Mosfet Mixer-Oscillator Circuit For Am Receivers Circuit
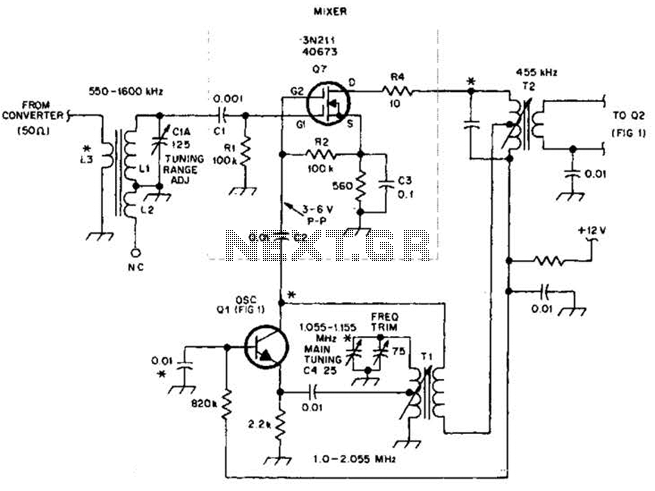
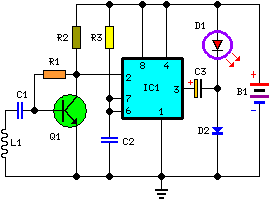
This circuit is an enhanced front end for upgrading a transistor AM receiver. This front end is beneficial when the radio is intended to function as a tunable IF amplifier with shortwave converters.
The circuit described serves as a sophisticated enhancement to a traditional transistor AM receiver, specifically designed to improve its performance and versatility. The upgraded front end is essential for applications where the receiver is utilized as a tunable intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier, particularly in conjunction with shortwave converters.
The design typically incorporates several key components, including RF amplifiers, mixers, and filters, which work together to optimize signal reception and processing. The RF amplifier is crucial for boosting weak signals captured by the antenna, ensuring that the subsequent stages of the receiver can operate effectively.
The mixer stage is responsible for converting the incoming RF signals to an IF signal, which is easier to process and can be filtered for unwanted noise. The tunable aspect of the circuit allows for the adjustment of the IF frequency, enabling the receiver to be tailored for various shortwave bands. This flexibility is vital for users seeking to enhance their listening experience across a wide range of frequencies.
Furthermore, the inclusion of high-quality components, such as low-noise transistors and precision capacitors, contributes to the overall performance of the circuit, minimizing distortion and maximizing sensitivity. The layout of the circuit should also be carefully considered to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance.
In summary, this upgraded front end circuit not only enhances the functionality of a standard AM receiver but also provides the necessary features to operate effectively with shortwave converters, making it an invaluable tool for radio enthusiasts and professionals alike. This circuit is an improved front end for upgrading a transistor AM receiver. This front end is useful when the radio is to be used as a tuneable IF amplifier with shortwave converters. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described serves as a sophisticated enhancement to a traditional transistor AM receiver, specifically designed to improve its performance and versatility. The upgraded front end is essential for applications where the receiver is utilized as a tunable intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier, particularly in conjunction with shortwave converters.
The design typically incorporates several key components, including RF amplifiers, mixers, and filters, which work together to optimize signal reception and processing. The RF amplifier is crucial for boosting weak signals captured by the antenna, ensuring that the subsequent stages of the receiver can operate effectively.
The mixer stage is responsible for converting the incoming RF signals to an IF signal, which is easier to process and can be filtered for unwanted noise. The tunable aspect of the circuit allows for the adjustment of the IF frequency, enabling the receiver to be tailored for various shortwave bands. This flexibility is vital for users seeking to enhance their listening experience across a wide range of frequencies.
Furthermore, the inclusion of high-quality components, such as low-noise transistors and precision capacitors, contributes to the overall performance of the circuit, minimizing distortion and maximizing sensitivity. The layout of the circuit should also be carefully considered to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance.
In summary, this upgraded front end circuit not only enhances the functionality of a standard AM receiver but also provides the necessary features to operate effectively with shortwave converters, making it an invaluable tool for radio enthusiasts and professionals alike. This circuit is an improved front end for upgrading a transistor AM receiver. This front end is useful when the radio is to be used as a tuneable IF amplifier with shortwave converters. 🔗 External reference