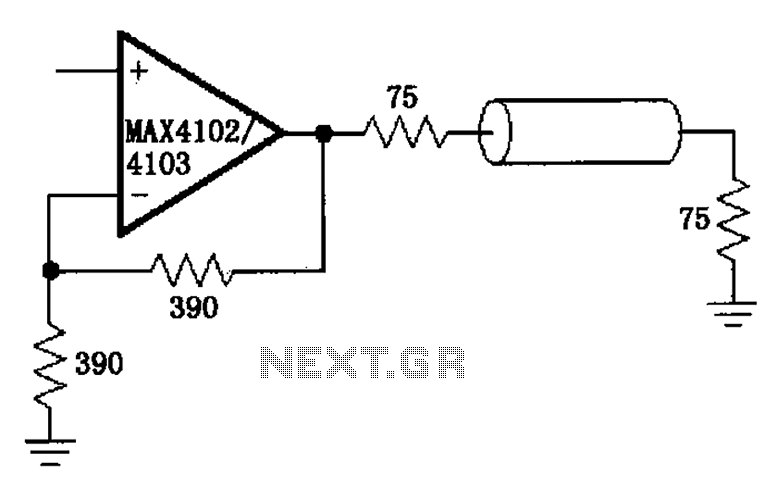
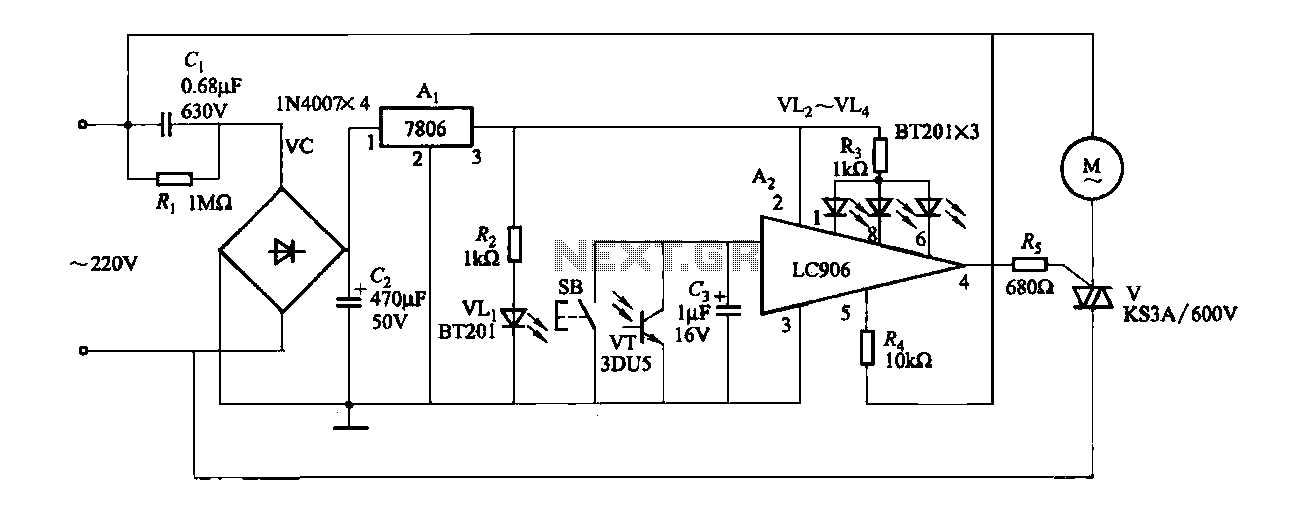
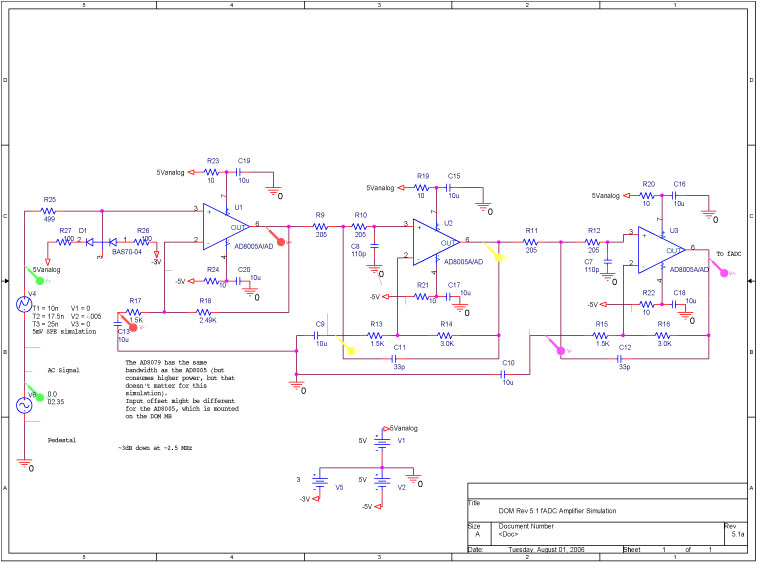
Logic Gates FM Transmitter Circuit
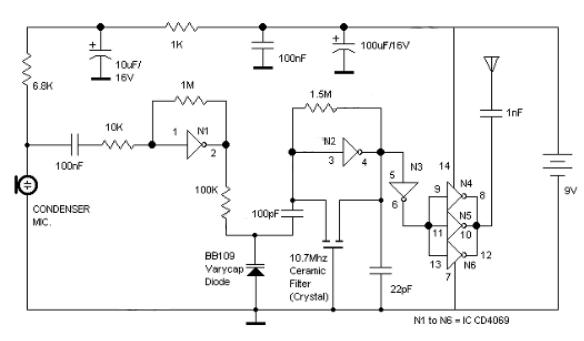
Logic Gates FM Transmitter Circuit Electronic Circuit Schematic Wiring Diagram.
The FM transmitter circuit utilizing logic gates is a fundamental electronic design that operates by modulating a carrier frequency with an audio signal. This circuit typically consists of various logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, which are used to process the input audio signal and generate the modulated output.
In a typical design, the circuit begins with an audio input stage where the sound signal is fed into the logic gates. The gates are configured to manipulate the signal according to the desired modulation scheme. For instance, an AND gate may be used to combine the audio signal with a high-frequency carrier wave generated by an oscillator circuit. The output from the AND gate then represents the modulated signal.
Next, the circuit may include a low-pass filter to eliminate any high-frequency noise and ensure that only the desired frequency range is transmitted. Following this stage, a power amplifier can be incorporated to boost the signal strength before transmission. The final output is then fed into an antenna, allowing the FM signal to be broadcast over a designated frequency range.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements for the circuit, ensuring that all components receive the appropriate voltage and current levels for optimal performance. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should also be implemented to minimize interference and enhance signal clarity.
