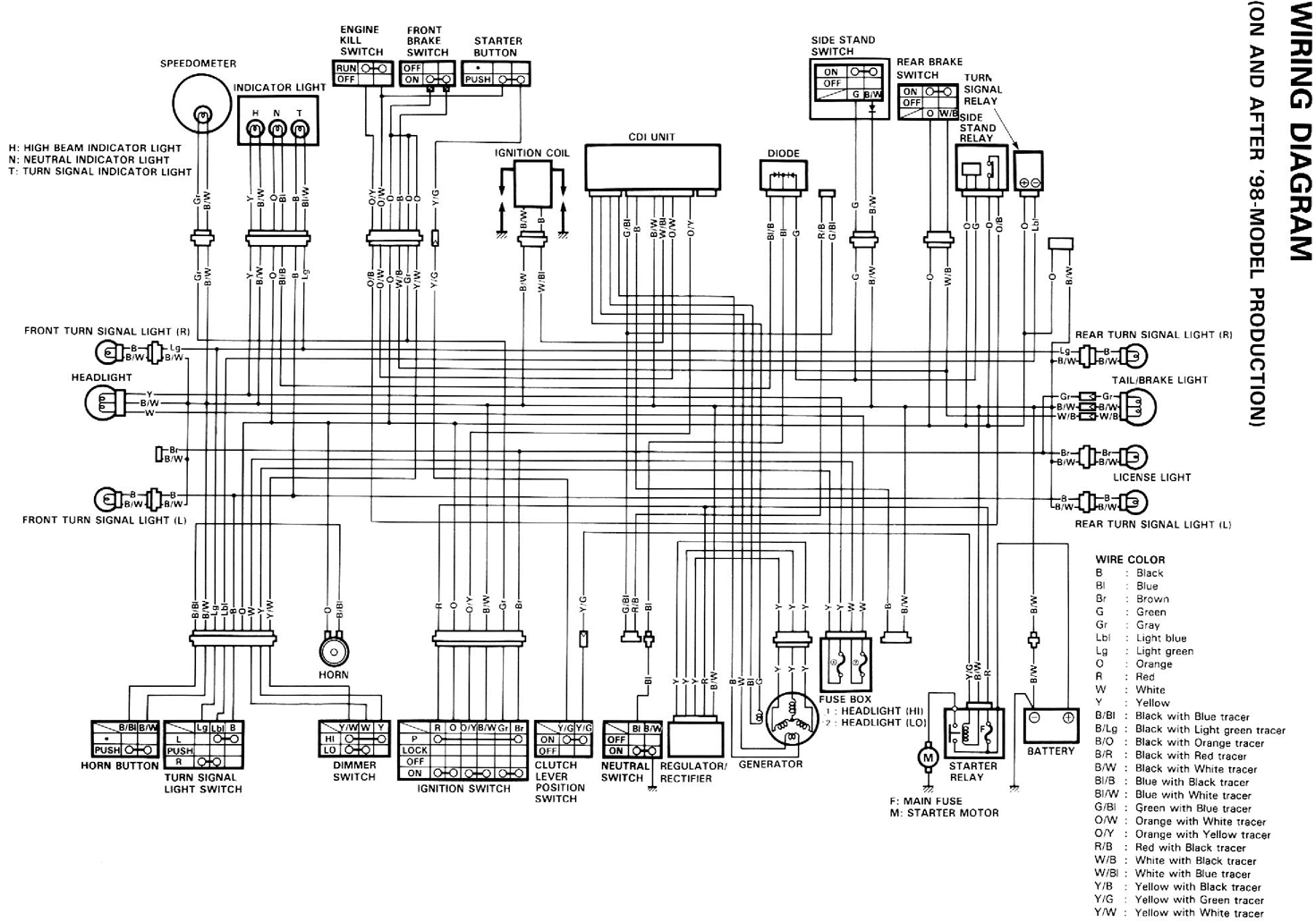
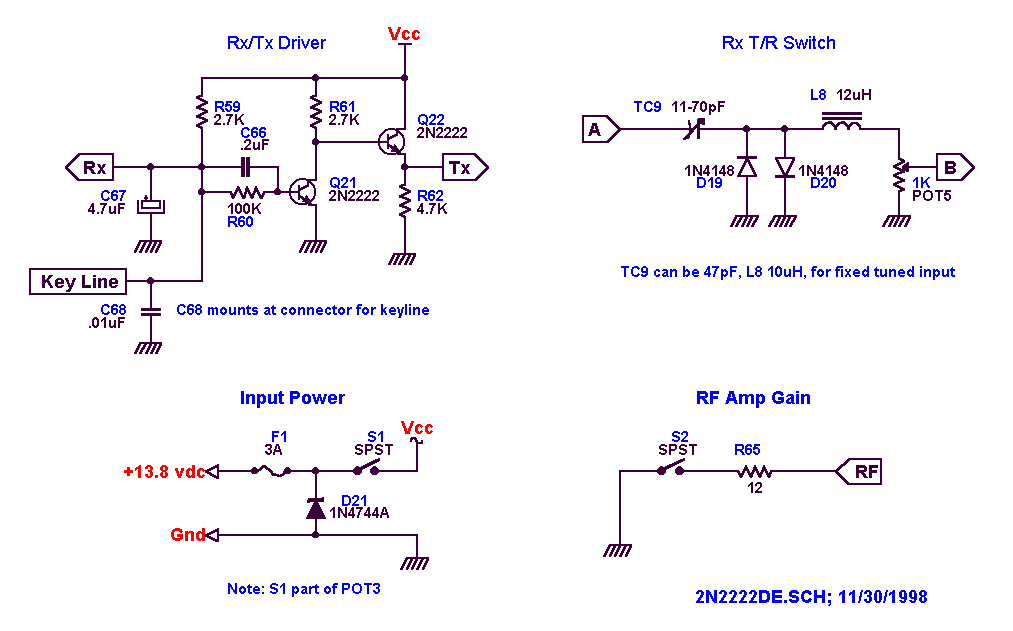
Lie Detector Circut Diagram
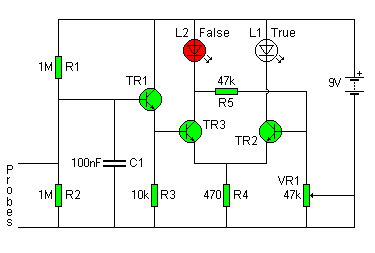
This circuit illustrates a Lie Detector Circuit Diagram. It is based on the principle that a person's skin resistance varies when they experience emotional stress.
The Lie Detector Circuit operates on the principle of galvanic skin response (GSR), which measures the electrical resistance of the skin. When a person becomes anxious or stressed, their skin resistance decreases due to increased perspiration and changes in sweat gland activity. This circuit typically employs a simple resistive divider configuration, where the skin resistance is one of the resistors in the divider.
The circuit often includes components such as an operational amplifier (op-amp) to amplify the small voltage changes resulting from the resistance variations. A microcontroller or a comparator may be used to process the amplified signal and provide a digital output indicating whether the subject is likely to be lying based on the detected skin resistance.
The power supply for the circuit is usually low voltage, often from batteries, to ensure safety during operation. Additional components might include a display unit to visualize the output, such as an LED or an LCD screen, which indicates the results of the lie detection test. Calibration is essential for accurate readings, requiring the circuit to be adjusted based on the individual’s baseline skin resistance under normal conditions.
For practical implementation, the electrodes used for measuring skin resistance should be non-invasive and comfortable for the subject. The circuit can be housed in a portable casing to allow for easy use in various environments. Overall, this Lie Detector Circuit serves as an interesting application of basic electronic principles to explore human psychological responses.This following circuit shows a Lie Detector Circuit Diagram. This circuit is based on the fact that a person`s skin resistance changes when they .. 🔗 External reference
