meter How to light an LED when a voltage hits a certain point
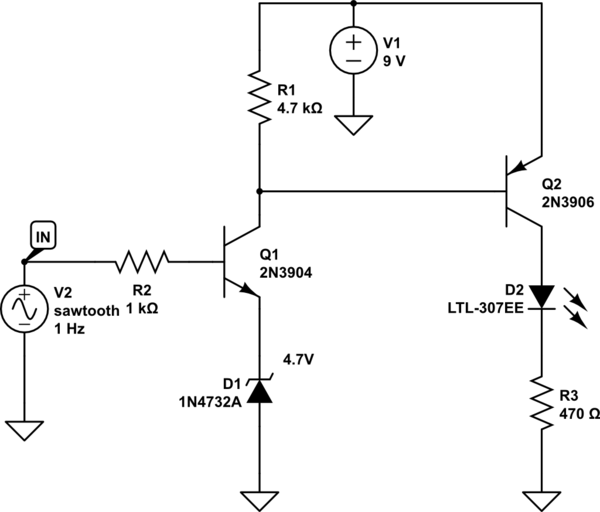
A LED is used to indicate when a DC voltage reaches 5 volts or more. The LED should be fully illuminated at 5 volts and not dim at 4.5 volts or lower. The circuit should be constructed using discrete components, such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, without any integrated circuits (ICs). The input voltage source does not need to be the same as that of the meter.
A potential solution for this circuit involves using a simple transistor-based voltage comparator configuration. The circuit can be constructed with a few discrete components, including resistors, a transistor, and an LED.
To achieve the desired functionality, a voltage divider can be created using two resistors. This divider will reduce the input voltage to a level suitable for comparison. The output of the voltage divider can be connected to the base of a transistor, which will act as a switch for the LED.
When the input voltage is below 5 volts, the voltage at the base of the transistor will be insufficient to turn it on, keeping the LED off. As the input voltage reaches 5 volts, the base voltage will exceed the transistor's threshold, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter and illuminating the LED at full brightness.
To ensure that the LED remains off until the input voltage reaches exactly 5 volts, the resistor values in the voltage divider must be carefully selected. A potentiometer can be included in the circuit to allow for fine-tuning of the threshold voltage, providing flexibility for different applications or voltage levels.
Additionally, a current-limiting resistor should be included in series with the LED to prevent excessive current flow, which could damage the LED. This resistor value can be calculated based on the supply voltage and the desired LED current.
In summary, this discrete component circuit will effectively indicate when the DC voltage reaches or exceeds 5 volts, achieving the requirement of full brightness at the threshold voltage and complete darkness below it.A LED to indicate when a DC voltage reaches 5 volts or more. I don`t want the LED to be dim when it is at 4. 5 or anything. I just want it to be full bright at 5, 0 bright at anything below 5. Is there a way I can do this with discrete components (no IC`s, just resistors, capacitors, transistors etc. ) I do not require the input has the same power source as the meter. Why the discrete component requirement I know you want to understand all of this stuff at the lowest level, but this can literally be done with a single op amp, a pot, a resistor and LED. Matt Young May 11 `13 at 20:47 Maybe an op-amp would work, I only have 2 though and I want to build a bunch with different voltages to trigger the LED.
I guess I could buy some if an OP-amp has many advantages over other components skyler May 11 `13 at 21:53 🔗 External reference
A potential solution for this circuit involves using a simple transistor-based voltage comparator configuration. The circuit can be constructed with a few discrete components, including resistors, a transistor, and an LED.
To achieve the desired functionality, a voltage divider can be created using two resistors. This divider will reduce the input voltage to a level suitable for comparison. The output of the voltage divider can be connected to the base of a transistor, which will act as a switch for the LED.
When the input voltage is below 5 volts, the voltage at the base of the transistor will be insufficient to turn it on, keeping the LED off. As the input voltage reaches 5 volts, the base voltage will exceed the transistor's threshold, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter and illuminating the LED at full brightness.
To ensure that the LED remains off until the input voltage reaches exactly 5 volts, the resistor values in the voltage divider must be carefully selected. A potentiometer can be included in the circuit to allow for fine-tuning of the threshold voltage, providing flexibility for different applications or voltage levels.
Additionally, a current-limiting resistor should be included in series with the LED to prevent excessive current flow, which could damage the LED. This resistor value can be calculated based on the supply voltage and the desired LED current.
In summary, this discrete component circuit will effectively indicate when the DC voltage reaches or exceeds 5 volts, achieving the requirement of full brightness at the threshold voltage and complete darkness below it.A LED to indicate when a DC voltage reaches 5 volts or more. I don`t want the LED to be dim when it is at 4. 5 or anything. I just want it to be full bright at 5, 0 bright at anything below 5. Is there a way I can do this with discrete components (no IC`s, just resistors, capacitors, transistors etc. ) I do not require the input has the same power source as the meter. Why the discrete component requirement I know you want to understand all of this stuff at the lowest level, but this can literally be done with a single op amp, a pot, a resistor and LED. Matt Young May 11 `13 at 20:47 Maybe an op-amp would work, I only have 2 though and I want to build a bunch with different voltages to trigger the LED.
I guess I could buy some if an OP-amp has many advantages over other components skyler May 11 `13 at 21:53 🔗 External reference