Motor protector circuit diagram 8
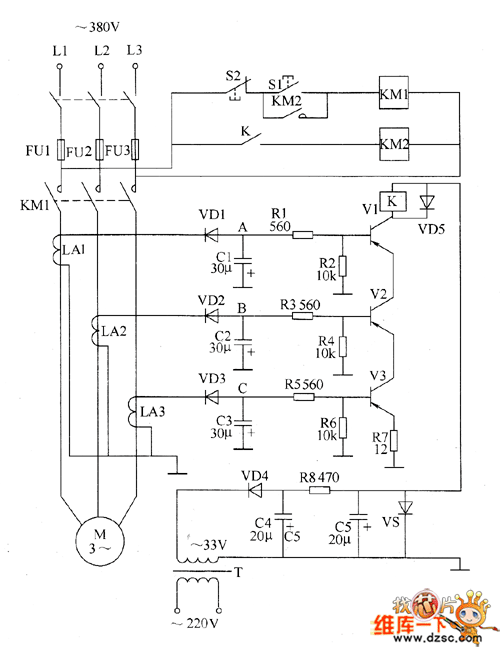
The motor protection circuit consists of a power supply circuit, a current detection circuit, and a protection control circuit, as depicted in the accompanying diagram. The power circuit includes a power transformer (T), a rectifier diode (VD4), filter capacitors (C4, C5), a current limiting resistor (R8), a Zener diode (VS), and additional components, which are utilized to generate...
The motor protection circuit is designed to safeguard motors from various electrical faults, ensuring reliable operation and longevity. The power supply circuit plays a crucial role in providing stable voltage and current to the entire system. The power transformer (T) steps down the input voltage to a suitable level for the circuit's operation. The rectifier diode (VD4) converts the alternating current (AC) output from the transformer into direct current (DC). Following this, the filter capacitors (C4 and C5) smooth out the rectified DC voltage, reducing ripple and providing a stable power source.
The current detection circuit is essential for monitoring the motor's operating conditions. It typically incorporates a current sensing element, such as a shunt resistor or a Hall effect sensor, to measure the current flowing to the motor. This information is fed into the protection control circuit, which evaluates the current levels against predefined thresholds. If an overcurrent condition is detected, the protection control circuit activates protective measures, such as disconnecting the motor from the power supply to prevent damage.
The current limiting resistor (R8) is included in the power circuit to manage inrush currents during motor startup, ensuring that the initial current draw does not exceed safe levels. The Zener diode (VS) serves as a voltage clamp, protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes that may occur during operation.
In summary, the motor protection circuit integrates these components to create a robust system that not only supplies power to the motor but also actively monitors its operational parameters to prevent damage due to electrical faults. The design emphasizes reliability and safety, making it suitable for various industrial and commercial applications.The motor protection circuit is composed of power supply circuit, current detection circuit and protection control circuit, the circuit is shown as the chart. Power circuit is composed of the power transformer T, rectifier diode VD4, filter capacitors C4, C5, current limiting resistor R8 and Zener diode VS and other components, the circuit is used to generat..
🔗 External reference
The motor protection circuit is designed to safeguard motors from various electrical faults, ensuring reliable operation and longevity. The power supply circuit plays a crucial role in providing stable voltage and current to the entire system. The power transformer (T) steps down the input voltage to a suitable level for the circuit's operation. The rectifier diode (VD4) converts the alternating current (AC) output from the transformer into direct current (DC). Following this, the filter capacitors (C4 and C5) smooth out the rectified DC voltage, reducing ripple and providing a stable power source.
The current detection circuit is essential for monitoring the motor's operating conditions. It typically incorporates a current sensing element, such as a shunt resistor or a Hall effect sensor, to measure the current flowing to the motor. This information is fed into the protection control circuit, which evaluates the current levels against predefined thresholds. If an overcurrent condition is detected, the protection control circuit activates protective measures, such as disconnecting the motor from the power supply to prevent damage.
The current limiting resistor (R8) is included in the power circuit to manage inrush currents during motor startup, ensuring that the initial current draw does not exceed safe levels. The Zener diode (VS) serves as a voltage clamp, protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes that may occur during operation.
In summary, the motor protection circuit integrates these components to create a robust system that not only supplies power to the motor but also actively monitors its operational parameters to prevent damage due to electrical faults. The design emphasizes reliability and safety, making it suitable for various industrial and commercial applications.The motor protection circuit is composed of power supply circuit, current detection circuit and protection control circuit, the circuit is shown as the chart. Power circuit is composed of the power transformer T, rectifier diode VD4, filter capacitors C4, C5, current limiting resistor R8 and Zener diode VS and other components, the circuit is used to generat..
🔗 External reference