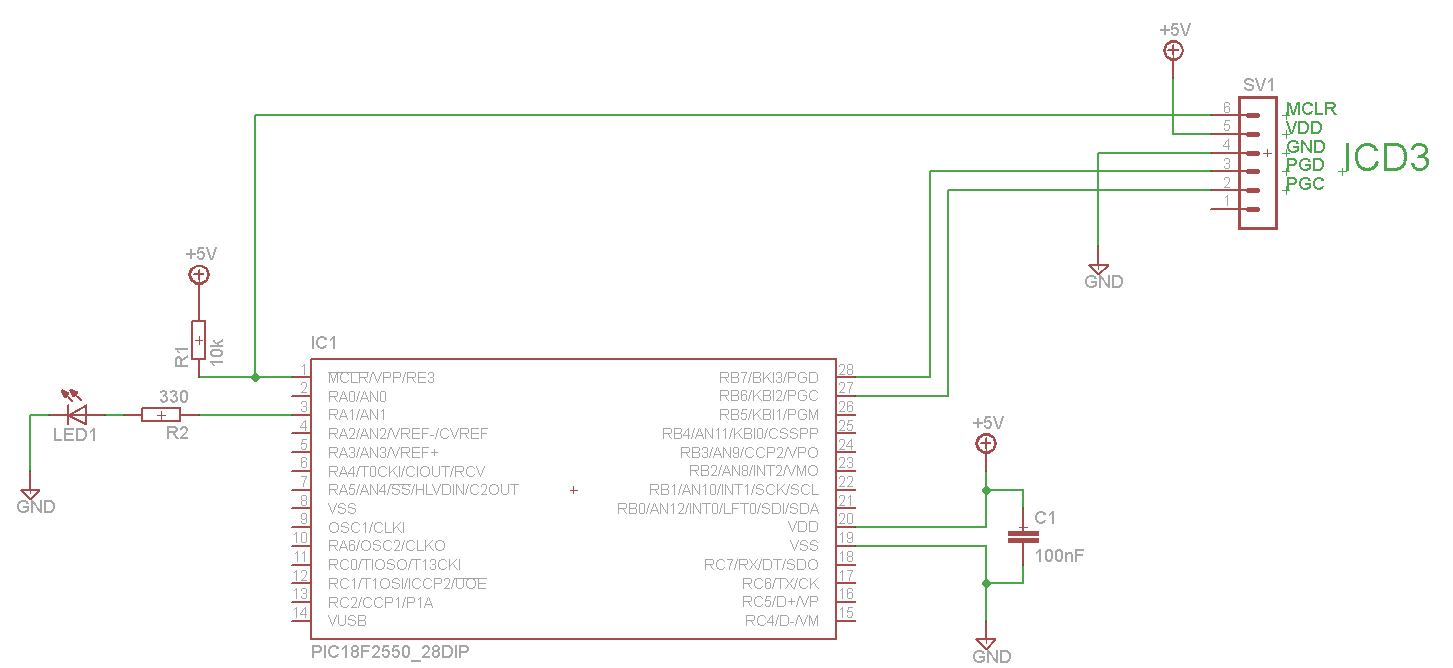
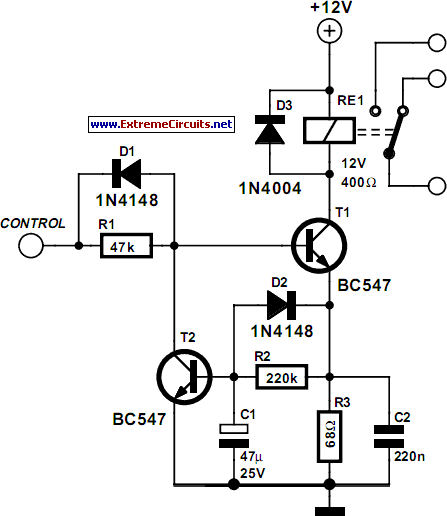
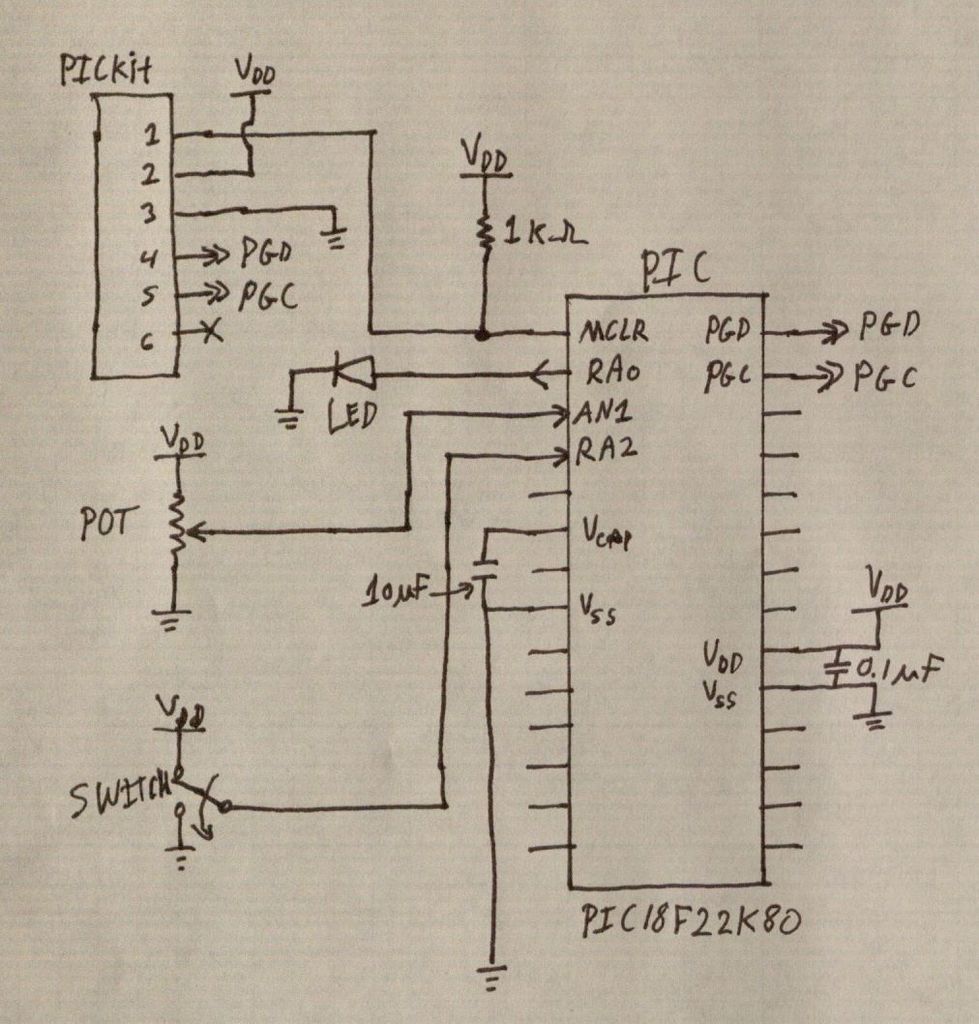
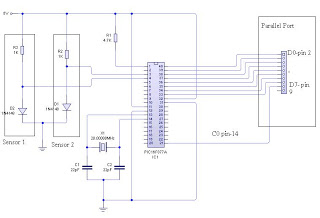
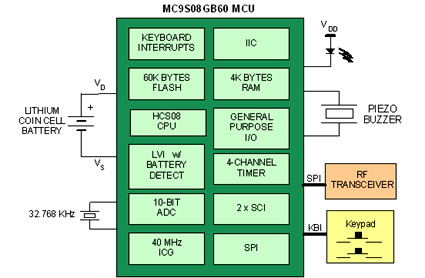
MONSTER Musical Tesla Coil with a Microcontroller
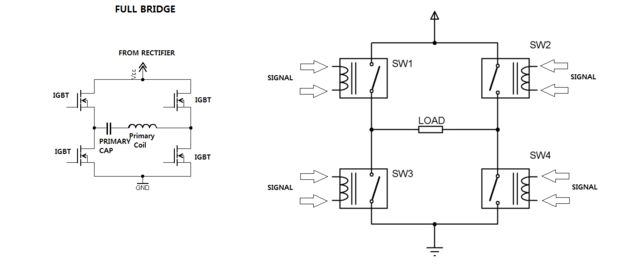
One of the most challenging aspects of constructing a solid-state Tesla coil is the bridge or switching circuit. The bridge switching circuit is the core component of the system.
The bridge switching circuit is essential for controlling the power delivery to the primary coil of the Tesla coil. It typically consists of a series of high-speed switching devices such as MOSFETs or IGBTs configured in a full-bridge arrangement. This configuration allows for the efficient conversion of DC voltage from a power source into a high-frequency AC signal, which is necessary for the operation of the Tesla coil.
The circuit requires careful design to ensure that the switching devices operate within their specified limits, particularly regarding voltage and current ratings. Additionally, appropriate gate drive circuitry must be implemented to provide the necessary control signals to the switching devices, enabling rapid on-off switching to produce the desired oscillation frequency.
Incorporating feedback mechanisms can enhance the performance of the bridge circuit. This may involve using current sensing resistors and operational amplifiers to monitor the output and adjust the switching timing to maintain stable operation under varying load conditions. Proper thermal management is also crucial, as the switching devices can generate significant heat during operation. Heat sinks or active cooling systems may be necessary to prevent thermal overload and ensure reliability.
