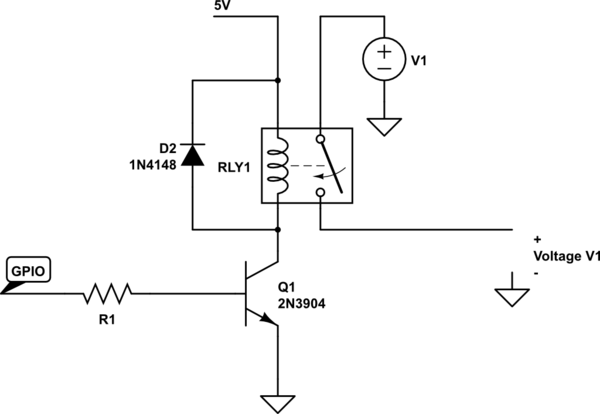
(N + 1) Wires Connect N Hall-Effect Switches
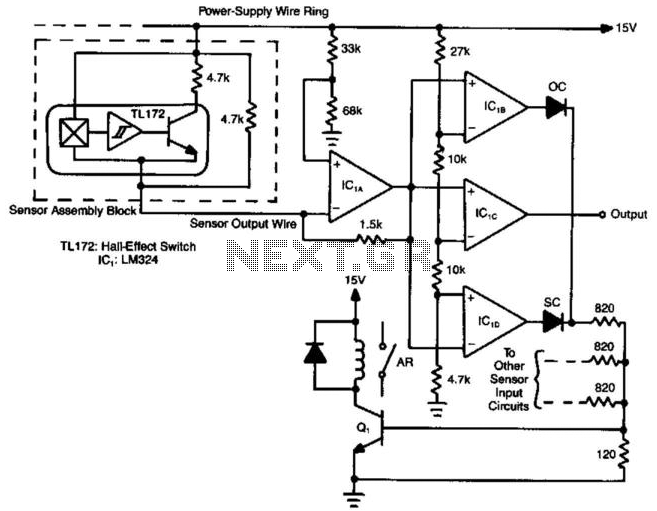
Hall-effect switches offer numerous benefits compared to mechanically and optically coupled switches. However, a significant disadvantage is their requirement for three wires per device. This circuit design reduces the wire count to N+1 wires for N devices. Amplifier IC1A is configured as a current-to-voltage converter that monitors the output current of the sensor assembly. When the Hall-effect switch is activated, the sensor's output current doubles from its quiescent value. Amplifier IC1B is set up as a comparator to detect this increase, and its output transitions to a low state when the Hall-effect switch is engaged. The circuit also incorporates a fault-detection mechanism. If any sensor output wire becomes disconnected, the corresponding LED will illuminate. In the event of a power-supply line interruption, multiple LEDs will activate. Additionally, a short circuit condition will also cause an LED to light up. Each time an LED activates, transistor Q1 is turned on, which triggers the alarm relay.
The circuit utilizes Hall-effect switches for their advantages, such as immunity to dust and moisture, and the absence of mechanical wear. The configuration of IC1A as a current-to-voltage converter is crucial for transforming the sensor output into a usable voltage signal. This setup allows for precise monitoring of the current changes that occur when the Hall-effect switch is actuated. The output from IC1A is fed into IC1B, which is configured as a comparator. This comparator is responsible for comparing the output voltage with a reference voltage. When the output current from the Hall-effect switch increases, indicating activation, IC1B detects this change and provides a low output signal, indicating that the switch is engaged.
The fault-detection feature enhances the reliability of the circuit by providing visual feedback through the use of LEDs. Each LED corresponds to a specific sensor output wire, allowing for easy identification of faults in the system. If a wire becomes open, the associated LED lights up, providing immediate notification of the issue. Similarly, if there is a power failure or short circuit, multiple indicators will activate, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of the circuit.
Transistor Q1 plays a critical role in the alarm system. When an LED is illuminated due to a fault condition, Q1 is activated, which can energize the alarm relay, triggering an alert. This mechanism ensures that any fault conditions are promptly addressed, improving the overall safety and reliability of the system. The design effectively minimizes wiring requirements while maintaining functionality and providing essential fault detection, making it a robust solution for applications utilizing Hall-effect switches. Hall-effect switches have several advantages over mechanically and optically coupled switches. Their major drawback is that they require three wires per device. This circuit, however, reduces this wire count to N+1 wires for devices. Amplifier IC1A is configured as a current-to-voltage converter. It senses the sensor assembly"s output current. When the Hall-effect switch is actuated, the sensor"s output current increases to twice its quiescent value. Amplifier IC1B, configured as a comparator, detects this increase. The comparator"s output goes low when the Hall-effect switch turns on. The circuit also contains a fault-detection function. If any sensor output wire is open, its corresponding LED will turn on. If the power-supply line opens, several LEDs will turn on. A short circuit will also turn an LED on. Every time an LED turns on, Ql turns on and the alarm relay is actuated. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes Hall-effect switches for their advantages, such as immunity to dust and moisture, and the absence of mechanical wear. The configuration of IC1A as a current-to-voltage converter is crucial for transforming the sensor output into a usable voltage signal. This setup allows for precise monitoring of the current changes that occur when the Hall-effect switch is actuated. The output from IC1A is fed into IC1B, which is configured as a comparator. This comparator is responsible for comparing the output voltage with a reference voltage. When the output current from the Hall-effect switch increases, indicating activation, IC1B detects this change and provides a low output signal, indicating that the switch is engaged.
The fault-detection feature enhances the reliability of the circuit by providing visual feedback through the use of LEDs. Each LED corresponds to a specific sensor output wire, allowing for easy identification of faults in the system. If a wire becomes open, the associated LED lights up, providing immediate notification of the issue. Similarly, if there is a power failure or short circuit, multiple indicators will activate, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of the circuit.
Transistor Q1 plays a critical role in the alarm system. When an LED is illuminated due to a fault condition, Q1 is activated, which can energize the alarm relay, triggering an alert. This mechanism ensures that any fault conditions are promptly addressed, improving the overall safety and reliability of the system. The design effectively minimizes wiring requirements while maintaining functionality and providing essential fault detection, making it a robust solution for applications utilizing Hall-effect switches. Hall-effect switches have several advantages over mechanically and optically coupled switches. Their major drawback is that they require three wires per device. This circuit, however, reduces this wire count to N+1 wires for devices. Amplifier IC1A is configured as a current-to-voltage converter. It senses the sensor assembly"s output current. When the Hall-effect switch is actuated, the sensor"s output current increases to twice its quiescent value. Amplifier IC1B, configured as a comparator, detects this increase. The comparator"s output goes low when the Hall-effect switch turns on. The circuit also contains a fault-detection function. If any sensor output wire is open, its corresponding LED will turn on. If the power-supply line opens, several LEDs will turn on. A short circuit will also turn an LED on. Every time an LED turns on, Ql turns on and the alarm relay is actuated. 🔗 External reference