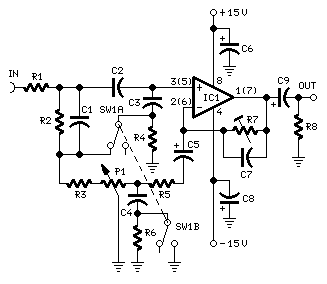
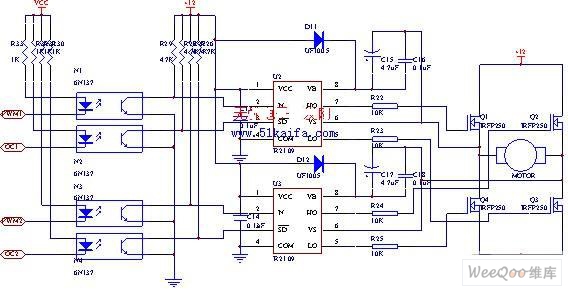
Logic Pulser Circuit

The logic pulser generates pulses at 500 Hz or 0.5 Hz. When the pulser's tip connects to an input that is already being driven high or low, the pulser senses the logic state and automatically pulses the input briefly to the opposite state.
The logic pulser is a versatile electronic component designed to produce precise pulse signals at specified frequencies, namely 500 Hz and 0.5 Hz. This device is particularly useful in digital circuits where it is necessary to toggle the state of an input signal. The operation of the logic pulser is predicated on its ability to detect the current logic level of the connected input.
When the tip of the pulser is connected to an input that is already being driven either high (logic level '1') or low (logic level '0'), the pulser employs a sensing mechanism to determine the existing state of the signal. Upon detection of the current logic level, the pulser generates a pulse that briefly transitions the input to the opposite state. For instance, if the input is high, the pulser will output a low pulse, and conversely, if the input is low, it will output a high pulse.
This functionality is crucial in various applications, including digital signal processing, testing, and debugging of electronic circuits. The ability to generate a controlled pulse that can invert the state of a signal allows for effective manipulation of logic levels in a circuit, thereby facilitating the development and testing of digital systems.
The design of the logic pulser typically includes a timing circuit to regulate the frequency of the output pulses, a detection circuit to sense the input state, and a driver circuit to produce the necessary output signal. The integration of these components ensures reliable operation and precise timing, making the logic pulser an essential tool in the arsenal of electronic engineers and technicians. The logic pulser generates pulses at 500 Hz or 0.5 Hz. When the pulser`s.tip connects to an input that is already being driven high or low, the pulser senses thelogic state and automatically pulses the input briefly to the opposite state. 🔗 External reference
The logic pulser is a versatile electronic component designed to produce precise pulse signals at specified frequencies, namely 500 Hz and 0.5 Hz. This device is particularly useful in digital circuits where it is necessary to toggle the state of an input signal. The operation of the logic pulser is predicated on its ability to detect the current logic level of the connected input.
When the tip of the pulser is connected to an input that is already being driven either high (logic level '1') or low (logic level '0'), the pulser employs a sensing mechanism to determine the existing state of the signal. Upon detection of the current logic level, the pulser generates a pulse that briefly transitions the input to the opposite state. For instance, if the input is high, the pulser will output a low pulse, and conversely, if the input is low, it will output a high pulse.
This functionality is crucial in various applications, including digital signal processing, testing, and debugging of electronic circuits. The ability to generate a controlled pulse that can invert the state of a signal allows for effective manipulation of logic levels in a circuit, thereby facilitating the development and testing of digital systems.
The design of the logic pulser typically includes a timing circuit to regulate the frequency of the output pulses, a detection circuit to sense the input state, and a driver circuit to produce the necessary output signal. The integration of these components ensures reliable operation and precise timing, making the logic pulser an essential tool in the arsenal of electronic engineers and technicians. The logic pulser generates pulses at 500 Hz or 0.5 Hz. When the pulser`s.tip connects to an input that is already being driven high or low, the pulser senses thelogic state and automatically pulses the input briefly to the opposite state. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713