Low Distortion Wien Bridge Oscillator
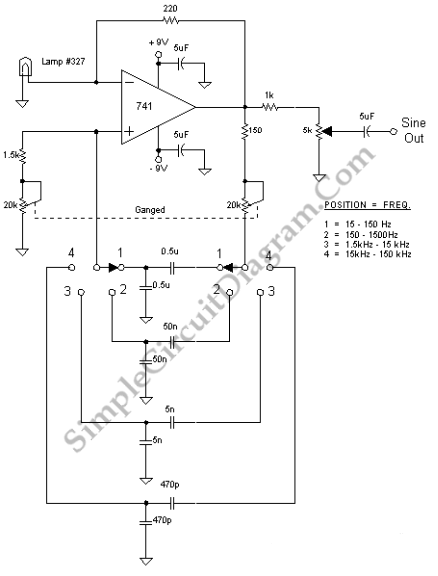
This Wien bridge oscillator utilizes an incandescent lamp to stabilize its amplitude. The amplitude stabilization results in a low distortion output and supports multiple frequencies.
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It is known for its ability to produce low-distortion outputs, which is essential in various applications, including audio signal generation and testing. The core of the oscillator consists of a bridge circuit that includes resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration to set the frequency of oscillation.
In this particular design, the use of an incandescent lamp serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it acts as a variable resistor, whose resistance changes with the temperature. This property allows for automatic gain control, which stabilizes the amplitude of the output signal. As the amplitude of the oscillation increases, the lamp heats up, causing its resistance to rise and thereby reducing the gain. Conversely, if the amplitude decreases, the lamp cools down, lowering its resistance and increasing the gain. This feedback mechanism ensures that the output remains stable and minimizes distortion.
The circuit typically includes an op-amp configured as a non-inverting amplifier to provide the necessary gain. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by changing the values of the resistors and capacitors in the bridge circuit. This flexibility allows the oscillator to operate at multiple frequencies, making it suitable for various applications.
Overall, the incorporation of an incandescent lamp in the Wien bridge oscillator design enhances its performance by providing effective amplitude stabilization, resulting in a high-quality, low-distortion sine wave output across a range of frequencies.This Wien bridge oscillator uses incandescent lamp to stabilize its amplitude. This amplitude stabilization gives a low distortion output. Multiple frequency.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It is known for its ability to produce low-distortion outputs, which is essential in various applications, including audio signal generation and testing. The core of the oscillator consists of a bridge circuit that includes resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration to set the frequency of oscillation.
In this particular design, the use of an incandescent lamp serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it acts as a variable resistor, whose resistance changes with the temperature. This property allows for automatic gain control, which stabilizes the amplitude of the output signal. As the amplitude of the oscillation increases, the lamp heats up, causing its resistance to rise and thereby reducing the gain. Conversely, if the amplitude decreases, the lamp cools down, lowering its resistance and increasing the gain. This feedback mechanism ensures that the output remains stable and minimizes distortion.
The circuit typically includes an op-amp configured as a non-inverting amplifier to provide the necessary gain. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by changing the values of the resistors and capacitors in the bridge circuit. This flexibility allows the oscillator to operate at multiple frequencies, making it suitable for various applications.
Overall, the incorporation of an incandescent lamp in the Wien bridge oscillator design enhances its performance by providing effective amplitude stabilization, resulting in a high-quality, low-distortion sine wave output across a range of frequencies.This Wien bridge oscillator uses incandescent lamp to stabilize its amplitude. This amplitude stabilization gives a low distortion output. Multiple frequency.. 🔗 External reference