Radiation Sensor Circuit
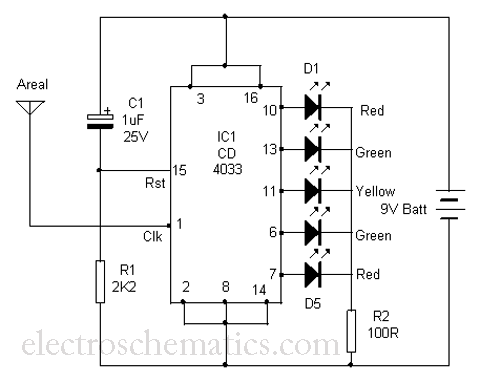
This is a simple tool designed to measure the level of radiation emitted by electrical or electronic devices. The circuit utilizes LEDs to create a running light pattern when it detects electromagnetic radiation from a source. It can detect radiation from devices such as computers or televisions from a distance of two feet or more. The circuit employs the CD4033 decade counter, which also functions as a driver for a seven-segment display. This integrated circuit has seven outputs that can be used to illuminate LEDs or a seven-segment display. The clock input (pin 1) of the IC is highly sensitive and can easily pick up energy from electromagnetic radiation, even from a considerable distance. This characteristic of the CD4033 is utilized to gauge the intensity of radiation. The reset pin (pin 15) of the IC is connected to capacitor C1 and resistor R1, allowing the IC to reset after completing a cycle, ensuring continuous operation until the input pulses stop. When the device is brought close to a television or CRT monitor, the LEDs will light up sequentially, creating a running light effect. The speed of this light pattern is proportional to the strength of the detected radiation. As the device is moved away from the monitor, the speed of the running light pattern decreases, eventually causing all LEDs to stop illuminating, indicating the absence of radiation. This device can be used to check various electrical instruments and mains wiring to assess their radiation emission levels.
The circuit is primarily based on the CD4033 decade counter, which is a CMOS integrated circuit designed for counting applications. It features a binary counting capability, which can be translated into visual signals through the LEDs. The circuit operates by capturing electromagnetic radiation, which induces a clock signal at the input pin of the CD4033. The sensitivity of the IC allows it to detect even weak signals, making it effective for monitoring radiation from common household appliances.
The LED outputs are configured in such a way that they light up in succession, creating a visual representation of the radiation intensity. The arrangement of the LEDs can be designed to provide a clear indication of the radiation level, with more LEDs lighting up as the radiation increases. The timing of the LED sequence is determined by the frequency of the clock signal generated by the radiation, which is influenced by the distance from the source.
Capacitor C1 and resistor R1 play a crucial role in resetting the IC after each cycle. This reset mechanism ensures that the counter returns to its initial state, allowing for continuous monitoring without manual intervention. The choice of values for C1 and R1 is critical, as they determine the timing of the reset and the responsiveness of the circuit to changes in radiation levels.
To enhance the usability of the device, it may incorporate a power supply circuit, ensuring that it operates reliably without fluctuations. Additionally, a housing could be designed to protect the circuit and provide a user-friendly interface, such as a calibration feature or a scale indicating radiation levels. Overall, this radiation detection tool serves as a practical solution for assessing the safety of electronic devices in various environments.Here is a simple tool to check the degree of radiation from an electric or electronic instrument. The LEDs in the circuit will give a running light pattern at the moment the circuit senses electromagnetic radiation from the device. It can detect radiation from the Computer or TV from a distance of 2 feet or more. ICCD4033is the decade counter with 7 segment display driver. It has seven outputs to drive LEDs or Seven segment display. The clock input (pin1) of IC isvery sensitiveand readily accepts energy from the electromagnetic radiation even from a long distance. This property of the IC CD4033 is exploited here to measure the intensity of radiation. The reset pin 15 of IC is connected to C1 and R1 to reset the IC after completing a cycle. So that the functioning of IC continues till the input pulses cease. Bring the areal close to the TV or CRT monitor of computer. All the LEDs light up one by one giving a running pattern. The speed of running light depends on the strength of radiation. Move away the unit from the monitor. As the diastance increases, speed of running light decreases. Finally all the LEDs stop glowing. This is the point without the radiation. Check all the electric instruments and mains wiring using the device and find out how much radiation is emitting.
🔗 External reference
The circuit is primarily based on the CD4033 decade counter, which is a CMOS integrated circuit designed for counting applications. It features a binary counting capability, which can be translated into visual signals through the LEDs. The circuit operates by capturing electromagnetic radiation, which induces a clock signal at the input pin of the CD4033. The sensitivity of the IC allows it to detect even weak signals, making it effective for monitoring radiation from common household appliances.
The LED outputs are configured in such a way that they light up in succession, creating a visual representation of the radiation intensity. The arrangement of the LEDs can be designed to provide a clear indication of the radiation level, with more LEDs lighting up as the radiation increases. The timing of the LED sequence is determined by the frequency of the clock signal generated by the radiation, which is influenced by the distance from the source.
Capacitor C1 and resistor R1 play a crucial role in resetting the IC after each cycle. This reset mechanism ensures that the counter returns to its initial state, allowing for continuous monitoring without manual intervention. The choice of values for C1 and R1 is critical, as they determine the timing of the reset and the responsiveness of the circuit to changes in radiation levels.
To enhance the usability of the device, it may incorporate a power supply circuit, ensuring that it operates reliably without fluctuations. Additionally, a housing could be designed to protect the circuit and provide a user-friendly interface, such as a calibration feature or a scale indicating radiation levels. Overall, this radiation detection tool serves as a practical solution for assessing the safety of electronic devices in various environments.Here is a simple tool to check the degree of radiation from an electric or electronic instrument. The LEDs in the circuit will give a running light pattern at the moment the circuit senses electromagnetic radiation from the device. It can detect radiation from the Computer or TV from a distance of 2 feet or more. ICCD4033is the decade counter with 7 segment display driver. It has seven outputs to drive LEDs or Seven segment display. The clock input (pin1) of IC isvery sensitiveand readily accepts energy from the electromagnetic radiation even from a long distance. This property of the IC CD4033 is exploited here to measure the intensity of radiation. The reset pin 15 of IC is connected to C1 and R1 to reset the IC after completing a cycle. So that the functioning of IC continues till the input pulses cease. Bring the areal close to the TV or CRT monitor of computer. All the LEDs light up one by one giving a running pattern. The speed of running light depends on the strength of radiation. Move away the unit from the monitor. As the diastance increases, speed of running light decreases. Finally all the LEDs stop glowing. This is the point without the radiation. Check all the electric instruments and mains wiring using the device and find out how much radiation is emitting.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713