The Lie Detector Circuit operates on the principle of galvanic skin response (GSR), which measures the electrical resistance of the skin. When a person becomes anxious or stressed, their skin resistance decreases due to increased perspiration and changes in sweat gland activity. This circuit typically employs a simple resistive divider configuration, where the skin resistance is one of the resistors in the divider.
The circuit often includes components such as an operational amplifier (op-amp) to amplify the small voltage changes resulting from the resistance variations. A microcontroller or a comparator may be used to process the amplified signal and provide a digital output indicating whether the subject is likely to be lying based on the detected skin resistance.
The power supply for the circuit is usually low voltage, often from batteries, to ensure safety during operation. Additional components might include a display unit to visualize the output, such as an LED or an LCD screen, which indicates the results of the lie detection test. Calibration is essential for accurate readings, requiring the circuit to be adjusted based on the individual’s baseline skin resistance under normal conditions.
For practical implementation, the electrodes used for measuring skin resistance should be non-invasive and comfortable for the subject. The circuit can be housed in a portable casing to allow for easy use in various environments. Overall, this Lie Detector Circuit serves as an interesting application of basic electronic principles to explore human psychological responses.This following circuit shows a Lie Detector Circuit Diagram. This circuit is based on the fact that a person`s skin resistance changes when they .. 🔗 External reference