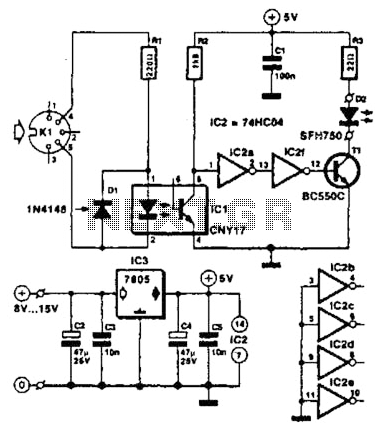
Safe Sync to Adapt Digital Camera to Higher Voltage Flash
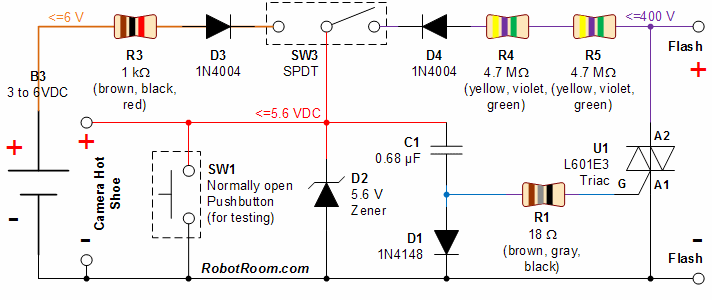
This circuit incorporates a datasheet-compliant trigger signal, reversed polarity protection, an optional test button, and the capability for battery operation. It utilizes either the U1 L601E3 or MAC97A8 triac, rated for 400 V and 1 A. When U1 is activated, the positive and negative wires of the flash are electrically connected, simulating the action of a camera hot shoe. A triac functions as a semiconductor switch, similar to a bipolar or MOSFET transistor, but it only conducts in either direction when triggered at the gate and remains on until the current flowing through it diminishes. This characteristic is advantageous for flash operation, as it allows the high voltage to dissipate fully, even if the camera does not maintain the trigger signal for the required duration. The R1 resistor, rated at 18 ohms, limits the gate current to U1, ensuring it remains below 1 amp and prolonging the trigger time to meet the minimum requirement of 2.5 µs, as specified in the L601E3 datasheet. This also restricts current across the camera hot shoe during discharge. The D1 diode, either a 1N4148 or 1N914, provides a unidirectional path that allows capacitor C1 to charge while preventing its discharge except through the triac gate. This diode is chosen for its low voltage drop, facilitating nearly complete charging of C1 compared to the 1N4004 diodes. The D2 diode, a 5.6 V Zener, safeguards the camera by capping the maximum voltage across the camera shoe to 5.6 V, mitigating the risk of damage from higher voltages. Conversely, a lower-voltage Zener diode may restrict the maximum charge voltage of capacitor C1, potentially hindering triac U1 from triggering. Resistors R4 and R5, each rated at 4.7 M ohms, limit current flow from the flash, thereby reducing voltage. Excessive current can damage the Zener diode, waste power, and cause erratic triggering of the flash. Two resistors are employed in series to handle high voltage scenarios, as a single resistor may not withstand the voltage across it. If a connection to a 400 V flash is not intended, resistance can be lowered to enhance cycle time, reducing the charging duration of the circuit from the flash. D3 and D4 are two 1N4004 diodes that act as unidirectional paths. In the event of reverse polarity connection (+ and - swapped), these diodes protect the camera from negative voltage across the hot shoe.
This circuit is designed to provide a reliable interface between a camera and a flash unit, ensuring proper operation while safeguarding sensitive components from potential damage. The triac serves as the primary switching element, allowing for controlled discharge of the flash capacitor while maintaining safety features such as reversed polarity protection through the use of diodes. The inclusion of resistors in the design not only manages current flow but also facilitates the necessary voltage drop to prevent damage to the Zener diode and the camera itself. The choice of components, including the specific triac and diodes, reflects a careful consideration of the operational requirements and safety parameters, ensuring that the circuit functions effectively within its specified limits. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-thought-out design that balances performance and protection for photographic applications involving flash photography.This circuit adds a datasheet-compliant trigger signal, reversed polarity protection, optional test button, and optional battery operation. U1 L601E3 or MAC97A8 triac. 400 V, 1 A. When U1 is enabled, the + and - wires of the flash are electrically connected, just as though the camera hot shoe had done so.
A triac is a semiconductor switch, similar to a bipolar or MOSFET transistor, except that it won`t conduct in either direction unless turned on at the gate, and it won`t turn off until the current across it subsides. This is beneficial for a flash, since it allows the high voltage to fully dissipate, even if the camera doesn`t assert the trigger signal long enough.
