Low cost fox hunting setup
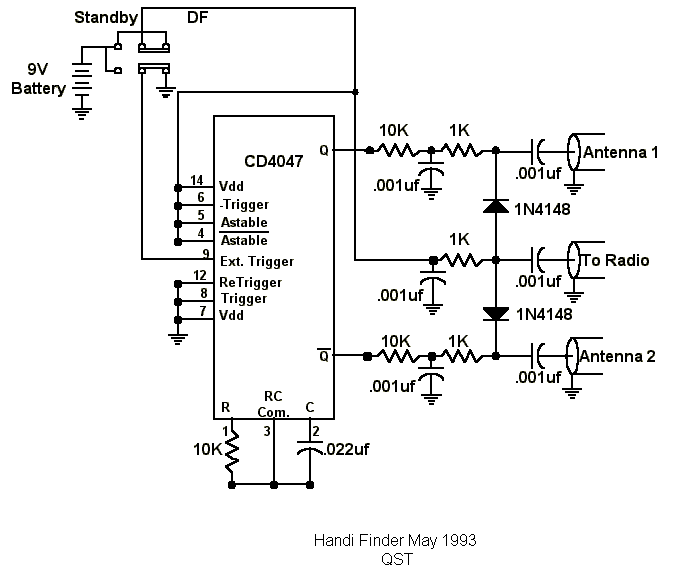
Interest in creating an antenna rig suitable for use with a handheld transceiver for fox hunting. Suggestions are sought for a cost-effective yet efficient solution.
To create an effective antenna rig for fox hunting using a handheld transceiver (HT), several factors must be considered, including antenna type, gain, directivity, and portability. A common choice for fox hunting applications is a directional antenna, which can significantly enhance signal reception and transmission in a specific direction, thus improving the chances of locating the target.
A Yagi-Uda antenna is often recommended due to its high gain and directivity. This antenna consists of a driven element, a reflector, and one or more directors, which can be constructed using lightweight materials such as aluminum tubing or wire for easy portability. The design can be scaled to the frequency of operation, ensuring optimal performance.
For a cost-effective solution, a simple dipole antenna can also be constructed. This can be achieved using two equal-length conductive elements, often made from copper wire, which can be mounted on a lightweight frame. The dipole antenna is easy to build and can be tuned to the desired frequency by adjusting the length of the elements.
In addition to the antenna itself, a suitable feedline is essential for connecting the antenna to the handheld transceiver. Coaxial cable is commonly used for this purpose, with a low-loss type preferred to minimize signal degradation. The use of appropriate connectors, such as SMA or BNC, ensures compatibility with the HT.
A portable mast or support structure is also advisable to elevate the antenna, which can further enhance performance by reducing ground interference. Various options for masts include telescoping poles or lightweight tripods that can be easily transported.
Overall, the design of the antenna rig should prioritize portability, ease of assembly, and efficiency to meet the needs of fox hunting applications. By using readily available materials and proven designs, an effective antenna rig can be constructed at a low cost.I'm interested in seeing if I can create an antenna rig that can be used with my ht for fox hunting. Anyone have any suggestions? Cheep, but effective is the operational words.. 🔗 External reference
To create an effective antenna rig for fox hunting using a handheld transceiver (HT), several factors must be considered, including antenna type, gain, directivity, and portability. A common choice for fox hunting applications is a directional antenna, which can significantly enhance signal reception and transmission in a specific direction, thus improving the chances of locating the target.
A Yagi-Uda antenna is often recommended due to its high gain and directivity. This antenna consists of a driven element, a reflector, and one or more directors, which can be constructed using lightweight materials such as aluminum tubing or wire for easy portability. The design can be scaled to the frequency of operation, ensuring optimal performance.
For a cost-effective solution, a simple dipole antenna can also be constructed. This can be achieved using two equal-length conductive elements, often made from copper wire, which can be mounted on a lightweight frame. The dipole antenna is easy to build and can be tuned to the desired frequency by adjusting the length of the elements.
In addition to the antenna itself, a suitable feedline is essential for connecting the antenna to the handheld transceiver. Coaxial cable is commonly used for this purpose, with a low-loss type preferred to minimize signal degradation. The use of appropriate connectors, such as SMA or BNC, ensures compatibility with the HT.
A portable mast or support structure is also advisable to elevate the antenna, which can further enhance performance by reducing ground interference. Various options for masts include telescoping poles or lightweight tripods that can be easily transported.
Overall, the design of the antenna rig should prioritize portability, ease of assembly, and efficiency to meet the needs of fox hunting applications. By using readily available materials and proven designs, an effective antenna rig can be constructed at a low cost.I'm interested in seeing if I can create an antenna rig that can be used with my ht for fox hunting. Anyone have any suggestions? Cheep, but effective is the operational words.. 🔗 External reference