Overall, the design and implementation of the bridge switching circuit are critical for the successful operation of a solid-state Tesla coil, influencing both its efficiency and performance characteristics.Perhaps the trickiest part in building a solid state tesla coil is the bridge or switching circuit. The bridge switching circuit is the heart of t.. 🔗 External reference
The bridge switching circuit is essential for controlling the power delivery to the primary coil of the Tesla coil. It typically consists of a series of high-speed switching devices such as MOSFETs or IGBTs configured in a full-bridge arrangement. This configuration allows for the efficient conversion of DC voltage from a power source into a high-frequency AC signal, which is necessary for the operation of the Tesla coil.
The circuit requires careful design to ensure that the switching devices operate within their specified limits, particularly regarding voltage and current ratings. Additionally, appropriate gate drive circuitry must be implemented to provide the necessary control signals to the switching devices, enabling rapid on-off switching to produce the desired oscillation frequency.
Incorporating feedback mechanisms can enhance the performance of the bridge circuit. This may involve using current sensing resistors and operational amplifiers to monitor the output and adjust the switching timing to maintain stable operation under varying load conditions. Proper thermal management is also crucial, as the switching devices can generate significant heat during operation. Heat sinks or active cooling systems may be necessary to prevent thermal overload and ensure reliability.
Overall, the design and implementation of the bridge switching circuit are critical for the successful operation of a solid-state Tesla coil, influencing both its efficiency and performance characteristics.Perhaps the trickiest part in building a solid state tesla coil is the bridge or switching circuit. The bridge switching circuit is the heart of t.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713