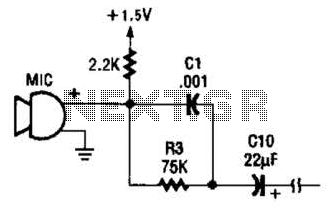
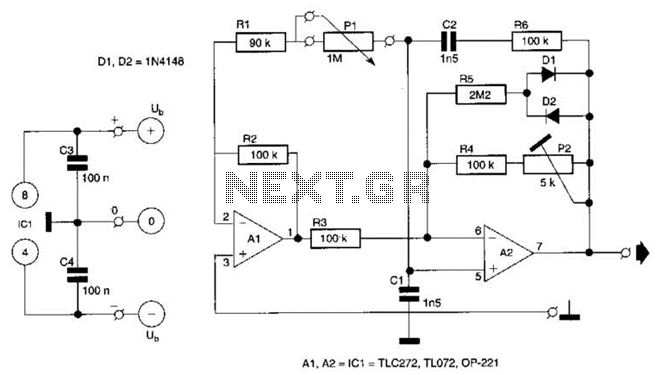
Mains Pulser Circuit
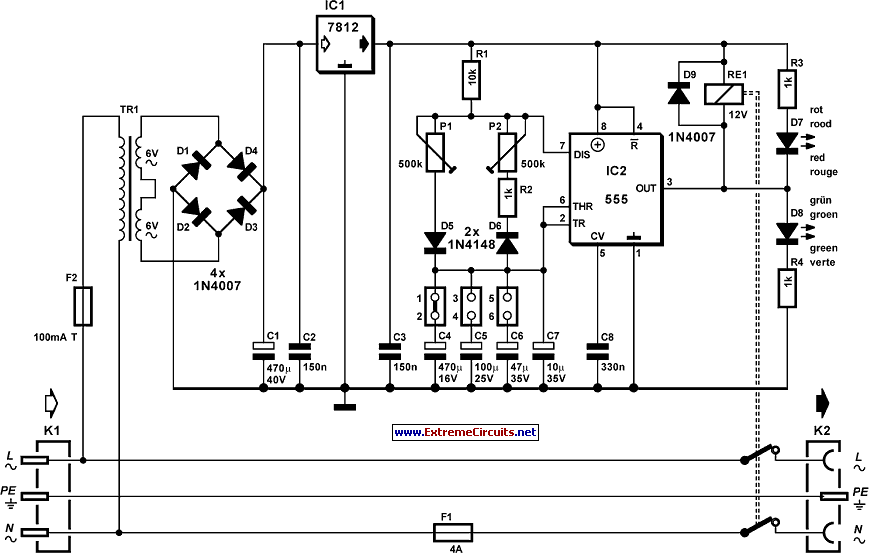
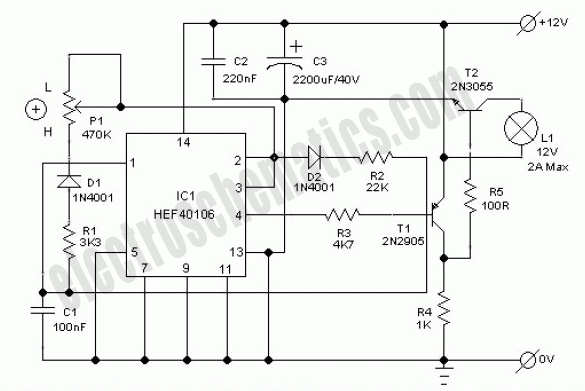
The pulser is designed to switch the mains voltage on and off at intervals ranging from just under one second to up to 10 minutes. This functionality is particularly useful for testing mains-operated equipment over extended periods or for the periodic operation of machinery. Transformer Tr1, along with the bridge rectifier and regulator IC1, provides a stable 12V supply for IC2 and the relay. The timer circuit is configured so that the capacitor responsible for determining the period can be charged and discharged independently. Four time ranges can be selected by changing capacitors using jumpers. Short-circuiting positions 1 and 2 results in the longest time interval, while short-circuiting none yields the shortest. In the latter case, the 10 µF capacitor connected to pins 2 and 6 of the timer IC sets the timing in conjunction with the associated resistors. The value of this capacitor can be adjusted to a slightly lower value if needed. Two preset potentiometers allow for the adjustment of the on and off periods. A 1k resistor in series with one of the presets establishes the minimum discharge time. The timer IC actuates a relay with double-pole contacts that switch the mains voltage. LEDs indicate the status of the mains voltage, with a red LED showing when the voltage is switched through and a green LED indicating when it is not. A 100mA slow fuse safeguards the mains transformer and low-voltage circuit, while a 4 A medium slow fuse protects the relay from overload.
