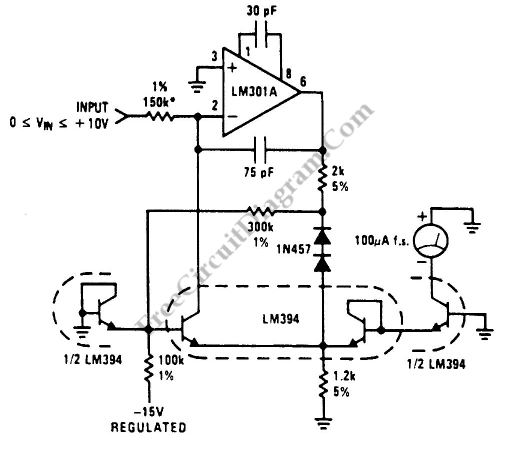
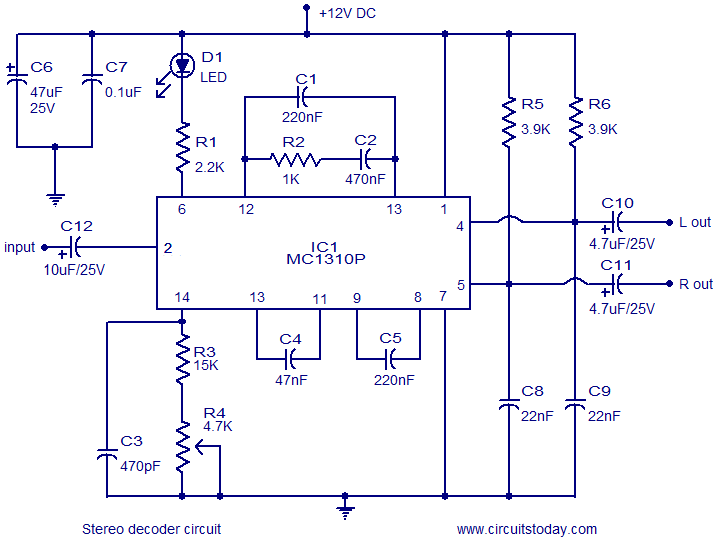
Low-Cost Logarithmic Converter Using Opamp and Transistor
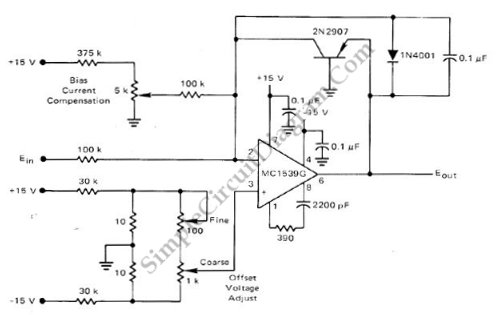
This low-cost logarithmic converter is constructed using an operational amplifier (op-amp) and a transistor. The circuit utilizes a Motorola MC1539G op-amp connected to a PNP transistor.
The logarithmic converter circuit is designed to convert linear input signals into logarithmic output signals, which is useful in various applications such as audio signal processing, sensor signal conditioning, and data acquisition systems. The Motorola MC1539G op-amp serves as the core component for signal amplification and processing. This op-amp features low noise and high gain, making it suitable for precision applications.
In this configuration, the op-amp is set up in a non-inverting mode to amplify the input signal. The output of the op-amp is then fed to a PNP transistor, which operates in the active region to provide the logarithmic response. The transistor's base is connected to the op-amp output, while the emitter is linked to the ground through a resistor. This configuration allows the circuit to produce a voltage output that is proportional to the logarithm of the input current, effectively compressing the dynamic range of the input signal.
Additional passive components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit to stabilize the op-amp, set the gain, and filter noise. The choice of these components will influence the performance characteristics of the logarithmic converter, including bandwidth, linearity, and temperature stability. Proper selection and arrangement of these components are essential to ensure that the circuit meets the desired specifications for its intended application.
Overall, this low-cost logarithmic converter circuit demonstrates an effective use of op-amp and transistor technology to achieve logarithmic signal processing, making it a valuable tool in electronic design and signal conditioning.This low-cost logarithmic converter is built using op-amp and transistor. This circuit uses a Motorola MC1539G op-amp which is connected to PNP transistor. To.. 🔗 External reference
The logarithmic converter circuit is designed to convert linear input signals into logarithmic output signals, which is useful in various applications such as audio signal processing, sensor signal conditioning, and data acquisition systems. The Motorola MC1539G op-amp serves as the core component for signal amplification and processing. This op-amp features low noise and high gain, making it suitable for precision applications.
In this configuration, the op-amp is set up in a non-inverting mode to amplify the input signal. The output of the op-amp is then fed to a PNP transistor, which operates in the active region to provide the logarithmic response. The transistor's base is connected to the op-amp output, while the emitter is linked to the ground through a resistor. This configuration allows the circuit to produce a voltage output that is proportional to the logarithm of the input current, effectively compressing the dynamic range of the input signal.
Additional passive components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit to stabilize the op-amp, set the gain, and filter noise. The choice of these components will influence the performance characteristics of the logarithmic converter, including bandwidth, linearity, and temperature stability. Proper selection and arrangement of these components are essential to ensure that the circuit meets the desired specifications for its intended application.
Overall, this low-cost logarithmic converter circuit demonstrates an effective use of op-amp and transistor technology to achieve logarithmic signal processing, making it a valuable tool in electronic design and signal conditioning.This low-cost logarithmic converter is built using op-amp and transistor. This circuit uses a Motorola MC1539G op-amp which is connected to PNP transistor. To.. 🔗 External reference