Mosfet circuit schematics
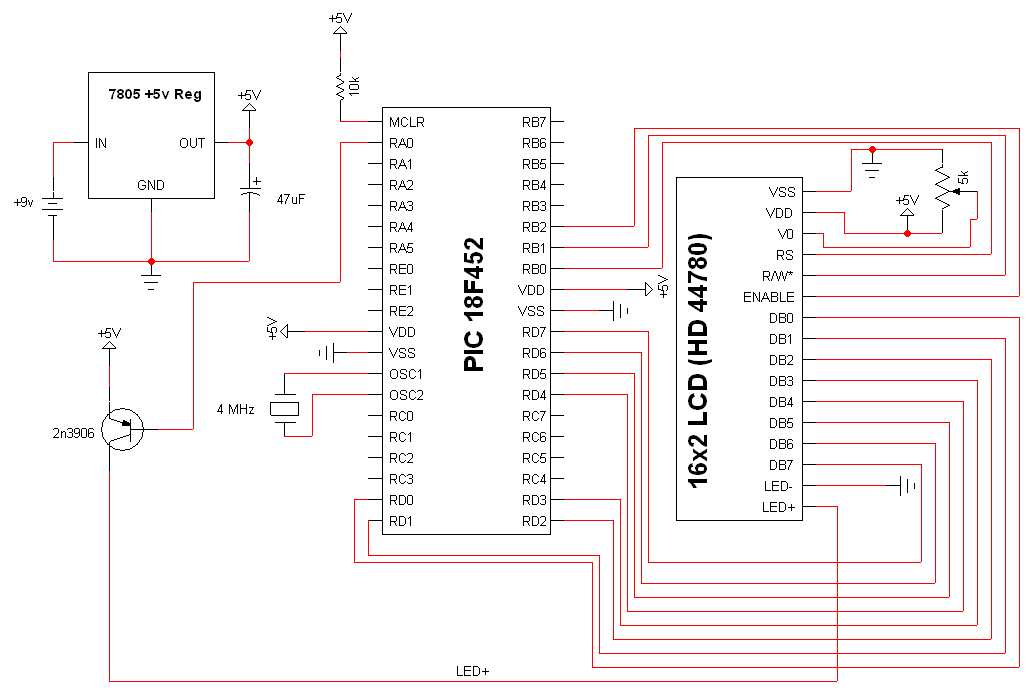
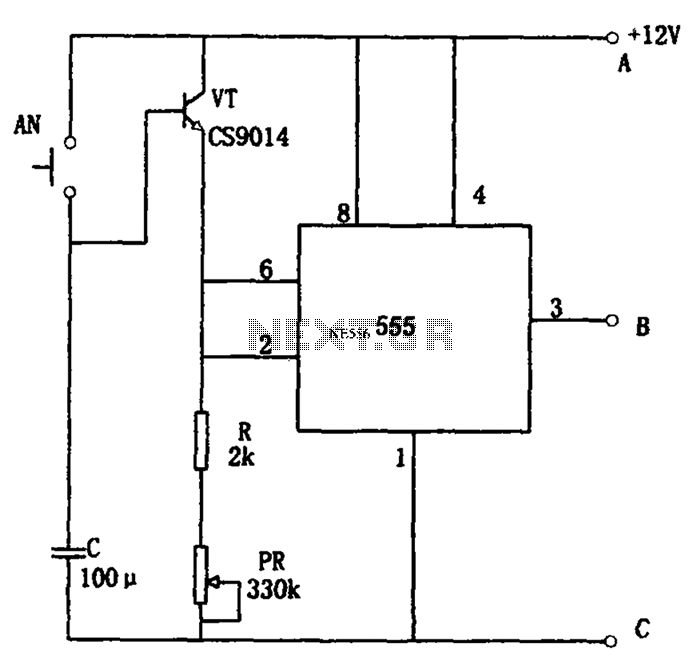
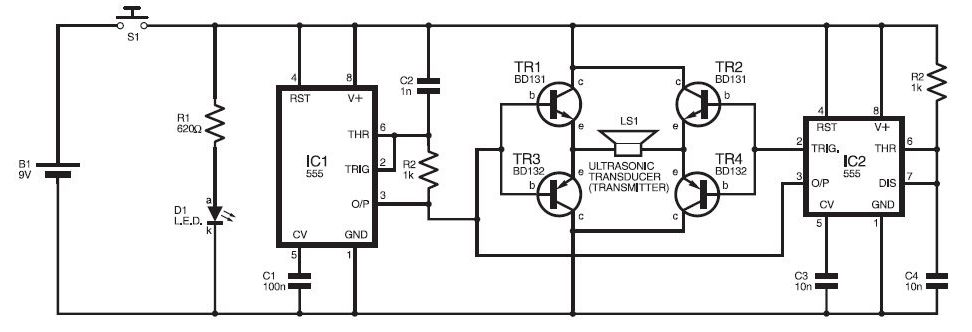
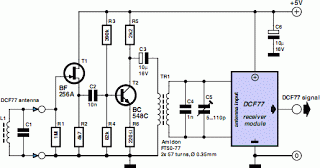
Two working examples have been assembled, one utilizing a PNP and an NPN transistor, and the other employing two MOSFETs. Both circuits function correctly, but as anticipated, the MOSFET circuit draws significantly less current (0.1 mA compared to 4.5 mA). Feedback, suggestions, and bug reports are welcome.
