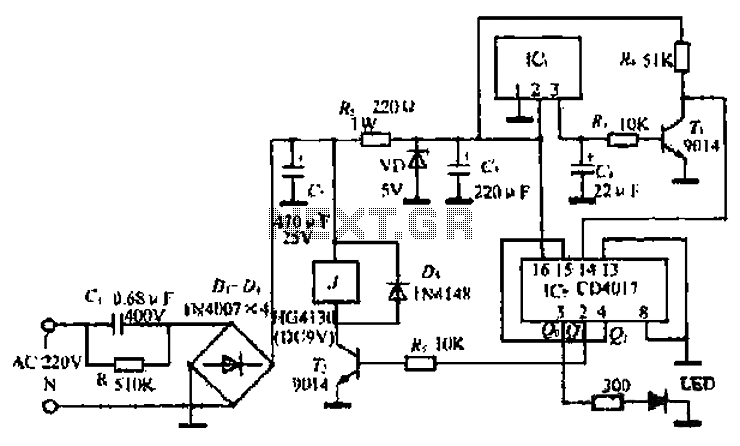
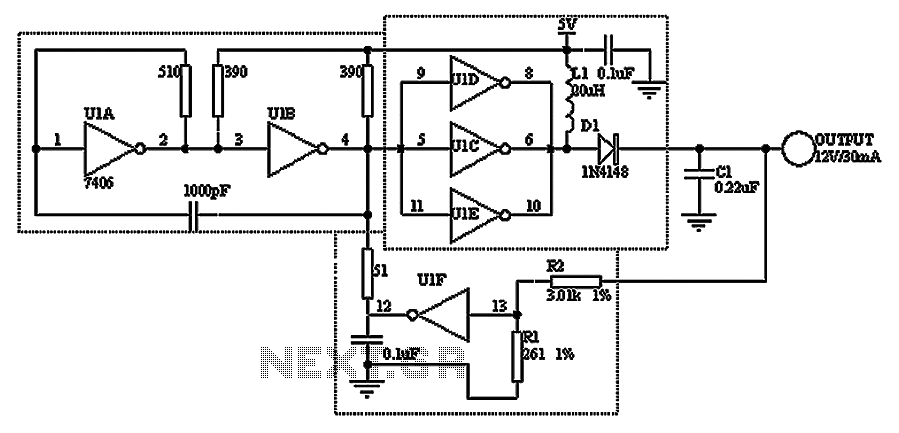
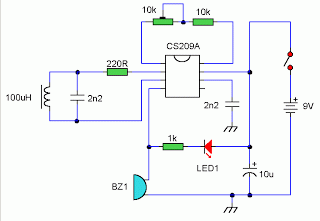
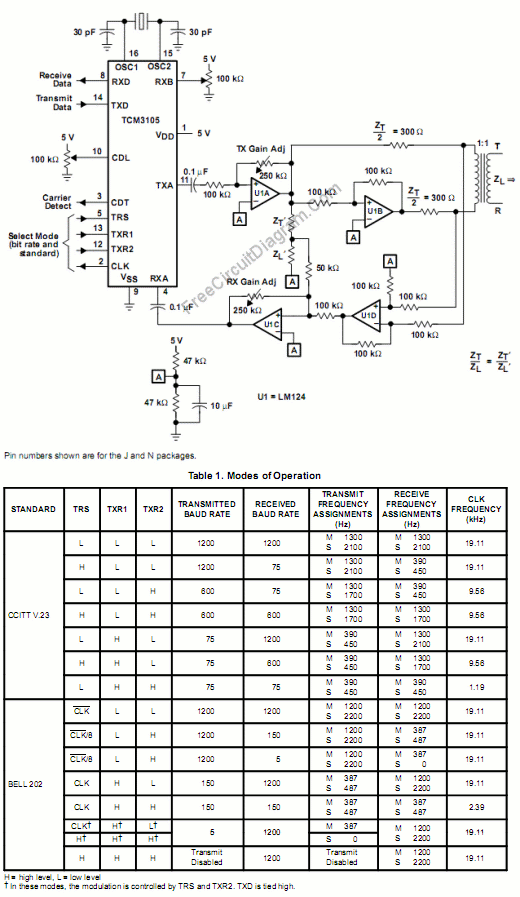
Long-Range IR Transmitter circuit
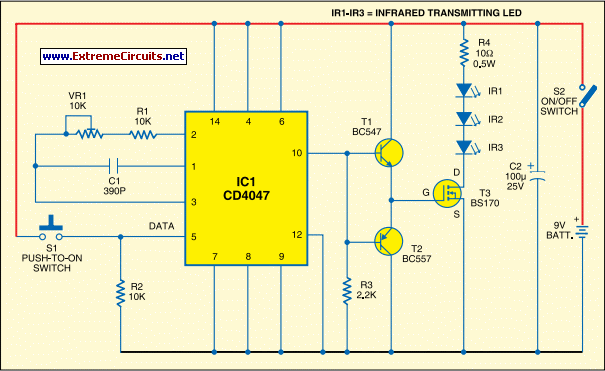
Most IR remotes operate effectively within a range of 5 meters. The complexity of the circuit increases when designing the IR transmitter for reliable operation over longer distances, such as 10 meters. To extend the range from 5 meters to 10 meters, it is necessary to quadruple the transmitted power. For a highly directional IR beam (very narrow beam), an IR laser pointer can be used as the source of the IR signal.
