Mobile Controlled Robot without microcontroller

A mobile-controlled robot is a mobile device that offers extensive wireless control capabilities to the robot, as long as the cell phone remains within signal range.
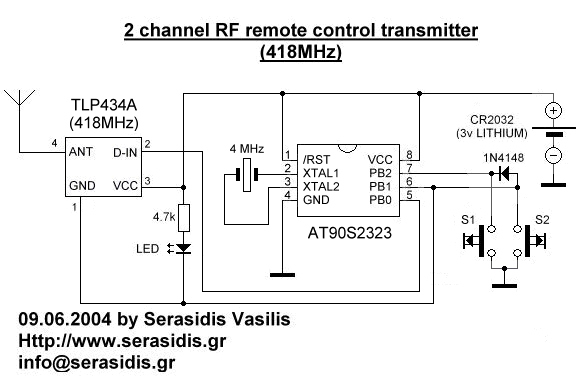
The mobile-controlled robot operates through a wireless communication interface, typically utilizing Bluetooth or Wi-Fi technology. The control system is designed to receive commands from a smartphone application, which serves as the user interface. The smartphone sends control signals to the robot, enabling it to perform various functions such as movement, obstacle avoidance, and task execution.
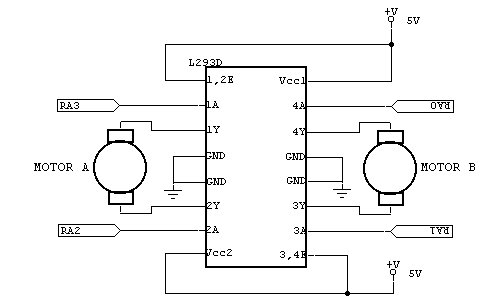
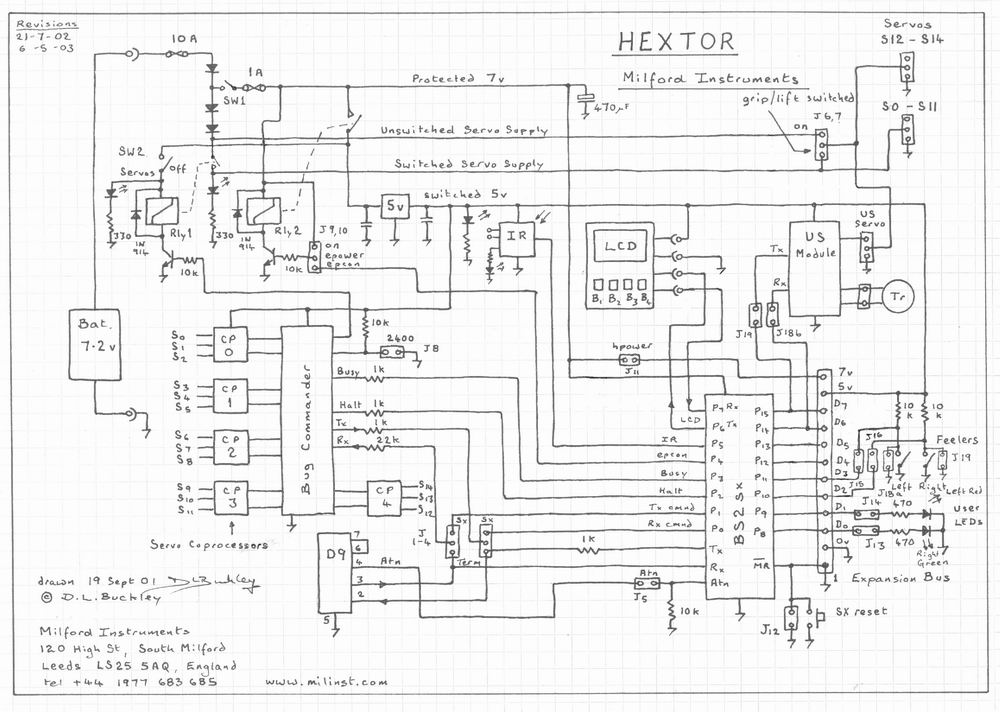
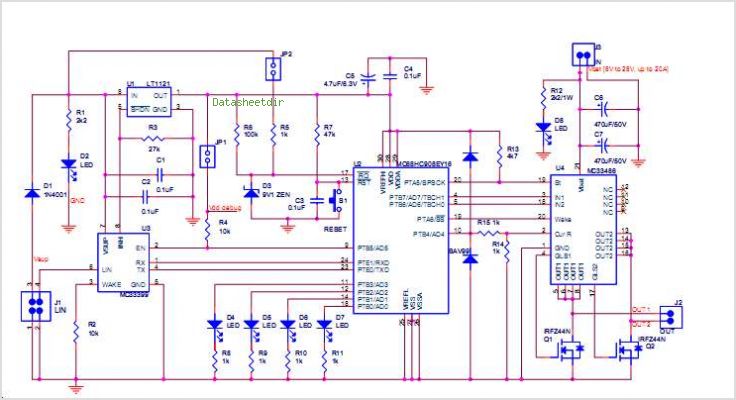
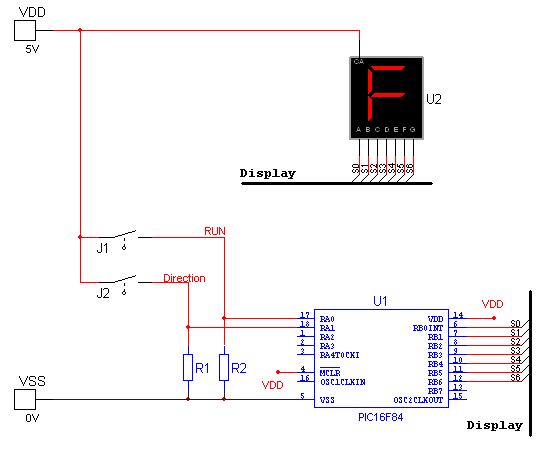
The core components of the robot include a microcontroller, motor drivers, and sensors. The microcontroller acts as the brain of the robot, processing incoming signals from the smartphone and translating them into actionable commands for the motors. Motor drivers are essential for controlling the speed and direction of the robot's wheels or tracks, allowing for precise maneuverability.
Sensors such as ultrasonic or infrared are often integrated into the robot to facilitate obstacle detection and navigation. These sensors provide real-time feedback to the microcontroller, enabling the robot to adjust its path and avoid collisions.
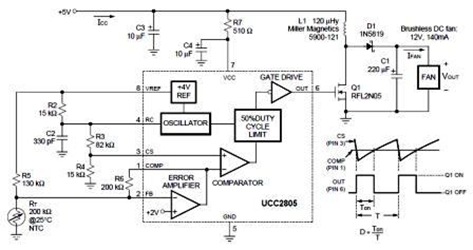
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the robot typically operates using rechargeable batteries, which must be selected based on the required voltage and current ratings for the motors and electronics.