R1 18 © resistor. This limits the current passing through the gate of U1; to keep the current below 1 amp and to extend the amount of time it remains triggered in order to meet the 2. 5 µs minimum. Both of these limits are specified by the L601E3 datasheet. Furthermore, this limits the amount of current across the camera hot shoe during discharge. D1 1N4148 or 1N914 diode. This is a one-way path that allows capacitor C1 to charge, but won`t allow it to discharge except through the gate of the triac.
(Pictures of the current flow are presented on the next page. ) The type of diode selected has a relatively low voltage drop, in comparison to the 1N4004 diodes, to allow C1 to charge almost completely. D2 5. 6 V Zener diode. This protects the camera by limiting the maximum voltage across the camera shoe to no more than 5. 6 V. A higher-voltage Zener diode runs the risk of damage to the camera. A lower-voltage Zener diode reduces the maximum charge voltage of capacitor C1, which may prevent triac U1 from triggering.
R4 and R5 Two 4. 7 M © resistors. These limit the amount of current that can flow from the flash, reducing voltage along the way. If too much current flows, the Zener diode can be damaged, it wastes power, and the flash may either constantly trigger or never trigger. Multiple resistors are used in series instead of a single resistor, since there is a limit on how much voltage a single resistor can handle across it.
If you are not going to connect up to a 400 V flash, you can reduce the resistance to speed cycle time (reduce the time it takes to charge the circuit from the flash). D3 and D4 Two 1N4004 diodes. These diodes are one-way paths. If the selected power source is connected backwards (reverse polarity, + and - swapped), it won`t harm the camera with a negative voltage across the hot shoe, because the diode
🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to provide a reliable interface between a camera and a flash unit, ensuring proper operation while safeguarding sensitive components from potential damage. The triac serves as the primary switching element, allowing for controlled discharge of the flash capacitor while maintaining safety features such as reversed polarity protection through the use of diodes. The inclusion of resistors in the design not only manages current flow but also facilitates the necessary voltage drop to prevent damage to the Zener diode and the camera itself. The choice of components, including the specific triac and diodes, reflects a careful consideration of the operational requirements and safety parameters, ensuring that the circuit functions effectively within its specified limits. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a well-thought-out design that balances performance and protection for photographic applications involving flash photography.This circuit adds a datasheet-compliant trigger signal, reversed polarity protection, optional test button, and optional battery operation. U1 L601E3 or MAC97A8 triac. 400 V, 1 A. When U1 is enabled, the + and - wires of the flash are electrically connected, just as though the camera hot shoe had done so.
A triac is a semiconductor switch, similar to a bipolar or MOSFET transistor, except that it won`t conduct in either direction unless turned on at the gate, and it won`t turn off until the current across it subsides. This is beneficial for a flash, since it allows the high voltage to fully dissipate, even if the camera doesn`t assert the trigger signal long enough.
R1 18 © resistor. This limits the current passing through the gate of U1; to keep the current below 1 amp and to extend the amount of time it remains triggered in order to meet the 2. 5 µs minimum. Both of these limits are specified by the L601E3 datasheet. Furthermore, this limits the amount of current across the camera hot shoe during discharge. D1 1N4148 or 1N914 diode. This is a one-way path that allows capacitor C1 to charge, but won`t allow it to discharge except through the gate of the triac.
(Pictures of the current flow are presented on the next page. ) The type of diode selected has a relatively low voltage drop, in comparison to the 1N4004 diodes, to allow C1 to charge almost completely. D2 5. 6 V Zener diode. This protects the camera by limiting the maximum voltage across the camera shoe to no more than 5. 6 V. A higher-voltage Zener diode runs the risk of damage to the camera. A lower-voltage Zener diode reduces the maximum charge voltage of capacitor C1, which may prevent triac U1 from triggering.
R4 and R5 Two 4. 7 M © resistors. These limit the amount of current that can flow from the flash, reducing voltage along the way. If too much current flows, the Zener diode can be damaged, it wastes power, and the flash may either constantly trigger or never trigger. Multiple resistors are used in series instead of a single resistor, since there is a limit on how much voltage a single resistor can handle across it.
If you are not going to connect up to a 400 V flash, you can reduce the resistance to speed cycle time (reduce the time it takes to charge the circuit from the flash). D3 and D4 Two 1N4004 diodes. These diodes are one-way paths. If the selected power source is connected backwards (reverse polarity, + and - swapped), it won`t harm the camera with a negative voltage across the hot shoe, because the diode
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713