LM3914 Low Power LED Voltmeter
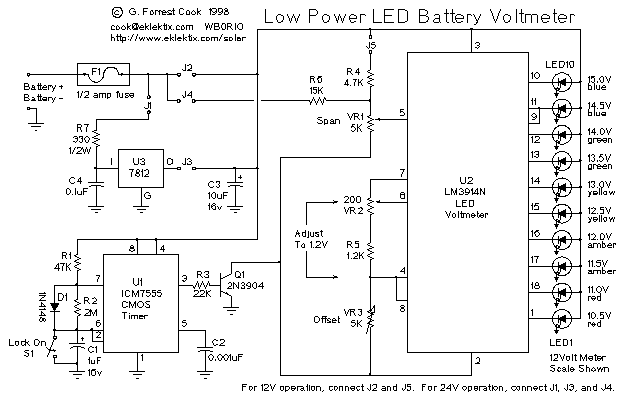
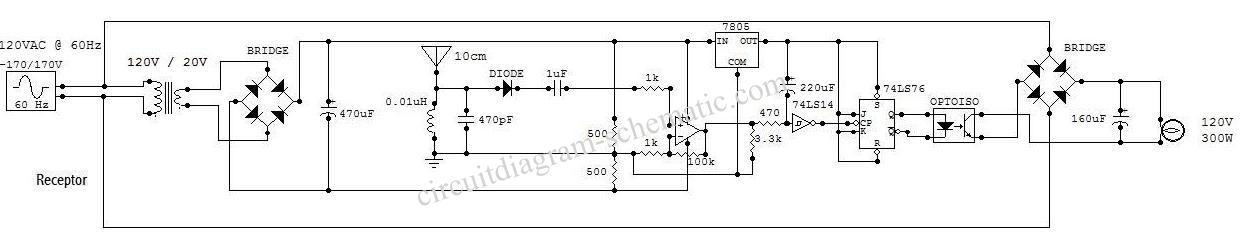
This is a low-power voltmeter circuit suitable for alternative energy systems operating on 12-volt and 24-volt batteries. The voltmeter features an expanded scale design, allowing it to display small voltage increments within the 10 to 16-volt range for 12-volt batteries and the 22 to 32-volt range for 24-volt batteries. The power consumption is as low as 14 mW when powered by 12V and 160 mW when powered by 24V. The meter can be configured to read equal steps across various upper and lower voltage limits. Power efficiency is enhanced through a low duty-cycle blinking mode, where LED indicators are activated briefly during a repeating two-second cycle. The circuit can be switched to a high-power mode, wherein the active LED remains continuously lit. Different colored LEDs can be employed for voltage level indicators, facilitating battery status reading in low-light conditions. With the introduction of blue LEDs, a visually appealing range of colors can be created using two each of red, amber, yellow, green, and blue LEDs. The circuit is also compatible with standard red LEDs. For outdoor use, ultra-bright LEDs are recommended, although visibility may still be affected by sunlight without a sun shield. Typical applications include monitoring portable battery-operated systems and serving as indoor wall-mounted charge indicators for home power systems. The estimated cost of the components is approximately $25.00 (USD), with most parts readily available, except for the optional blue LEDs, which are more expensive at several dollars each compared to around 15 cents for other colors. The circuit can be constructed using either the CMOS ICM7555 timer or the more widely used bipolar 555 timer, with the former offering improved efficiency for small battery applications. The voltmeter integrates well with solar charge controllers and low voltage disconnect circuits as described in Home Power issues #60 and #63.
This low-power voltmeter circuit is designed to effectively monitor battery voltage levels in alternative energy systems, ensuring that users can maintain optimal battery performance. The expanded scale voltmeter is particularly beneficial for applications requiring precise voltage readings, as it allows for small voltage increments to be displayed clearly. The low power consumption of the circuit is a critical feature, especially for systems relying on limited energy sources such as solar panels.
The blinking mode of the LED indicators not only conserves battery life but also provides a user-friendly interface that minimizes distractions. In the high-power mode, the continuous illumination of the LED can be advantageous for quick checks in environments where immediate visibility is required. The choice of LED colors enhances both functionality and aesthetic appeal, allowing users to customize the display according to their preferences.
When selecting components, the use of the CMOS ICM7555 timer is recommended for applications where energy efficiency is paramount, particularly in systems with small batteries. This choice can significantly extend the operational life of the battery, making it an ideal solution for portable applications.
Furthermore, the compatibility with common charge controllers and low voltage disconnect circuits underscores the versatility of this voltmeter circuit. By integrating such systems, users can ensure that their batteries are not only monitored but also protected from over-discharge, thereby enhancing the longevity and reliability of their energy systems. Overall, this voltmeter circuit is a valuable addition to any alternative energy setup, providing essential monitoring capabilities while maintaining low power consumption.This is a low power voltmeter circuit that can be used with alternative energy systems that run on 12 and 24 volt batteries. The voltmeter is an expanded scale type that indicates small voltage steps over the 10 to 16 volt range for 12 volt batteries and over the 22 to 32 volt range for 24 volt batteries.
