Design of Temperature-Controlled PWM Boost Converter Circuit
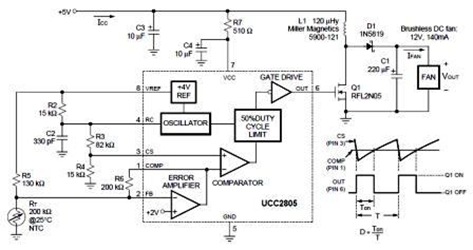
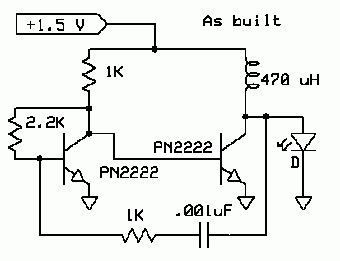
A temperature-controlled pulse-width-modulator (PWM) boost converter circuit diagram is illustrated in the following figure. This boost converter is designed to operate a 12V fan using a 5V supply while maintaining temperature control.
The temperature-controlled PWM boost converter circuit operates by stepping up a lower voltage (5V) to a higher voltage (12V) suitable for driving a fan. The circuit typically consists of several key components: a PWM controller, an inductor, a diode, a capacitor, and a temperature sensor.
The PWM controller modulates the duty cycle of the output voltage, allowing the fan speed to be adjusted based on temperature readings. The temperature sensor monitors the ambient temperature and sends feedback to the PWM controller. As the temperature increases, the PWM controller adjusts the duty cycle to increase the output voltage, thereby increasing the fan speed to enhance cooling. Conversely, as the temperature decreases, the fan speed is reduced to save power and minimize noise.
The inductor stores energy during the ON phase of the PWM signal and releases it during the OFF phase, contributing to the voltage boost. The diode allows current to flow in one direction, preventing backflow and ensuring efficient energy transfer to the output capacitor, which smooths the output voltage.
This configuration enables efficient thermal management in applications where temperature regulation is crucial, such as in electronic devices that generate heat. The ability to operate from a lower voltage supply while providing a higher output voltage makes this circuit versatile for various applications, including cooling systems in computers and other electronic equipment.Temperature controlled pulse-width-modulator (PWM) boost converter circuit diagram is shown in the following figure. The boost converter may provide temperature-controlled operation of 12V fan from 5V supply 🔗 External reference
The temperature-controlled PWM boost converter circuit operates by stepping up a lower voltage (5V) to a higher voltage (12V) suitable for driving a fan. The circuit typically consists of several key components: a PWM controller, an inductor, a diode, a capacitor, and a temperature sensor.
The PWM controller modulates the duty cycle of the output voltage, allowing the fan speed to be adjusted based on temperature readings. The temperature sensor monitors the ambient temperature and sends feedback to the PWM controller. As the temperature increases, the PWM controller adjusts the duty cycle to increase the output voltage, thereby increasing the fan speed to enhance cooling. Conversely, as the temperature decreases, the fan speed is reduced to save power and minimize noise.
The inductor stores energy during the ON phase of the PWM signal and releases it during the OFF phase, contributing to the voltage boost. The diode allows current to flow in one direction, preventing backflow and ensuring efficient energy transfer to the output capacitor, which smooths the output voltage.
This configuration enables efficient thermal management in applications where temperature regulation is crucial, such as in electronic devices that generate heat. The ability to operate from a lower voltage supply while providing a higher output voltage makes this circuit versatile for various applications, including cooling systems in computers and other electronic equipment.Temperature controlled pulse-width-modulator (PWM) boost converter circuit diagram is shown in the following figure. The boost converter may provide temperature-controlled operation of 12V fan from 5V supply 🔗 External reference