make this simple delay on timer circuit
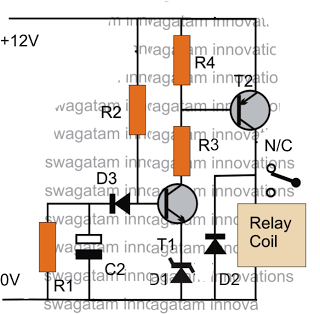
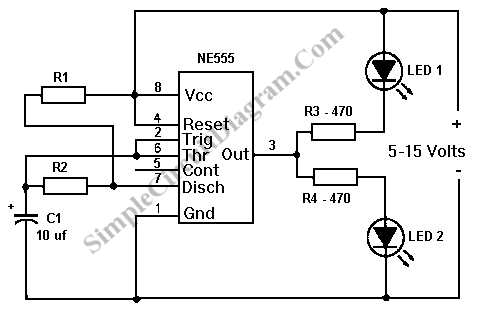
The post discusses a simple delay ON circuit that enables a connected load at the output to be activated with a predetermined delay after the power switch is turned ON. This circuit can be utilized in various applications that require an initial delay before the connected load is powered up. The provided diagram is straightforward and effectively illustrates the necessary operations, with the added benefit of a variable delay period, making the setup highly useful for the intended applications. When the load requiring the delay ON action is connected across the relay contacts, the 12V DC flows through R2 upon power activation. Initially, capacitor C2 acts as a short circuit to ground, preventing current from reaching the base of transistor T1. Once C2 charges to a voltage level of 0.3 to 0.6V (the zener voltage), T1 switches ON, activating T2 and subsequently the relay, which in turn powers the load.
An automatic voltage stabilizer rated at 1KVA exhibits a defect where it outputs a very high voltage for approximately 1.5 seconds upon being switched ON, causing frequent fusing of CFLs and bulbs before stabilizing to an acceptable voltage. The stabilizer comprises an auto-transformer and four 24V relays, each connected to a separate circuit that includes a 10K preset resistor, a BC547 transistor, a zener diode, a BDX53BFP NPN Darlington pair transistor IC, two capacitors (220uF/63V and 100uF/40V), four diodes, and additional resistors. These circuits are powered by a step-down transformer, and the outputs are taken across the corresponding 100uF/40V capacitor and fed to the respective relay.
To address the issue, it is suggested to investigate whether one of the relays is momentarily connecting the wrong contacts to the output or if one of the relays is taking longer to stabilize with the correct voltage after power ON. Given the presence of multiple relays, tracing the fault may be challenging. Implementing the delay ON timer circuit described earlier could effectively resolve this problem by ensuring that the output is activated only after a delay, allowing sufficient time for the internal relays to stabilize with the correct voltages across their output contacts.
The delay ON circuit operates effectively by utilizing a capacitor to create a time delay before activating the load. The capacitor charges through a resistor, creating a time constant that determines the delay duration. The variable resistor can be adjusted to set the desired delay period, making the circuit adaptable to various applications. The use of transistors as switches allows for efficient control of the relay, enabling the load to be powered only after the delay, thus preventing any premature voltage spikes from reaching the connected devices. This configuration is particularly beneficial in scenarios where sensitive electronic equipment is used, as it protects against potential damage caused by voltage fluctuations during startup.
In summary, the delay ON circuit provides a reliable solution for managing power supply issues in systems with multiple relays, ensuring that the connected load is activated only after the necessary stabilization period. This design enhances the longevity and reliability of both the stabilizer and the connected devices.The post explains a simple delay ON circuit which allows the connected load at the output to be switched ON with some predetermined delay after power switch ON. The explained circuit can be used for all applications which calls for an initial delay ON feature for the connected load after the mains power is switched ON.
The shown diagram is pretty straightforward yet provides the necessary actions very impressively, moreover the delay period is variable making the set up extremely useful for the proposed applications. Assuming the load which requires the delay ON action being connected across the relay contacts, when power is switched ON, the 12V DC passes via R2 but is unable to reach the base of T1 because initially, C2 acts as a short across ground.
Once C2 charges up to a level which develops a potential of 0. 3 to 0. 6V (+zener voltage) at the base of T1, T1 is instantly switched ON, toggling T2, and the relaysubsequently. finally the load gets switched ON too. I have a 1KVA automatic voltage stabilizer. It has one defect that when it is switched on, very high voltage is outputted for about 1. 5s (therefore cfls and bulb got fused frequently) after that the voltage becomes OK. I have opened the stabilizer it consist of an auto-transformer, 4 24V relay each relay connected to aseparatecircuit(each consisting of 10K preset, BC547, zener diode, BDX53BFP npn darlington pair transistor IC, 220uF/63v capacitor, 100uF/40V capacitor, 4 diodes and some resistors).
