MOSFET Power Amplifier
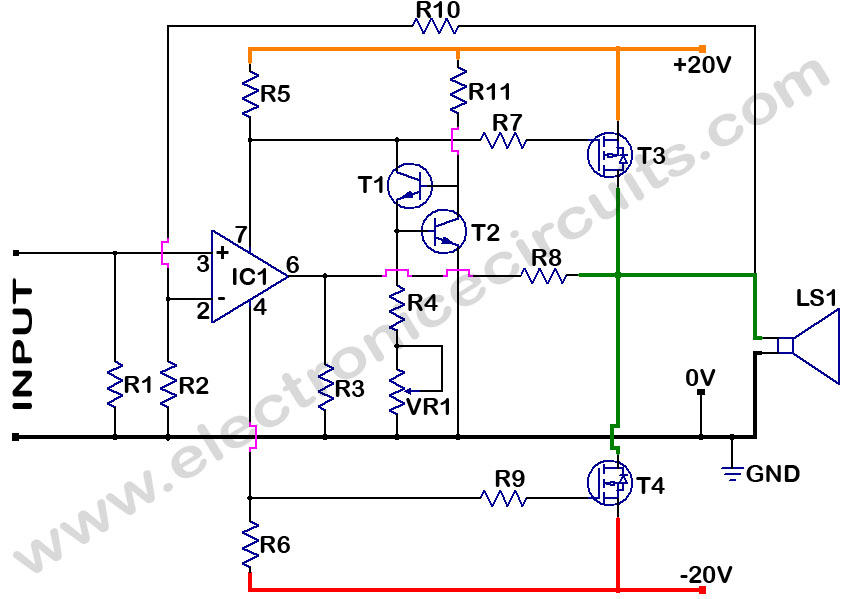
MOSFET Power Amplifier Circuit diagrams. Two complementary MOSFETs are used to deliver 20W into 8Ω.
The described MOSFET power amplifier circuit utilizes two complementary MOSFETs, which are arranged in a push-pull configuration to efficiently amplify audio signals. The circuit is designed to deliver a power output of 20 watts into an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for various audio amplification applications.
In this configuration, one MOSFET is responsible for amplifying the positive half of the input signal, while the other amplifies the negative half. This complementary operation ensures that the output signal closely follows the input waveform, resulting in minimal distortion and improved linearity.
Key components of the circuit include the two complementary MOSFETs, typically an N-channel and a P-channel device. The choice of MOSFETs is crucial, as they must be able to handle the required voltage and current levels while maintaining low on-resistance to minimize power loss. Additional components may include biasing resistors to set the operating point of the MOSFETs, coupling capacitors to block DC offsets, and feedback components to stabilize the amplifier's gain and frequency response.
The power supply for the amplifier must be capable of providing sufficient voltage and current to drive the output stage effectively. A well-designed power supply will also include filtering capacitors to reduce ripple and noise, ensuring a clean power source for the amplifier.
Thermal management is another important aspect of the design, as the MOSFETs will generate heat during operation. Adequate heatsinking must be provided to dissipate this heat and prevent thermal runaway conditions that could damage the devices.
Overall, this MOSFET power amplifier circuit represents a robust solution for audio amplification, leveraging the advantages of complementary MOSFET technology to achieve high efficiency and performance.MOSFET Power Amplifier Circuit diagrams Two complementary MOSFETs are used to deliver 20W into 8?. PARTS.. 🔗 External reference
The described MOSFET power amplifier circuit utilizes two complementary MOSFETs, which are arranged in a push-pull configuration to efficiently amplify audio signals. The circuit is designed to deliver a power output of 20 watts into an 8-ohm load, making it suitable for various audio amplification applications.
In this configuration, one MOSFET is responsible for amplifying the positive half of the input signal, while the other amplifies the negative half. This complementary operation ensures that the output signal closely follows the input waveform, resulting in minimal distortion and improved linearity.
Key components of the circuit include the two complementary MOSFETs, typically an N-channel and a P-channel device. The choice of MOSFETs is crucial, as they must be able to handle the required voltage and current levels while maintaining low on-resistance to minimize power loss. Additional components may include biasing resistors to set the operating point of the MOSFETs, coupling capacitors to block DC offsets, and feedback components to stabilize the amplifier's gain and frequency response.
The power supply for the amplifier must be capable of providing sufficient voltage and current to drive the output stage effectively. A well-designed power supply will also include filtering capacitors to reduce ripple and noise, ensuring a clean power source for the amplifier.
Thermal management is another important aspect of the design, as the MOSFETs will generate heat during operation. Adequate heatsinking must be provided to dissipate this heat and prevent thermal runaway conditions that could damage the devices.
Overall, this MOSFET power amplifier circuit represents a robust solution for audio amplification, leveraging the advantages of complementary MOSFET technology to achieve high efficiency and performance.MOSFET Power Amplifier Circuit diagrams Two complementary MOSFETs are used to deliver 20W into 8?. PARTS.. 🔗 External reference