Overall, a mobile-controlled robot presents a versatile platform for various applications, including education, entertainment, and research, demonstrating the integration of mobile technology with robotics.A Mobile Controlled Robot is a mobile device, which provides wide-range of wireless control ability to your robot unless your cell phone gets out of signal.. 🔗 External reference
The mobile-controlled robot operates through a wireless communication interface, typically utilizing Bluetooth or Wi-Fi technology. The control system is designed to receive commands from a smartphone application, which serves as the user interface. The smartphone sends control signals to the robot, enabling it to perform various functions such as movement, obstacle avoidance, and task execution.
The core components of the robot include a microcontroller, motor drivers, and sensors. The microcontroller acts as the brain of the robot, processing incoming signals from the smartphone and translating them into actionable commands for the motors. Motor drivers are essential for controlling the speed and direction of the robot's wheels or tracks, allowing for precise maneuverability.
Sensors such as ultrasonic or infrared are often integrated into the robot to facilitate obstacle detection and navigation. These sensors provide real-time feedback to the microcontroller, enabling the robot to adjust its path and avoid collisions.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the robot typically operates using rechargeable batteries, which must be selected based on the required voltage and current ratings for the motors and electronics.
Overall, a mobile-controlled robot presents a versatile platform for various applications, including education, entertainment, and research, demonstrating the integration of mobile technology with robotics.A Mobile Controlled Robot is a mobile device, which provides wide-range of wireless control ability to your robot unless your cell phone gets out of signal.. 🔗 External reference