The design of an infrared (IR) remote control system involves several key components and considerations to achieve extended range and reliability. Standard IR remotes typically function at a distance of approximately 5 meters, which is sufficient for most consumer electronics. However, when the requirement is to extend the operational range to 10 meters, it is essential to enhance the power output of the transmitter. Specifically, to achieve this doubling of range, the emitted power must be increased by a factor of four due to the inverse square law, which states that the intensity of the signal decreases with the square of the distance from the source.
To implement this, the circuit design will require a more robust IR LED or an array of IR LEDs capable of delivering the necessary output power. The choice of the LED should consider factors such as wavelength, efficiency, and thermal management. Additionally, a suitable driver circuit must be designed to handle the increased current requirements for the LEDs, which may entail the use of a transistor or a dedicated LED driver IC to ensure stable operation.
For applications requiring a highly directional IR beam, an IR laser pointer can be employed as the signal source. Laser diodes produce a coherent light beam that can be focused to a narrow angle, making them ideal for applications where precise targeting of the IR signal is necessary. The incorporation of lenses or reflectors can further enhance the directionality of the beam, allowing for effective communication over longer distances without significant dispersion.
In summary, the design of an IR remote control system for extended range involves an increase in transmitted power, careful selection of components, and potential use of laser technology to achieve a highly directional signal. Proper circuit design, including power management and signal modulation techniques, is crucial to ensure reliable operation within the desired range.Most of the IR remotes work reliably within a range of 5 metres. The circuit complexity increases if you design the IR transmitter for reliable operation over a longer range, say, metres. To double the range from 5 metres to metres, you need to increase the transmitted power four times. If you wish to real i se a highly directional IR beam (very narrow beam), you can suitably use an IR laser pointer as the IR signal source..
🔗 External reference
The design of an infrared (IR) remote control system involves several key components and considerations to achieve extended range and reliability. Standard IR remotes typically function at a distance of approximately 5 meters, which is sufficient for most consumer electronics. However, when the requirement is to extend the operational range to 10 meters, it is essential to enhance the power output of the transmitter. Specifically, to achieve this doubling of range, the emitted power must be increased by a factor of four due to the inverse square law, which states that the intensity of the signal decreases with the square of the distance from the source.
To implement this, the circuit design will require a more robust IR LED or an array of IR LEDs capable of delivering the necessary output power. The choice of the LED should consider factors such as wavelength, efficiency, and thermal management. Additionally, a suitable driver circuit must be designed to handle the increased current requirements for the LEDs, which may entail the use of a transistor or a dedicated LED driver IC to ensure stable operation.
For applications requiring a highly directional IR beam, an IR laser pointer can be employed as the signal source. Laser diodes produce a coherent light beam that can be focused to a narrow angle, making them ideal for applications where precise targeting of the IR signal is necessary. The incorporation of lenses or reflectors can further enhance the directionality of the beam, allowing for effective communication over longer distances without significant dispersion.
In summary, the design of an IR remote control system for extended range involves an increase in transmitted power, careful selection of components, and potential use of laser technology to achieve a highly directional signal. Proper circuit design, including power management and signal modulation techniques, is crucial to ensure reliable operation within the desired range.Most of the IR remotes work reliably within a range of 5 metres. The circuit complexity increases if you design the IR transmitter for reliable operation over a longer range, say, metres. To double the range from 5 metres to metres, you need to increase the transmitted power four times. If you wish to real i se a highly directional IR beam (very narrow beam), you can suitably use an IR laser pointer as the IR signal source..
🔗 External reference