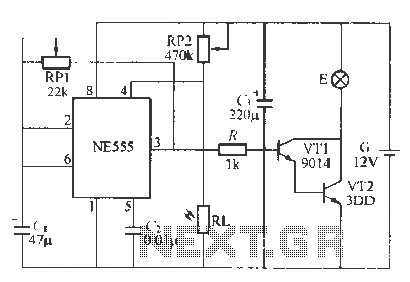
lm358 alkaline battery charger circuit
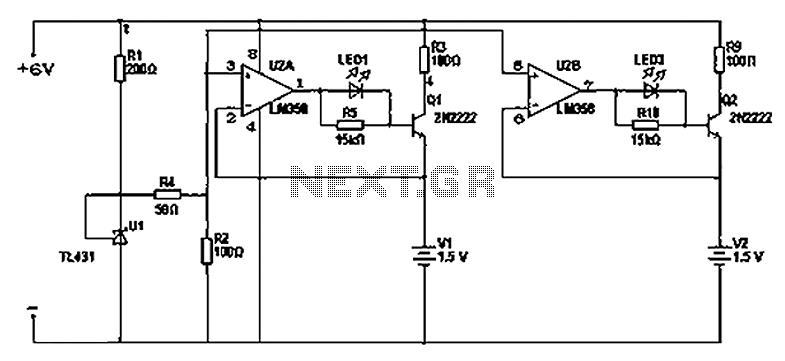
There are two differing opinions regarding the charging of alkaline batteries. Some assert that charging is effective, while others caution against it due to the risk of explosion. It is acknowledged that rechargeable alkaline batteries can typically endure 30 to 50 charge cycles. The contrasting outcomes stem from the methods employed for charging control. It is clear that some alkaline batteries can be charged, but non-rechargeable alkaline batteries may indeed pose an explosion risk when charged. This warning may also serve as a self-protection disclaimer from manufacturers. The critical factor in charging alkaline batteries is temperature; as long as the temperature remains stable during charging, the process can be completed successfully. Proper charging methods include: 1. A small current of 50 mA; 2. Charging voltage should be 1.7V, but the battery should be at 1.3V. Some individuals have reported failures in charging due to various issues, primarily related to the charger. If the charger current exceeds 50 mA, particularly with fast chargers that provide currents above 200 mA, excessive heat can lead to leakage or even explosion. Using a nickel-metal hydride charger for alkaline batteries can result in overcharging, as these chargers may lack an automatic cutoff feature. The ideal charger should automatically stop charging at around 1.42V, while alkaline batteries typically reach full charge at approximately 1.7V. Thus, a lower cutoff voltage can lead to inadequate charging. It is also advised not to wait until the battery is fully depleted before recharging, as this can diminish the effectiveness of the battery. It is generally recommended that the voltage of alkaline batteries not fall below 1.3V. Therefore, when charging alkaline batteries, it is essential to use a qualified charger with a current of about 50 mA and a cutoff voltage of approximately 1.7V. There are chargers available specifically for alkaline batteries that utilize a simple circuit with a charging voltage of 1.7V and a current of 50 mA. A basic circuit can be constructed using components such as the LM358 and TL431 to achieve an automatic cutoff at 1.67V, with a low cost of around two yuan.
Rechargeable alkaline manganese batteries are developed from alkaline manganese batteries and are mercury-free due to the use of new additives and zinc, often referred to as mercury-free alkaline manganese batteries. This development does not alter the original discharge characteristics of alkaline batteries while allowing charging up to dozens or hundreds of times. Alkaline manganese batteries were initially developed in 1882, with further advancements in 1912, and became operational before 1949. The use of KOH as an electrolyte instead of NH4Cl has significantly improved discharge current and specific energy. Key features include: 1. An open circuit voltage of 1.5V; 2. A wide operating temperature range of -20°C to 60°C, making them suitable for use in cold climates; 3. Continuous high-current discharge capacity that is approximately five times greater than that of acidic zinc-manganese batteries; 4. Good low-temperature discharge performance. Charging cycles for these batteries are generally less than 30, typically ranging from 10 to 20 cycles, and they can easily lose charge capacity if not used with a special charger. Can alkaline batteries charging problem, there are two different versions. Some say you can charge, the effect is very good. Some say absolutely can not charge the battery desc ribed suggests there is a risk of explosion. Indeed, indeed rechargeable alkaline batteries, the charge number is about 30-50 times. Actually due to the charging control method, resulting in two distinct consequences. First, the alkaline battery can be charged is not in doubt, while the battery description, mentioned non-rechargeable alkaline batteries, charging may cause an explosion. This is also true, but note that this wording is likely cause an explosion. You can also be understood as a kind of self-protection declaration of exemption manufacturers. Key alkaline batteries is temperature. As long as the temperature does not appear able to do when charging the battery, you can successfully complete the charging process, the correct charging method has several requirements: 1.
Small current 50MA 2. However charge 1.7V, but put 1.3V Some people try charging after practice, can not charge categorically said that the reason can not be recharged into the electric, electricity short time, leakage, explosion and other problems, mostly charger problem, if the charger current is too large, far more than 50ma, as some quick charger charging current 200ma above, is a direct consequence of the high temperature of the battery feels hot, light leak, serious will explode. Some people use nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery charger to charge the low-end of the charger does not automatically stop charging function, charging time will cause the battery to overcharge occurs leakage and explosion.
Better charger with automatic stop charging function, but is generally set to stop the charging voltage nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery 1.42V, while alkaline battery full voltage of about 1.7V. Therefore, the voltage is too low, the feeling is recharged into the electric, electricity short time, no effect.
