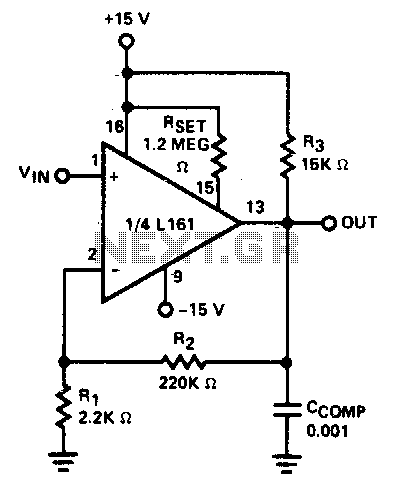
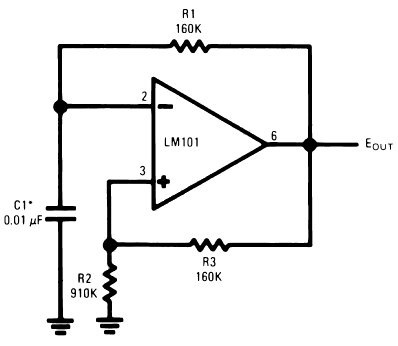
Modular Buffer Preamplifier in Class A Operation
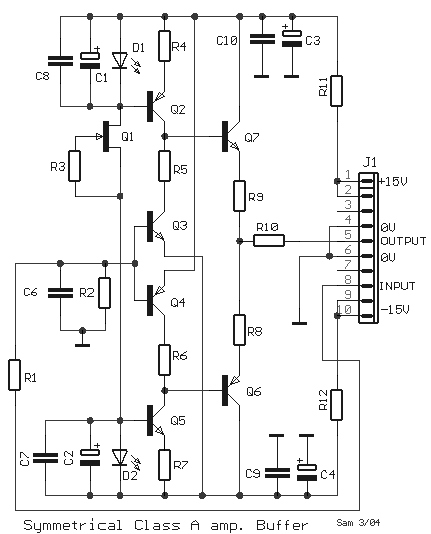
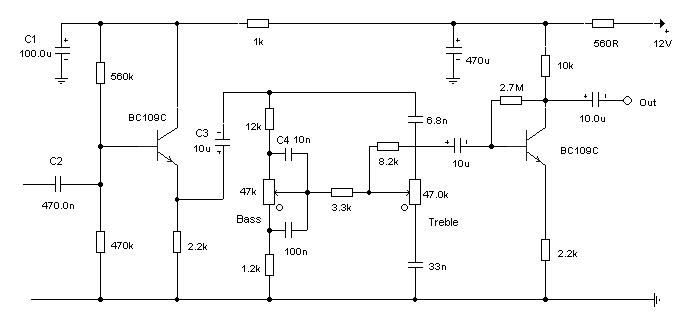
The circuit was designed to create a modular Class A buffer preamplifier to isolate stages in an audio circuit. BF245 is a general-purpose N-Channel JFET used in this design.
The modular Class A buffer preamplifier serves as an essential component in audio circuits, providing impedance matching and signal isolation between different stages of audio processing. The use of a Class A configuration ensures that the amplifier operates with low distortion, maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The BF245, a general-purpose N-Channel Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), is selected for its favorable characteristics, including low noise and high input impedance, making it ideal for audio applications. In this circuit, the BF245 operates in the linear region, where it functions as a voltage follower. This configuration allows the output voltage to closely follow the input voltage, effectively buffering the audio signal.
The circuit typically includes biasing resistors to set the operating point of the BF245, ensuring that it remains in the active region throughout the audio signal's dynamic range. Capacitors may be employed at the input and output to block any DC components, allowing only the AC audio signals to pass through.
To enhance performance further, careful attention must be paid to the layout of the circuit board to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect the audio quality. Additionally, power supply decoupling capacitors are recommended to filter out any noise from the power source, ensuring clean operation of the preamplifier.
Overall, this modular Class A buffer preamplifier design using the BF245 JFET provides a reliable and effective means of isolating audio stages while preserving signal fidelity.The circuit was designed to create a modular Class A buffer preamplifier in order to isolate stages in an audio circuit. BF245 a general purpose N-Chann.. 🔗 External reference
The modular Class A buffer preamplifier serves as an essential component in audio circuits, providing impedance matching and signal isolation between different stages of audio processing. The use of a Class A configuration ensures that the amplifier operates with low distortion, maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The BF245, a general-purpose N-Channel Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), is selected for its favorable characteristics, including low noise and high input impedance, making it ideal for audio applications. In this circuit, the BF245 operates in the linear region, where it functions as a voltage follower. This configuration allows the output voltage to closely follow the input voltage, effectively buffering the audio signal.
The circuit typically includes biasing resistors to set the operating point of the BF245, ensuring that it remains in the active region throughout the audio signal's dynamic range. Capacitors may be employed at the input and output to block any DC components, allowing only the AC audio signals to pass through.
To enhance performance further, careful attention must be paid to the layout of the circuit board to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect the audio quality. Additionally, power supply decoupling capacitors are recommended to filter out any noise from the power source, ensuring clean operation of the preamplifier.
Overall, this modular Class A buffer preamplifier design using the BF245 JFET provides a reliable and effective means of isolating audio stages while preserving signal fidelity.The circuit was designed to create a modular Class A buffer preamplifier in order to isolate stages in an audio circuit. BF245 a general purpose N-Chann.. 🔗 External reference