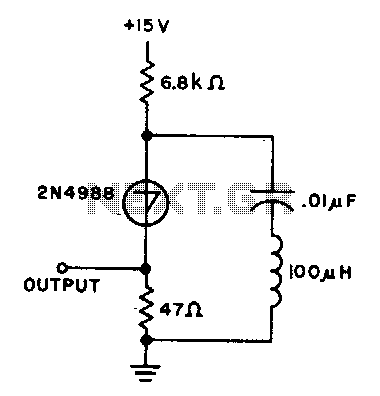
Miller oscillator
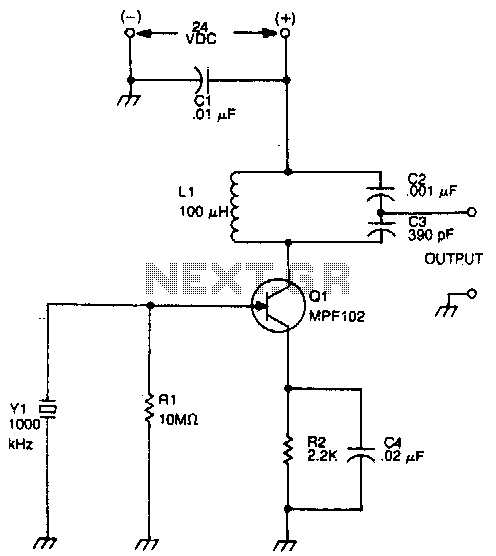
The drain of the JFET Miller oscillator is tuned to the resonant frequency of the crystal by an LC tank circuit.
The JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) Miller oscillator is a type of oscillator circuit that utilizes the properties of a JFET to generate oscillations. In this configuration, the drain terminal of the JFET is connected to an LC tank circuit, which consists of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). This tank circuit is crucial for determining the oscillation frequency.
The resonant frequency of the LC tank circuit is given by the formula:
\[ f_0 = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}} \]
where \( f_0 \) is the resonant frequency, \( L \) is the inductance, and \( C \) is the capacitance. The design of the tank circuit allows it to resonate at the same frequency as the crystal, ensuring that the oscillator operates efficiently.
The JFET in the Miller oscillator configuration also provides gain and feedback. The feedback loop is formed by connecting a portion of the output signal from the drain back to the gate of the JFET. This feedback is essential for sustaining oscillations. The gain provided by the JFET must be sufficient to overcome losses in the circuit to maintain continuous oscillation.
In summary, the JFET Miller oscillator's design, which incorporates an LC tank circuit tuned to the resonant frequency of a crystal, enables the generation of stable oscillations. This configuration is widely used in applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as in radio frequency (RF) circuits and signal processing systems. Proper selection of the inductor and capacitor values is essential to achieve the desired frequency characteristics while ensuring stability and reliability in the oscillator's performance.The drain of the JFET Miller oscillator is tuned to the resonant frequency of the crystal by an LC tank circuit. 🔗 External reference
The JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) Miller oscillator is a type of oscillator circuit that utilizes the properties of a JFET to generate oscillations. In this configuration, the drain terminal of the JFET is connected to an LC tank circuit, which consists of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). This tank circuit is crucial for determining the oscillation frequency.
The resonant frequency of the LC tank circuit is given by the formula:
\[ f_0 = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}} \]
where \( f_0 \) is the resonant frequency, \( L \) is the inductance, and \( C \) is the capacitance. The design of the tank circuit allows it to resonate at the same frequency as the crystal, ensuring that the oscillator operates efficiently.
The JFET in the Miller oscillator configuration also provides gain and feedback. The feedback loop is formed by connecting a portion of the output signal from the drain back to the gate of the JFET. This feedback is essential for sustaining oscillations. The gain provided by the JFET must be sufficient to overcome losses in the circuit to maintain continuous oscillation.
In summary, the JFET Miller oscillator's design, which incorporates an LC tank circuit tuned to the resonant frequency of a crystal, enables the generation of stable oscillations. This configuration is widely used in applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as in radio frequency (RF) circuits and signal processing systems. Proper selection of the inductor and capacitor values is essential to achieve the desired frequency characteristics while ensuring stability and reliability in the oscillator's performance.The drain of the JFET Miller oscillator is tuned to the resonant frequency of the crystal by an LC tank circuit. 🔗 External reference