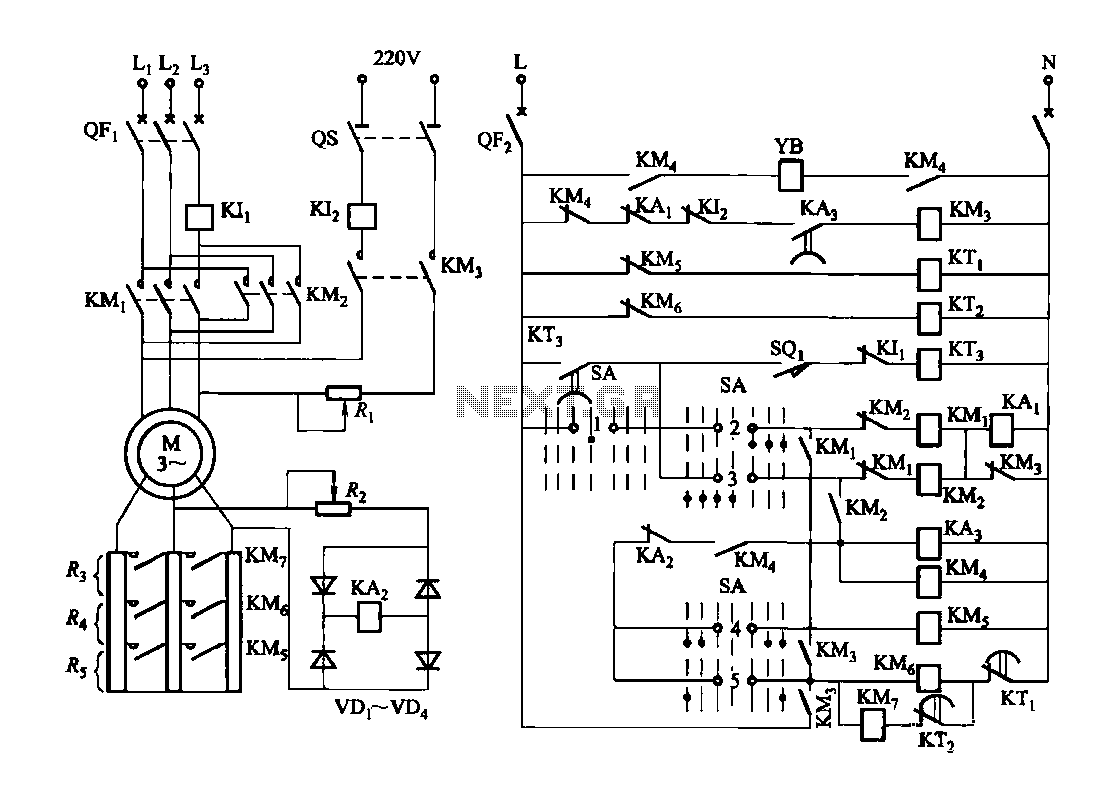
Loudness control
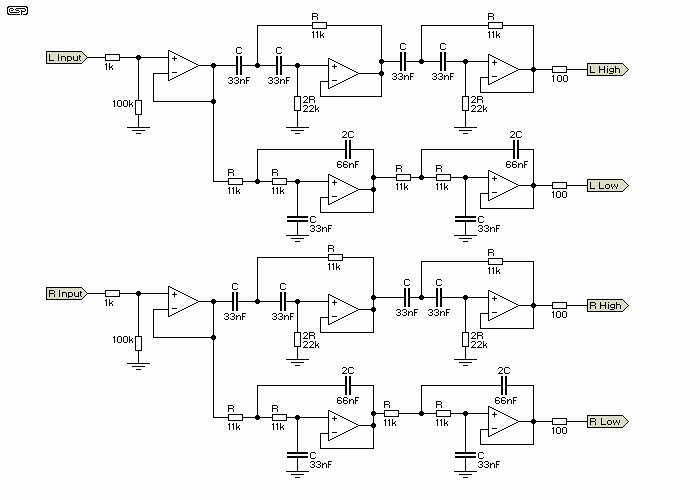
An operational amplifier such as the NE5532 should be used. The desired frequency must be calculated for each block: one for flat, one for bass, and one for high frequencies. It is important to include a buffer at the first stage. Trimpots or fixed resistors can be utilized, along with buttons to activate specific functions within the circuit. The specific implementation will depend on the application, which requires individual consideration.
