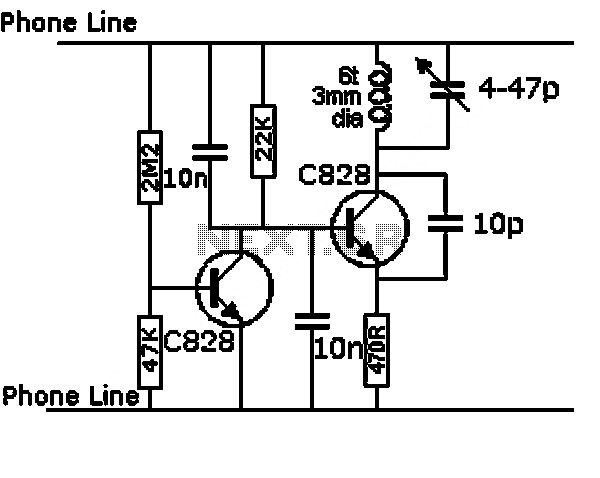
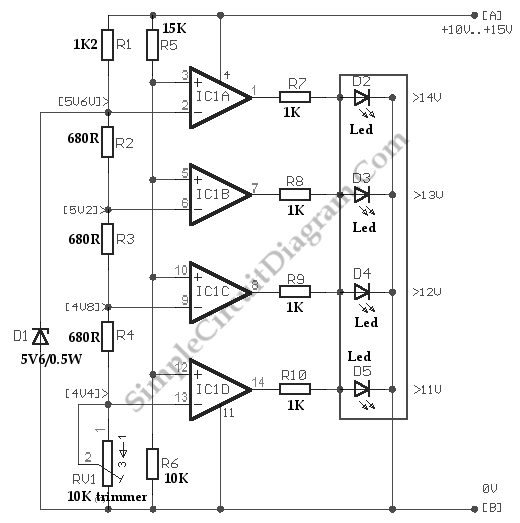
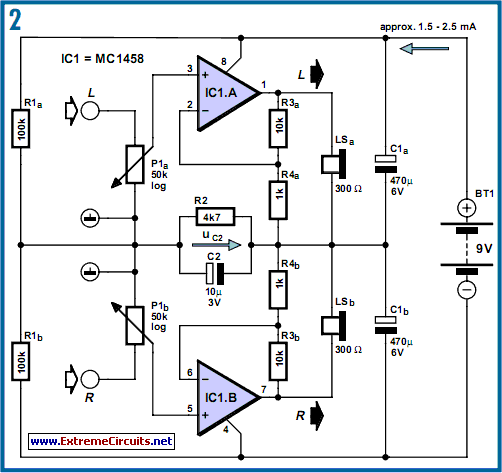
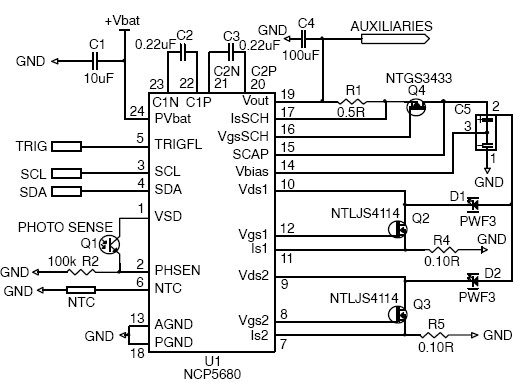
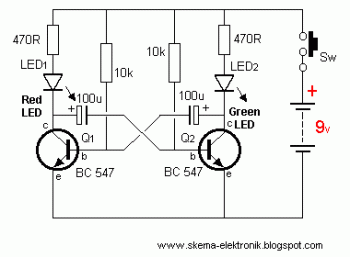
making led flash every 0 6 seconds
A question about electronics involves a project to create a simple circuit that causes an LED to flash.
To design a circuit that makes an LED flash, a basic understanding of electronic components and their configurations is essential. The simplest method to achieve an LED flashing effect is by using a resistor, a capacitor, and a transistor in conjunction with the LED.
The circuit can be constructed using the following components:
1. **LED (Light Emitting Diode)**: This is the primary output component that will emit light when current flows through it. The LED should be rated for the desired voltage and current specifications.
2. **Resistor**: A current-limiting resistor is required to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, based on the supply voltage and the forward voltage drop of the LED.
3. **Capacitor**: The capacitor will be used to store charge and control the timing of the LED flashing. The capacitance value will determine the duration of the flash and the interval between flashes.
4. **Transistor**: A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET) can be used as a switch to turn the LED on and off. The transistor will be driven by the capacitor, allowing it to control the flow of current to the LED.
The circuit operates by charging the capacitor through the resistor. Once the capacitor reaches a certain voltage, it activates the transistor, allowing current to flow through the LED, causing it to light up. As the capacitor discharges, the voltage drops, turning off the transistor and extinguishing the LED. This cycle repeats, creating a flashing effect.
To implement this circuit, the following steps should be taken:
1. Connect the resistor in series with the LED to limit the current.
2. Connect the capacitor in parallel with the LED and resistor.
3. Use the transistor to control the LED; connect the base of the transistor to the junction between the resistor and capacitor.
4. Ensure that the power supply voltage is appropriate for the LED and that the components are rated for the expected operating conditions.
By adjusting the values of the resistor and capacitor, the flashing rate of the LED can be modified to achieve the desired effect. This simple circuit can serve as a foundational project for understanding basic electronic principles and components.Tweet Hey guys, I have a question about electronics. One project ive been intending to do is something simple: make a circuit which makes an LED flash .. 🔗 External reference
To design a circuit that makes an LED flash, a basic understanding of electronic components and their configurations is essential. The simplest method to achieve an LED flashing effect is by using a resistor, a capacitor, and a transistor in conjunction with the LED.
The circuit can be constructed using the following components:
1. **LED (Light Emitting Diode)**: This is the primary output component that will emit light when current flows through it. The LED should be rated for the desired voltage and current specifications.
2. **Resistor**: A current-limiting resistor is required to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, based on the supply voltage and the forward voltage drop of the LED.
3. **Capacitor**: The capacitor will be used to store charge and control the timing of the LED flashing. The capacitance value will determine the duration of the flash and the interval between flashes.
4. **Transistor**: A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET) can be used as a switch to turn the LED on and off. The transistor will be driven by the capacitor, allowing it to control the flow of current to the LED.
The circuit operates by charging the capacitor through the resistor. Once the capacitor reaches a certain voltage, it activates the transistor, allowing current to flow through the LED, causing it to light up. As the capacitor discharges, the voltage drops, turning off the transistor and extinguishing the LED. This cycle repeats, creating a flashing effect.
To implement this circuit, the following steps should be taken:
1. Connect the resistor in series with the LED to limit the current.
2. Connect the capacitor in parallel with the LED and resistor.
3. Use the transistor to control the LED; connect the base of the transistor to the junction between the resistor and capacitor.
4. Ensure that the power supply voltage is appropriate for the LED and that the components are rated for the expected operating conditions.
By adjusting the values of the resistor and capacitor, the flashing rate of the LED can be modified to achieve the desired effect. This simple circuit can serve as a foundational project for understanding basic electronic principles and components.Tweet Hey guys, I have a question about electronics. One project ive been intending to do is something simple: make a circuit which makes an LED flash .. 🔗 External reference