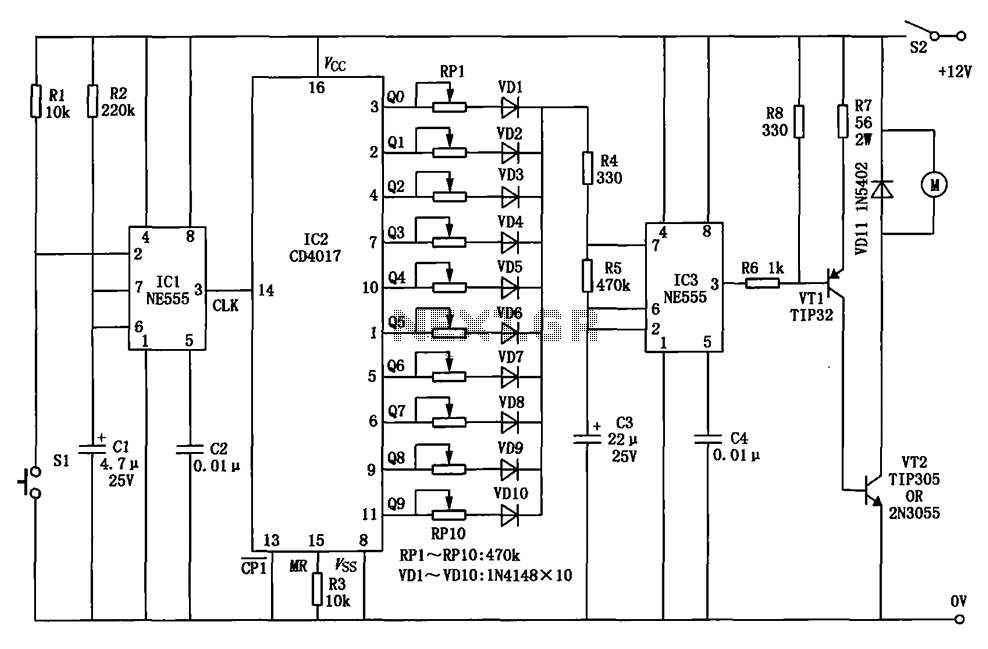
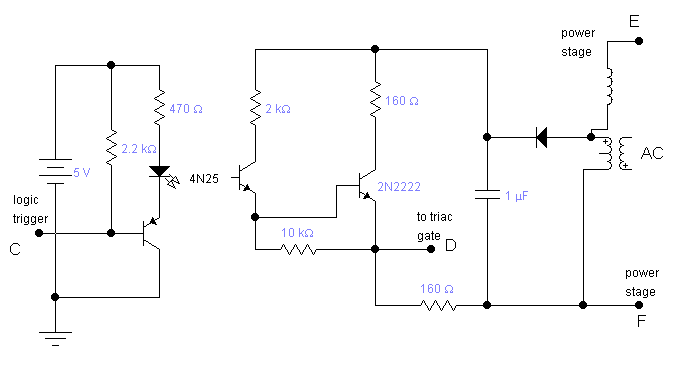
led lights using analog flip flop circuit diagram
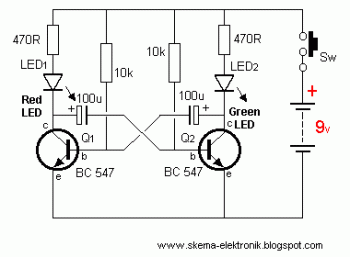
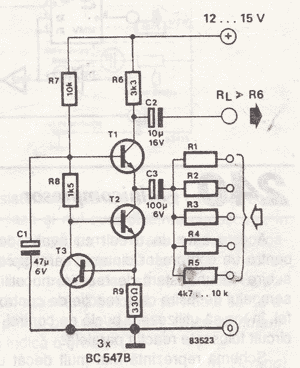
This circuit is designed to drive a total of 42 LEDs, assuming a forward voltage of approximately 2.2V per LED and a forward current of around 21mA for adequate brightness. If the specifications of the LEDs differ significantly, modifications to the design will be necessary. The circuit utilizes a 2N3904 transistor, which is a general-purpose NPN transistor suitable for audio and switching applications, similar to the component indicated in the provided schematic.
The LED driving circuit functions by providing the necessary current and voltage to illuminate the LEDs effectively. Each LED in the series configuration requires a specific forward voltage to operate correctly, and the total voltage drop across all 42 LEDs must be accounted for in the power supply design. For 42 LEDs at 2.2V each, the total forward voltage required is approximately 92.4V (42 x 2.2V).
To achieve the desired forward current of 21mA, a current-limiting resistor should be included in the circuit. This resistor is essential for preventing excessive current from damaging the LEDs. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law: R = (V_supply - V_total) / I, where V_supply is the voltage from the power source, V_total is the total forward voltage drop across the LEDs, and I is the desired current (21mA in this case).
The 2N3904 transistor acts as a switch to control the flow of current to the LEDs. When a suitable base current is applied to the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus powering the LEDs. The base resistor should be calculated to ensure that sufficient base current is provided to saturate the transistor, allowing it to operate efficiently in the switching mode.
In summary, this circuit design requires careful consideration of the power supply voltage, current-limiting resistors, and the transistor's switching characteristics to ensure reliable operation of the LED array. Adjustments may be necessary based on the specific characteristics of the LEDs used in the application.This will drive a total of 42 LEDs. It is based on the assumption that the forward voltage of your LEDs is ~2. 2V, and that they will be bright enough with a forward current of ~21mA. If yours are a lot different, I will have to modify the design. The 2n3904 is a general purpose NPN audio/switching transistor which should be similar to the one show n in the schematic you posted. 🔗 External reference
The LED driving circuit functions by providing the necessary current and voltage to illuminate the LEDs effectively. Each LED in the series configuration requires a specific forward voltage to operate correctly, and the total voltage drop across all 42 LEDs must be accounted for in the power supply design. For 42 LEDs at 2.2V each, the total forward voltage required is approximately 92.4V (42 x 2.2V).
To achieve the desired forward current of 21mA, a current-limiting resistor should be included in the circuit. This resistor is essential for preventing excessive current from damaging the LEDs. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law: R = (V_supply - V_total) / I, where V_supply is the voltage from the power source, V_total is the total forward voltage drop across the LEDs, and I is the desired current (21mA in this case).
The 2N3904 transistor acts as a switch to control the flow of current to the LEDs. When a suitable base current is applied to the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus powering the LEDs. The base resistor should be calculated to ensure that sufficient base current is provided to saturate the transistor, allowing it to operate efficiently in the switching mode.
In summary, this circuit design requires careful consideration of the power supply voltage, current-limiting resistors, and the transistor's switching characteristics to ensure reliable operation of the LED array. Adjustments may be necessary based on the specific characteristics of the LEDs used in the application.This will drive a total of 42 LEDs. It is based on the assumption that the forward voltage of your LEDs is ~2. 2V, and that they will be bright enough with a forward current of ~21mA. If yours are a lot different, I will have to modify the design. The 2n3904 is a general purpose NPN audio/switching transistor which should be similar to the one show n in the schematic you posted. 🔗 External reference