In summary, the logic gates FM transmitter circuit is a versatile and efficient design that leverages digital logic components to achieve analog signal modulation, making it suitable for various applications in audio transmission and wireless communication.Logic Gates FM Transmitter Circuit Electronic Circuit Schematic Wiring Diagram. 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit utilizing logic gates is a fundamental electronic design that operates by modulating a carrier frequency with an audio signal. This circuit typically consists of various logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, which are used to process the input audio signal and generate the modulated output.
In a typical design, the circuit begins with an audio input stage where the sound signal is fed into the logic gates. The gates are configured to manipulate the signal according to the desired modulation scheme. For instance, an AND gate may be used to combine the audio signal with a high-frequency carrier wave generated by an oscillator circuit. The output from the AND gate then represents the modulated signal.
Next, the circuit may include a low-pass filter to eliminate any high-frequency noise and ensure that only the desired frequency range is transmitted. Following this stage, a power amplifier can be incorporated to boost the signal strength before transmission. The final output is then fed into an antenna, allowing the FM signal to be broadcast over a designated frequency range.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements for the circuit, ensuring that all components receive the appropriate voltage and current levels for optimal performance. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should also be implemented to minimize interference and enhance signal clarity.
In summary, the logic gates FM transmitter circuit is a versatile and efficient design that leverages digital logic components to achieve analog signal modulation, making it suitable for various applications in audio transmission and wireless communication.Logic Gates FM Transmitter Circuit Electronic Circuit Schematic Wiring Diagram. 🔗 External reference