These circuits are powered by a step down transformer and output of these circuit are taken across corresponding 100uF/40V capacitor and fed to corresponding relay. What to do in order to tackle the problem. please help me. Hand drawn circuit diagram is attached. The problem in the above circuit might be due to two reasons: one of the relays is switching ON momentarily connecting the wrong contacts with the output, or one of the responsible relays is settling down with the correct voltages a little while after power switch ON.
Since there are more than one relay, tracing out the fault and correcting it can be a bit tedious. the circuit of a delay ON timer explained in the above article could be actually very effective for the discussed purpose. The above wiring would instantly take care of the issues as now the output would switch after some time during power witch ONs, allowing enough time for the internal relays to settle down with the correct voltages across their output contacts.
🔗 External reference
An automatic voltage stabilizer rated at 1KVA exhibits a defect where it outputs a very high voltage for approximately 1.5 seconds upon being switched ON, causing frequent fusing of CFLs and bulbs before stabilizing to an acceptable voltage. The stabilizer comprises an auto-transformer and four 24V relays, each connected to a separate circuit that includes a 10K preset resistor, a BC547 transistor, a zener diode, a BDX53BFP NPN Darlington pair transistor IC, two capacitors (220uF/63V and 100uF/40V), four diodes, and additional resistors. These circuits are powered by a step-down transformer, and the outputs are taken across the corresponding 100uF/40V capacitor and fed to the respective relay.
To address the issue, it is suggested to investigate whether one of the relays is momentarily connecting the wrong contacts to the output or if one of the relays is taking longer to stabilize with the correct voltage after power ON. Given the presence of multiple relays, tracing the fault may be challenging. Implementing the delay ON timer circuit described earlier could effectively resolve this problem by ensuring that the output is activated only after a delay, allowing sufficient time for the internal relays to stabilize with the correct voltages across their output contacts.
The delay ON circuit operates effectively by utilizing a capacitor to create a time delay before activating the load. The capacitor charges through a resistor, creating a time constant that determines the delay duration. The variable resistor can be adjusted to set the desired delay period, making the circuit adaptable to various applications. The use of transistors as switches allows for efficient control of the relay, enabling the load to be powered only after the delay, thus preventing any premature voltage spikes from reaching the connected devices. This configuration is particularly beneficial in scenarios where sensitive electronic equipment is used, as it protects against potential damage caused by voltage fluctuations during startup.
In summary, the delay ON circuit provides a reliable solution for managing power supply issues in systems with multiple relays, ensuring that the connected load is activated only after the necessary stabilization period. This design enhances the longevity and reliability of both the stabilizer and the connected devices.The post explains a simple delay ON circuit which allows the connected load at the output to be switched ON with some predetermined delay after power switch ON. The explained circuit can be used for all applications which calls for an initial delay ON feature for the connected load after the mains power is switched ON.
The shown diagram is pretty straightforward yet provides the necessary actions very impressively, moreover the delay period is variable making the set up extremely useful for the proposed applications. Assuming the load which requires the delay ON action being connected across the relay contacts, when power is switched ON, the 12V DC passes via R2 but is unable to reach the base of T1 because initially, C2 acts as a short across ground.
Once C2 charges up to a level which develops a potential of 0. 3 to 0. 6V (+zener voltage) at the base of T1, T1 is instantly switched ON, toggling T2, and the relaysubsequently. finally the load gets switched ON too. I have a 1KVA automatic voltage stabilizer. It has one defect that when it is switched on, very high voltage is outputted for about 1. 5s (therefore cfls and bulb got fused frequently) after that the voltage becomes OK. I have opened the stabilizer it consist of an auto-transformer, 4 24V relay each relay connected to aseparatecircuit(each consisting of 10K preset, BC547, zener diode, BDX53BFP npn darlington pair transistor IC, 220uF/63v capacitor, 100uF/40V capacitor, 4 diodes and some resistors).
These circuits are powered by a step down transformer and output of these circuit are taken across corresponding 100uF/40V capacitor and fed to corresponding relay. What to do in order to tackle the problem. please help me. Hand drawn circuit diagram is attached. The problem in the above circuit might be due to two reasons: one of the relays is switching ON momentarily connecting the wrong contacts with the output, or one of the responsible relays is settling down with the correct voltages a little while after power switch ON.
Since there are more than one relay, tracing out the fault and correcting it can be a bit tedious. the circuit of a delay ON timer explained in the above article could be actually very effective for the discussed purpose. The above wiring would instantly take care of the issues as now the output would switch after some time during power witch ONs, allowing enough time for the internal relays to settle down with the correct voltages across their output contacts.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713