An electronic schematic utilizing the NE5532 operational amplifier can be designed to create a versatile audio processing circuit. The NE5532 is a dual low-noise operational amplifier known for its high performance, making it suitable for audio applications. The circuit can be divided into three main frequency response blocks: flat, bass, and treble.
The flat block serves as a reference point, allowing the audio signal to pass through without significant alteration. This block should be configured to maintain a unity gain, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved.
The bass block is designed to enhance low-frequency signals. To achieve this, a low-pass filter configuration can be employed, which will allow frequencies below a certain cutoff to pass while attenuating higher frequencies. The cutoff frequency can be calculated using the formula \( f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC} \), where \( R \) is the resistance and \( C \) is the capacitance in the filter circuit.
The treble block focuses on amplifying high-frequency signals. This can be implemented using a high-pass filter, which permits frequencies above a specified cutoff to pass through. Similar to the bass block, the cutoff frequency can be calculated using the same formula, adjusting the values of \( R \) and \( C \) to suit the desired frequency response.
A buffer stage should be included at the input of the circuit to prevent loading effects that could degrade the signal. This buffer can be implemented using one of the NE5532 op-amps configured as a voltage follower, providing high input impedance and low output impedance.
To facilitate user interaction, trimpots or fixed resistors can be integrated into the circuit to allow for manual adjustment of gain or frequency response. Additionally, buttons can be implemented to switch between the different processing modes (flat, bass, treble), enabling the user to select the desired sound profile.
Overall, this schematic provides a flexible audio processing solution, allowing for tailored frequency response adjustments while maintaining high audio fidelity. Proper attention to component selection and configuration will ensure optimal performance in the intended application.First you will have to use a opamp like ne5532, than calculate the frequency you want on each block(on block for flat, one for bass and one for high), don`t forget to put a buffer on the first stage, you can use trimpots or fixed resistor and some bottons to activate what you want on the circuit. Specific for your aplication you will have to do it by yourself, but i can help. First you will have to use a opamp like ne5532, than calculate the frequency you want on each block(on block for flat, one for bass and one for high), don`t forget to put a buffer on the first stage, you can use trimpots or fixed resistor and some bottons to activate what you want on the circuit. 🔗 External reference
An electronic schematic utilizing the NE5532 operational amplifier can be designed to create a versatile audio processing circuit. The NE5532 is a dual low-noise operational amplifier known for its high performance, making it suitable for audio applications. The circuit can be divided into three main frequency response blocks: flat, bass, and treble.
The flat block serves as a reference point, allowing the audio signal to pass through without significant alteration. This block should be configured to maintain a unity gain, ensuring that the signal integrity is preserved.
The bass block is designed to enhance low-frequency signals. To achieve this, a low-pass filter configuration can be employed, which will allow frequencies below a certain cutoff to pass while attenuating higher frequencies. The cutoff frequency can be calculated using the formula \( f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi RC} \), where \( R \) is the resistance and \( C \) is the capacitance in the filter circuit.
The treble block focuses on amplifying high-frequency signals. This can be implemented using a high-pass filter, which permits frequencies above a specified cutoff to pass through. Similar to the bass block, the cutoff frequency can be calculated using the same formula, adjusting the values of \( R \) and \( C \) to suit the desired frequency response.
A buffer stage should be included at the input of the circuit to prevent loading effects that could degrade the signal. This buffer can be implemented using one of the NE5532 op-amps configured as a voltage follower, providing high input impedance and low output impedance.
To facilitate user interaction, trimpots or fixed resistors can be integrated into the circuit to allow for manual adjustment of gain or frequency response. Additionally, buttons can be implemented to switch between the different processing modes (flat, bass, treble), enabling the user to select the desired sound profile.
Overall, this schematic provides a flexible audio processing solution, allowing for tailored frequency response adjustments while maintaining high audio fidelity. Proper attention to component selection and configuration will ensure optimal performance in the intended application.First you will have to use a opamp like ne5532, than calculate the frequency you want on each block(on block for flat, one for bass and one for high), don`t forget to put a buffer on the first stage, you can use trimpots or fixed resistor and some bottons to activate what you want on the circuit. Specific for your aplication you will have to do it by yourself, but i can help. First you will have to use a opamp like ne5532, than calculate the frequency you want on each block(on block for flat, one for bass and one for high), don`t forget to put a buffer on the first stage, you can use trimpots or fixed resistor and some bottons to activate what you want on the circuit. 🔗 External reference