The pulser circuit operates by utilizing a timer IC configured in a monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired application. The timer's timing intervals are set by selecting capacitors of different values, which can be easily modified through jumper settings. This flexibility allows users to tailor the timing characteristics to specific needs, whether for testing equipment or machinery operation.
The power supply section, consisting of transformer Tr1, the bridge rectifier, and regulator IC1, ensures that a stable 12V output is maintained, which is critical for the reliable operation of the timer and relay. The relay, controlled by the timer IC, features double-pole contacts that can handle the switching of mains voltage, ensuring that both the live and neutral lines are appropriately managed for safety.
The inclusion of indicator LEDs provides visual feedback on the operation of the circuit, enhancing usability by allowing operators to quickly ascertain the status of the mains supply. The protective fuses are vital components that prevent damage to the circuit and connected devices from potential overloads or short circuits, ensuring robust and safe operation over time.
Overall, this pulser circuit is a versatile tool for various applications requiring timed control of mains voltage, combining safety features with user-friendly adjustments to meet different operational requirements.The pulser is intended to switch the mains voltage on and off at intervals between just under a second and up to 10 minutes. This is useful, for instance, when a mains-operated equipment is to be tested for long periods, or for periodic switching of machinery.
Transformer Tr1, the bridge rectifier, and regulator IC1 provide a stable 12V supply ra il for IC2 and the relay. The timer is arranged so that the period-determining capacitor can be charged and discharged independently. Four time ranges can be selected by selecting capacitors with the aid of jumpers. Short-circuiting positions 1 and 2 gives the longest time, and short-circuiting none the shortest. In the latter case, the 10 µF capacitor at pins 2 and 6 of the timer IC determines the time with the relevant resistors.
The value of this capacitor may be chosen slightly lower. The two preset potentiometers enable the on and off periods to be set. The 1k resistor in series with one of the presets determines the minimum discharge time. The timer IC switches a relay whose double-pole contacts switch the mains voltage. The LEDs indicate whether the mains voltage is switched through (red) or not (green). The 100mA slow fuse protects the mains transformer and low-voltage circuit. The 4 A medium slow fuse protects the relay against overload. 🔗 External reference
The pulser circuit operates by utilizing a timer IC configured in a monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired application. The timer's timing intervals are set by selecting capacitors of different values, which can be easily modified through jumper settings. This flexibility allows users to tailor the timing characteristics to specific needs, whether for testing equipment or machinery operation.
The power supply section, consisting of transformer Tr1, the bridge rectifier, and regulator IC1, ensures that a stable 12V output is maintained, which is critical for the reliable operation of the timer and relay. The relay, controlled by the timer IC, features double-pole contacts that can handle the switching of mains voltage, ensuring that both the live and neutral lines are appropriately managed for safety.
The inclusion of indicator LEDs provides visual feedback on the operation of the circuit, enhancing usability by allowing operators to quickly ascertain the status of the mains supply. The protective fuses are vital components that prevent damage to the circuit and connected devices from potential overloads or short circuits, ensuring robust and safe operation over time.
Overall, this pulser circuit is a versatile tool for various applications requiring timed control of mains voltage, combining safety features with user-friendly adjustments to meet different operational requirements.The pulser is intended to switch the mains voltage on and off at intervals between just under a second and up to 10 minutes. This is useful, for instance, when a mains-operated equipment is to be tested for long periods, or for periodic switching of machinery.
Transformer Tr1, the bridge rectifier, and regulator IC1 provide a stable 12V supply ra il for IC2 and the relay. The timer is arranged so that the period-determining capacitor can be charged and discharged independently. Four time ranges can be selected by selecting capacitors with the aid of jumpers. Short-circuiting positions 1 and 2 gives the longest time, and short-circuiting none the shortest. In the latter case, the 10 µF capacitor at pins 2 and 6 of the timer IC determines the time with the relevant resistors.
The value of this capacitor may be chosen slightly lower. The two preset potentiometers enable the on and off periods to be set. The 1k resistor in series with one of the presets determines the minimum discharge time. The timer IC switches a relay whose double-pole contacts switch the mains voltage. The LEDs indicate whether the mains voltage is switched through (red) or not (green). The 100mA slow fuse protects the mains transformer and low-voltage circuit. The 4 A medium slow fuse protects the relay against overload. 🔗 External reference