Power consumption can be as low as 14mw wh en operated from 12V and 160mw when operated from 24V. It is possible to set the meter to read equal steps across a variety of upper and lower voltages. The meter saves power by operating in a low duty-cycle blinking mode where the LED indicators are only on and consuming power briefly during a repeating 2 second cycle. The circuit may be switched to a high power mode where the active LED stays on at all times. Different colored LEDs may be used for the voltage level indicators, this allows the battery state to be read in the dark.
With the new blue LEDs, it is possible to have a nice looking rainbow of colors using two each of red, amber, yellow, green, and blue LEDs. The circuit will also work with inexpensive and common red LEDs. If the circuit is to be used in sunlight, ultra-bright LEDs should be used, although even those may be hard to read without some kind of sun shield.
Typical uses include the monitoring of portable battery operated systems and indoor wall mounted home power system charge indicators. The cost of the parts for the circuit is around $25. 00 (US) and the parts are commonly available, except for the optional blue LEDs. If blue LEDS are used, expect to pay a premium for them, they cost several dollars each, compared to around 15 cents for the other colors.
The blue LEDs do look nice in any case. The circuit may be built with either the CMOS ICM7555 timer or the more common bipolar 555 timer. The 7555 timer will provide much more efficient operation and should be used for systems with small batteries. The volt meter works nicely with the solar charge controller and low voltage disconnect circuits described in the home-brew section of Home Power #60 and #63.
🔗 External reference
This low-power voltmeter circuit is designed to effectively monitor battery voltage levels in alternative energy systems, ensuring that users can maintain optimal battery performance. The expanded scale voltmeter is particularly beneficial for applications requiring precise voltage readings, as it allows for small voltage increments to be displayed clearly. The low power consumption of the circuit is a critical feature, especially for systems relying on limited energy sources such as solar panels.
The blinking mode of the LED indicators not only conserves battery life but also provides a user-friendly interface that minimizes distractions. In the high-power mode, the continuous illumination of the LED can be advantageous for quick checks in environments where immediate visibility is required. The choice of LED colors enhances both functionality and aesthetic appeal, allowing users to customize the display according to their preferences.
When selecting components, the use of the CMOS ICM7555 timer is recommended for applications where energy efficiency is paramount, particularly in systems with small batteries. This choice can significantly extend the operational life of the battery, making it an ideal solution for portable applications.
Furthermore, the compatibility with common charge controllers and low voltage disconnect circuits underscores the versatility of this voltmeter circuit. By integrating such systems, users can ensure that their batteries are not only monitored but also protected from over-discharge, thereby enhancing the longevity and reliability of their energy systems. Overall, this voltmeter circuit is a valuable addition to any alternative energy setup, providing essential monitoring capabilities while maintaining low power consumption.This is a low power voltmeter circuit that can be used with alternative energy systems that run on 12 and 24 volt batteries. The voltmeter is an expanded scale type that indicates small voltage steps over the 10 to 16 volt range for 12 volt batteries and over the 22 to 32 volt range for 24 volt batteries.
Power consumption can be as low as 14mw wh en operated from 12V and 160mw when operated from 24V. It is possible to set the meter to read equal steps across a variety of upper and lower voltages. The meter saves power by operating in a low duty-cycle blinking mode where the LED indicators are only on and consuming power briefly during a repeating 2 second cycle. The circuit may be switched to a high power mode where the active LED stays on at all times. Different colored LEDs may be used for the voltage level indicators, this allows the battery state to be read in the dark.
With the new blue LEDs, it is possible to have a nice looking rainbow of colors using two each of red, amber, yellow, green, and blue LEDs. The circuit will also work with inexpensive and common red LEDs. If the circuit is to be used in sunlight, ultra-bright LEDs should be used, although even those may be hard to read without some kind of sun shield.
Typical uses include the monitoring of portable battery operated systems and indoor wall mounted home power system charge indicators. The cost of the parts for the circuit is around $25. 00 (US) and the parts are commonly available, except for the optional blue LEDs. If blue LEDS are used, expect to pay a premium for them, they cost several dollars each, compared to around 15 cents for the other colors.
The blue LEDs do look nice in any case. The circuit may be built with either the CMOS ICM7555 timer or the more common bipolar 555 timer. The 7555 timer will provide much more efficient operation and should be used for systems with small batteries. The volt meter works nicely with the solar charge controller and low voltage disconnect circuits described in the home-brew section of Home Power #60 and #63.
🔗 External reference