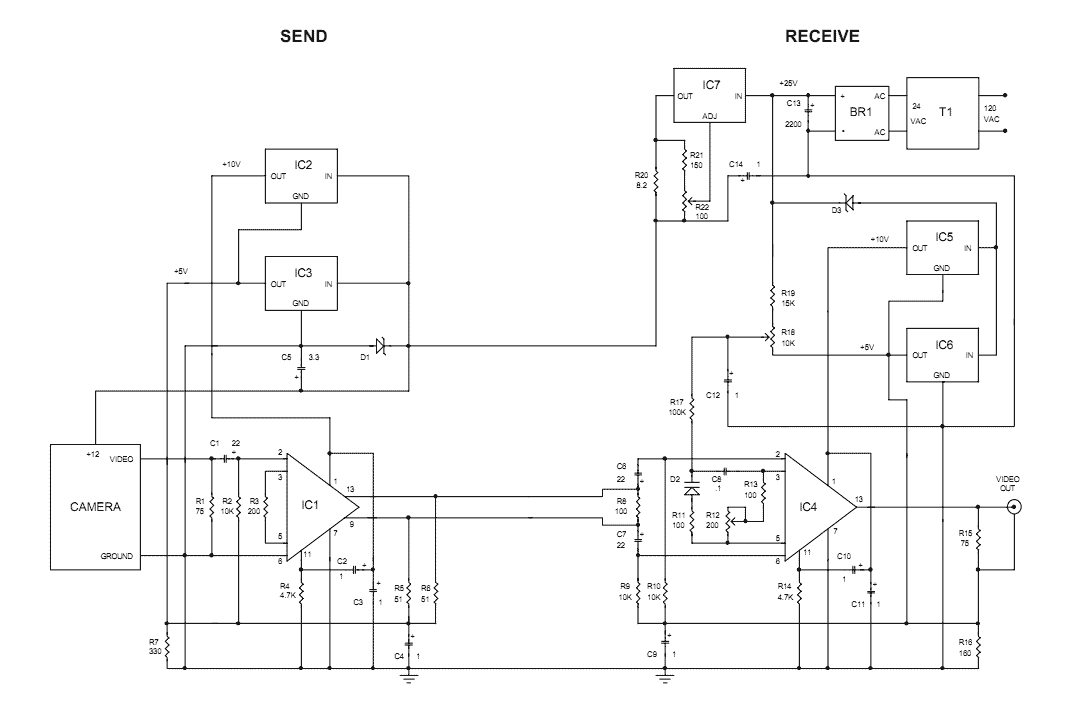
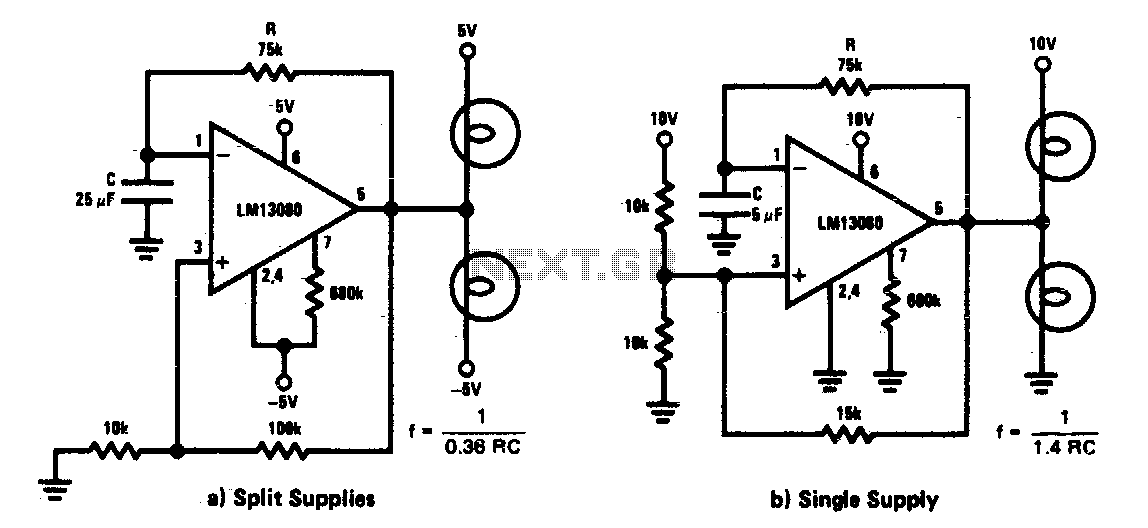
LM359 1MHz Balanced Line Driver
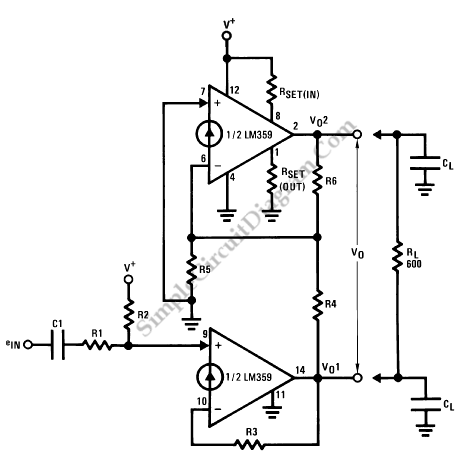
Balanced signals consist of two lines that have opposite phases and should be received with a differential input receiver. Balanced signals are employed in many applications.
Balanced signals are primarily used in audio and communication systems to minimize noise and interference. They are characterized by sending an identical signal on two conductors, with one conductor carrying the signal in its original phase and the other carrying it in an inverted phase. This configuration allows for the cancellation of any noise that may be induced equally on both lines during transmission.
In a typical balanced signal circuit, the differential input receiver is designed to detect the voltage difference between the two lines. This is crucial because it enhances the immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which are common in environments where electronic signals are transmitted. The differential receiver amplifies only the difference between the two signals, effectively rejecting any common-mode noise that may have been picked up along the transmission path.
Balanced signal circuits often utilize twisted pair cables, where the two conductors are twisted together to further enhance noise cancellation. This twisting helps to ensure that any external noise affects both conductors equally, allowing the differential receiver to negate this noise.
In practical applications, balanced signals are commonly used in professional audio equipment, such as microphones, mixing consoles, and amplifiers, as well as in data communication systems like Ethernet, where signal integrity is paramount. The implementation of balanced signaling techniques significantly improves the performance and reliability of electronic systems in noisy environments.Balanced signal consist of two lines that have opposite phases, and should be received with differential input receiver. Balanced signal is employed in many.. 🔗 External reference
Balanced signals are primarily used in audio and communication systems to minimize noise and interference. They are characterized by sending an identical signal on two conductors, with one conductor carrying the signal in its original phase and the other carrying it in an inverted phase. This configuration allows for the cancellation of any noise that may be induced equally on both lines during transmission.
In a typical balanced signal circuit, the differential input receiver is designed to detect the voltage difference between the two lines. This is crucial because it enhances the immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which are common in environments where electronic signals are transmitted. The differential receiver amplifies only the difference between the two signals, effectively rejecting any common-mode noise that may have been picked up along the transmission path.
Balanced signal circuits often utilize twisted pair cables, where the two conductors are twisted together to further enhance noise cancellation. This twisting helps to ensure that any external noise affects both conductors equally, allowing the differential receiver to negate this noise.
In practical applications, balanced signals are commonly used in professional audio equipment, such as microphones, mixing consoles, and amplifiers, as well as in data communication systems like Ethernet, where signal integrity is paramount. The implementation of balanced signaling techniques significantly improves the performance and reliability of electronic systems in noisy environments.Balanced signal consist of two lines that have opposite phases, and should be received with differential input receiver. Balanced signal is employed in many.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713