LM723 voltage regulator circuit diagram consisting of cars
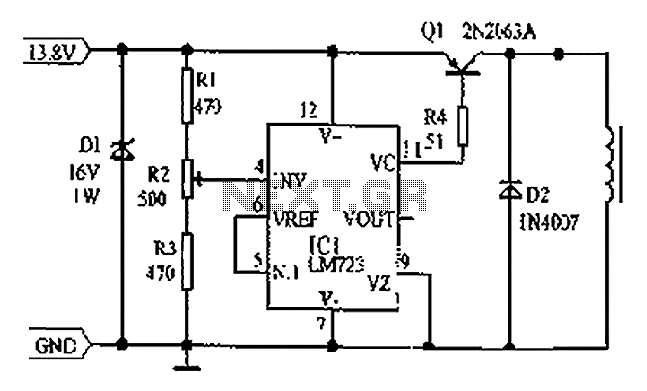
Cars are equipped with a circuit that includes an LM723 regulator, which can serve as a replacement for traditional automobile generator systems that utilize electromechanical charging regulators. This circuit offers superior performance compared to conventional systems. It ensures that a 12V lead-acid battery does not become undercharged or overcharged, thereby extending the battery's lifespan. The LM723 in this circuit functions as a switching regulator to control the excitation current of the generator. The resistance R2 is configured to maintain the charging voltage at a standard level of over 13.8V for car batteries. The transistor Q1 used in this circuit is a 2N2063A (SK3009), rated for 10A and is a PNP type.
The circuit design incorporates the LM723 voltage regulator, which is a versatile and reliable component widely used in power supply applications. In this configuration, the LM723 is employed as a switching regulator to optimize the charging process of the lead-acid battery. This method improves efficiency by minimizing energy losses typically associated with linear regulation.
The primary function of the LM723 is to regulate the output voltage to a stable level, ensuring that the battery receives the appropriate voltage for charging without exceeding the safe limits. The standard charging voltage for a 12V lead-acid battery is typically around 13.8V, and the circuit is designed to maintain this voltage under varying load conditions. This is achieved through feedback mechanisms that monitor the output voltage and adjust the excitation current supplied to the generator accordingly.
Resistor R2 plays a critical role in this circuit by setting the desired output voltage level. Its value is chosen to ensure that the voltage remains stable and does not fall below or exceed the specified threshold, which is crucial for battery health and longevity.
The use of the 2N2063A transistor as Q1 allows for efficient control of the current flowing to the generator's excitation coil. As a PNP transistor, it is well-suited for high-side switching applications, providing a robust means of controlling the power delivered to the generator. Rated at 10A, it can handle the necessary current levels without overheating or failing, ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, this circuit represents an advanced approach to automotive battery management, replacing traditional systems with a more efficient and reliable solution that extends battery life and enhances performance. Cars are fixed as shown in the circuit composed of LM723 regulator circuit, it can replace the use of an automobile generator system consisting of electromechanical charging re gulator, performance is better than the latter. It makes 12V lead - acid battery will not charge less than or overcharge, thus extending battery life. Circuit LM723 used as a switching regulator for controlling the generator excitation current. R2 resistance is conditioned so that the charging voltage can be maintained at a standard car battery voltage over 13.8V.
Q1 is 2N2063A (SK3009), 10A, PNP transistors.
The circuit design incorporates the LM723 voltage regulator, which is a versatile and reliable component widely used in power supply applications. In this configuration, the LM723 is employed as a switching regulator to optimize the charging process of the lead-acid battery. This method improves efficiency by minimizing energy losses typically associated with linear regulation.
The primary function of the LM723 is to regulate the output voltage to a stable level, ensuring that the battery receives the appropriate voltage for charging without exceeding the safe limits. The standard charging voltage for a 12V lead-acid battery is typically around 13.8V, and the circuit is designed to maintain this voltage under varying load conditions. This is achieved through feedback mechanisms that monitor the output voltage and adjust the excitation current supplied to the generator accordingly.
Resistor R2 plays a critical role in this circuit by setting the desired output voltage level. Its value is chosen to ensure that the voltage remains stable and does not fall below or exceed the specified threshold, which is crucial for battery health and longevity.
The use of the 2N2063A transistor as Q1 allows for efficient control of the current flowing to the generator's excitation coil. As a PNP transistor, it is well-suited for high-side switching applications, providing a robust means of controlling the power delivered to the generator. Rated at 10A, it can handle the necessary current levels without overheating or failing, ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, this circuit represents an advanced approach to automotive battery management, replacing traditional systems with a more efficient and reliable solution that extends battery life and enhances performance. Cars are fixed as shown in the circuit composed of LM723 regulator circuit, it can replace the use of an automobile generator system consisting of electromechanical charging re gulator, performance is better than the latter. It makes 12V lead - acid battery will not charge less than or overcharge, thus extending battery life. Circuit LM723 used as a switching regulator for controlling the generator excitation current. R2 resistance is conditioned so that the charging voltage can be maintained at a standard car battery voltage over 13.8V.
Q1 is 2N2063A (SK3009), 10A, PNP transistors.