But then there is the battery discharge means is do not wait until the battery is completely recharged, this operation, even the best batteries will be able to charge three, five, and poor results. Usually recommended Nanfu alkaline battery voltage is not lower than 1.3V. So, if you intend to alkaline batteries, there must be a qualified charger, the charging current of about 50ma, charging cut-off voltage of about 1.7V.
Look at your home charger it. There are selling alkaline battery charger, the so-called patent products. In fact, the charging voltage 1.7V current 50ma simple circuit. Use existing parts on hand and LM358 TL431, I made a simple circuit cut-off voltage 1.67V automatically stop charging, cost two yuan only. Interested friends for a reference. Instructions: Rechargeable alkaline manganese batteries: is developed on the basis of the alkaline manganese batteries, mercury-free due to the use of new additives and zinc, also called mercury-free alkaline manganese batteries.
This does not change the original battery discharge characteristics of alkaline batteries at the same time, but also is charged with dozens to hundreds of times more affordable. Alkaline manganese batteries referred to as the alkaline manganese batteries, it is successfully developed in 1882, it had been developed in 1912, to come into operation before 1949.
It was found that when using KOH electrolyte solution instead of doing NH4Cl electrolyte, the electrolyte, or whether there are major changes in the structure of the battery discharge current and specific energy can be significantly improved. It features: 1. The open circuit voltage of 1.5V; 2. The wide operating temperature range between -20 ~ 60, suitable for use in Alpine regions; 3. Continuous high-current discharge capacity is about five times the acidic zinc-manganese batteries; 4.
It is also good low temperature discharge performance. Charging times in less than 30 times, usually 10-20 times, special charger, very easy to lose charge capacity.
Rechargeable alkaline manganese batteries are developed from alkaline manganese batteries and are mercury-free due to the use of new additives and zinc, often referred to as mercury-free alkaline manganese batteries. This development does not alter the original discharge characteristics of alkaline batteries while allowing charging up to dozens or hundreds of times. Alkaline manganese batteries were initially developed in 1882, with further advancements in 1912, and became operational before 1949. The use of KOH as an electrolyte instead of NH4Cl has significantly improved discharge current and specific energy. Key features include: 1. An open circuit voltage of 1.5V; 2. A wide operating temperature range of -20°C to 60°C, making them suitable for use in cold climates; 3. Continuous high-current discharge capacity that is approximately five times greater than that of acidic zinc-manganese batteries; 4. Good low-temperature discharge performance. Charging cycles for these batteries are generally less than 30, typically ranging from 10 to 20 cycles, and they can easily lose charge capacity if not used with a special charger. Can alkaline batteries charging problem, there are two different versions. Some say you can charge, the effect is very good. Some say absolutely can not charge the battery desc ribed suggests there is a risk of explosion. Indeed, indeed rechargeable alkaline batteries, the charge number is about 30-50 times. Actually due to the charging control method, resulting in two distinct consequences. First, the alkaline battery can be charged is not in doubt, while the battery description, mentioned non-rechargeable alkaline batteries, charging may cause an explosion. This is also true, but note that this wording is likely cause an explosion. You can also be understood as a kind of self-protection declaration of exemption manufacturers. Key alkaline batteries is temperature. As long as the temperature does not appear able to do when charging the battery, you can successfully complete the charging process, the correct charging method has several requirements: 1.
Small current 50MA 2. However charge 1.7V, but put 1.3V Some people try charging after practice, can not charge categorically said that the reason can not be recharged into the electric, electricity short time, leakage, explosion and other problems, mostly charger problem, if the charger current is too large, far more than 50ma, as some quick charger charging current 200ma above, is a direct consequence of the high temperature of the battery feels hot, light leak, serious will explode. Some people use nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery charger to charge the low-end of the charger does not automatically stop charging function, charging time will cause the battery to overcharge occurs leakage and explosion.
Better charger with automatic stop charging function, but is generally set to stop the charging voltage nickel-metal hydride rechargeable battery 1.42V, while alkaline battery full voltage of about 1.7V. Therefore, the voltage is too low, the feeling is recharged into the electric, electricity short time, no effect.
But then there is the battery discharge means is do not wait until the battery is completely recharged, this operation, even the best batteries will be able to charge three, five, and poor results. Usually recommended Nanfu alkaline battery voltage is not lower than 1.3V. So, if you intend to alkaline batteries, there must be a qualified charger, the charging current of about 50ma, charging cut-off voltage of about 1.7V.
Look at your home charger it. There are selling alkaline battery charger, the so-called patent products. In fact, the charging voltage 1.7V current 50ma simple circuit. Use existing parts on hand and LM358 TL431, I made a simple circuit cut-off voltage 1.67V automatically stop charging, cost two yuan only. Interested friends for a reference. Instructions: Rechargeable alkaline manganese batteries: is developed on the basis of the alkaline manganese batteries, mercury-free due to the use of new additives and zinc, also called mercury-free alkaline manganese batteries.
This does not change the original battery discharge characteristics of alkaline batteries at the same time, but also is charged with dozens to hundreds of times more affordable. Alkaline manganese batteries referred to as the alkaline manganese batteries, it is successfully developed in 1882, it had been developed in 1912, to come into operation before 1949.
It was found that when using KOH electrolyte solution instead of doing NH4Cl electrolyte, the electrolyte, or whether there are major changes in the structure of the battery discharge current and specific energy can be significantly improved. It features: 1. The open circuit voltage of 1.5V; 2. The wide operating temperature range between -20 ~ 60, suitable for use in Alpine regions; 3. Continuous high-current discharge capacity is about five times the acidic zinc-manganese batteries; 4.
It is also good low temperature discharge performance. Charging times in less than 30 times, usually 10-20 times, special charger, very easy to lose charge capacity.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713