The described circuit examples highlight the differences in operational characteristics between bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). The first circuit, which incorporates a PNP and an NPN transistor, demonstrates the use of BJTs in switching applications. In this configuration, the PNP transistor is typically used to switch the positive side of the load, while the NPN transistor switches the ground side. The current consumption of 4.5 mA indicates that the BJT configuration requires a higher base current to maintain saturation compared to the MOSFET configuration.
In contrast, the second circuit utilizing two MOSFETs showcases the advantages of field-effect transistors in terms of efficiency. The significantly lower current draw of 0.1 mA is a result of the high input impedance of MOSFETs, which allows for minimal gate current. This characteristic makes MOSFETs ideal for applications where power consumption is critical, such as in battery-operated devices.
The schematic for the BJT circuit would include the PNP transistor connected to the positive voltage supply, with the load connected to the collector and the emitter grounded. The base of the PNP transistor would be driven by a control signal through a resistor. The NPN transistor would be connected similarly, with the load connected to the collector and the emitter grounded, and the base driven by the same or a complementary control signal.
For the MOSFET circuit, the schematic would depict two MOSFETs arranged in a similar manner, with the first MOSFET controlling the load connected to the positive supply and the second MOSFET providing a return path to ground. The gate of each MOSFET would be driven by a control signal, ensuring that they are turned on and off as needed with minimal gate current.
Overall, these examples illustrate the practical applications of BJTs and MOSFETs in electronic circuits, showcasing their respective advantages in current consumption and efficiency. Feedback on these designs would be beneficial for further refinement and optimization.Sid, I put together two working examples, one using a PNP and NPN transistor, and one using two MOSFETs. Both work fine, but as expected the MOSFET circuit consumes much less current (0.1 mA vs. 4.5 mA). Comments, suggestions, and bug reports gratefully received.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit examples highlight the differences in operational characteristics between bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). The first circuit, which incorporates a PNP and an NPN transistor, demonstrates the use of BJTs in switching applications. In this configuration, the PNP transistor is typically used to switch the positive side of the load, while the NPN transistor switches the ground side. The current consumption of 4.5 mA indicates that the BJT configuration requires a higher base current to maintain saturation compared to the MOSFET configuration.
In contrast, the second circuit utilizing two MOSFETs showcases the advantages of field-effect transistors in terms of efficiency. The significantly lower current draw of 0.1 mA is a result of the high input impedance of MOSFETs, which allows for minimal gate current. This characteristic makes MOSFETs ideal for applications where power consumption is critical, such as in battery-operated devices.
The schematic for the BJT circuit would include the PNP transistor connected to the positive voltage supply, with the load connected to the collector and the emitter grounded. The base of the PNP transistor would be driven by a control signal through a resistor. The NPN transistor would be connected similarly, with the load connected to the collector and the emitter grounded, and the base driven by the same or a complementary control signal.
For the MOSFET circuit, the schematic would depict two MOSFETs arranged in a similar manner, with the first MOSFET controlling the load connected to the positive supply and the second MOSFET providing a return path to ground. The gate of each MOSFET would be driven by a control signal, ensuring that they are turned on and off as needed with minimal gate current.
Overall, these examples illustrate the practical applications of BJTs and MOSFETs in electronic circuits, showcasing their respective advantages in current consumption and efficiency. Feedback on these designs would be beneficial for further refinement and optimization.Sid, I put together two working examples, one using a PNP and NPN transistor, and one using two MOSFETs. Both work fine, but as expected the MOSFET circuit consumes much less current (0.1 mA vs. 4.5 mA). Comments, suggestions, and bug reports gratefully received.. 🔗 External reference