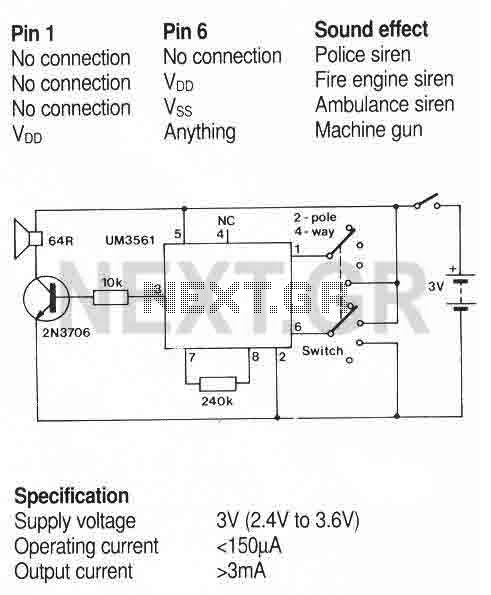
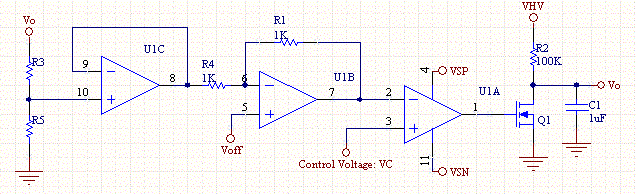
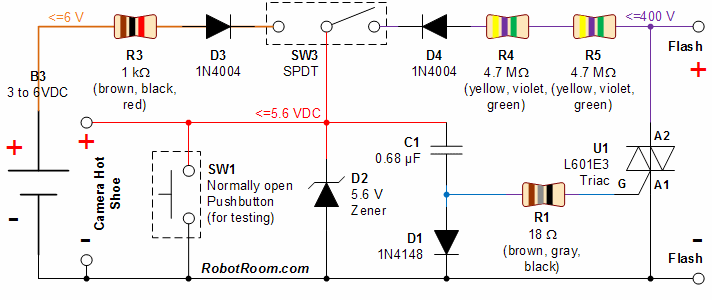
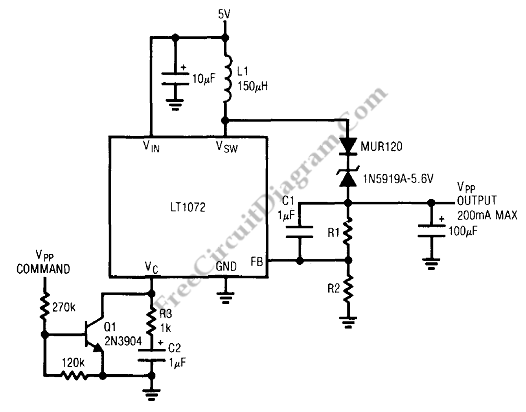
Linear voltage ramp generator
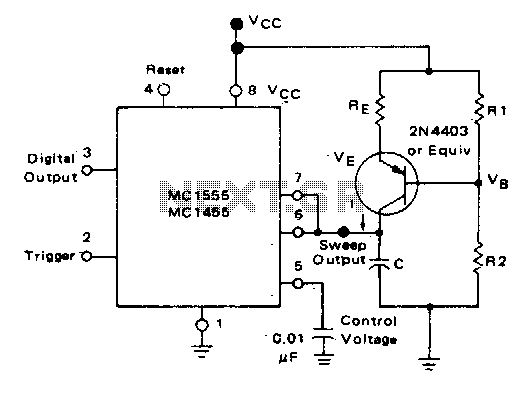
In the monostable mode, the resistor can be replaced by a constant current source to provide a linear ramp voltage. The capacitor still charges from 0 to 2/3 Vcc.
In a monostable multivibrator configuration, the circuit typically consists of a timing resistor, a timing capacitor, and a trigger input. When a trigger pulse is applied, the output transitions from a low state to a high state for a predetermined duration, determined by the RC time constant.
In this specific configuration, the resistor can be substituted with a constant current source, which allows the capacitor to charge at a linear rate rather than an exponential rate. This modification enables a more predictable and controlled ramp voltage across the capacitor. The linear ramp voltage is particularly useful in applications requiring precise timing or signal shaping.
As the capacitor charges, it progresses from an initial voltage of 0 volts to a maximum of 2/3 Vcc, where Vcc represents the supply voltage. The time taken for the capacitor to reach this threshold can be calculated using the relationship between the constant current, capacitance, and voltage change. The formula governing the charging behavior in this scenario is derived from the basic capacitor charging equation, modified to account for the constant current source.
The output of the monostable multivibrator will return to a low state once the capacitor voltage reaches the threshold of 2/3 Vcc, effectively terminating the output pulse. This characteristic makes the circuit suitable for various applications, including pulse width modulation, timers, and signal conditioning, where a precise output pulse width is essential.
Overall, the integration of a constant current source in place of a resistor in a monostable configuration enhances the linearity of the voltage ramp, providing improved performance in timing applications.In the monostable mode, the resistor can be replaced by aconstant current source to provide a linear ramp voltage The capacitor still charges from 0 to 2/3 Vcc. 🔗 External reference
In a monostable multivibrator configuration, the circuit typically consists of a timing resistor, a timing capacitor, and a trigger input. When a trigger pulse is applied, the output transitions from a low state to a high state for a predetermined duration, determined by the RC time constant.
In this specific configuration, the resistor can be substituted with a constant current source, which allows the capacitor to charge at a linear rate rather than an exponential rate. This modification enables a more predictable and controlled ramp voltage across the capacitor. The linear ramp voltage is particularly useful in applications requiring precise timing or signal shaping.
As the capacitor charges, it progresses from an initial voltage of 0 volts to a maximum of 2/3 Vcc, where Vcc represents the supply voltage. The time taken for the capacitor to reach this threshold can be calculated using the relationship between the constant current, capacitance, and voltage change. The formula governing the charging behavior in this scenario is derived from the basic capacitor charging equation, modified to account for the constant current source.
The output of the monostable multivibrator will return to a low state once the capacitor voltage reaches the threshold of 2/3 Vcc, effectively terminating the output pulse. This characteristic makes the circuit suitable for various applications, including pulse width modulation, timers, and signal conditioning, where a precise output pulse width is essential.
Overall, the integration of a constant current source in place of a resistor in a monostable configuration enhances the linearity of the voltage ramp, providing improved performance in timing applications.In the monostable mode, the resistor can be replaced by aconstant current source to provide a linear ramp voltage The capacitor still charges from 0 to 2/3 Vcc. 🔗 External reference