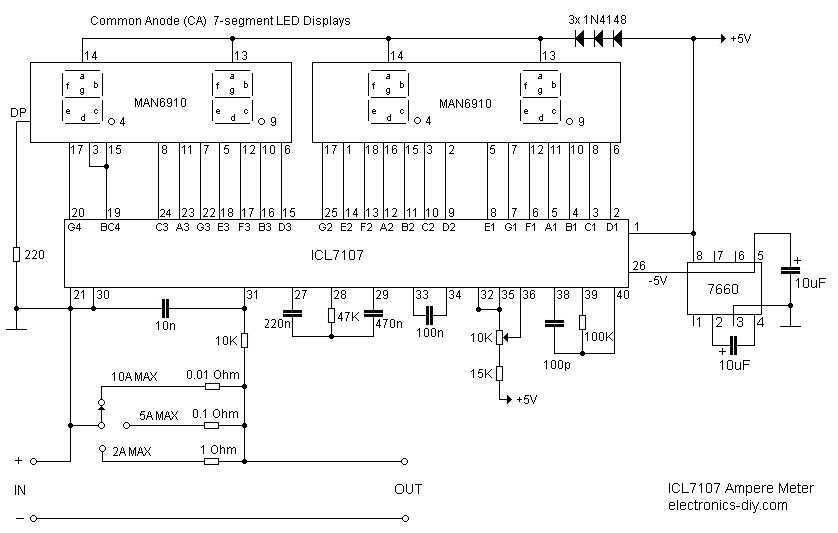
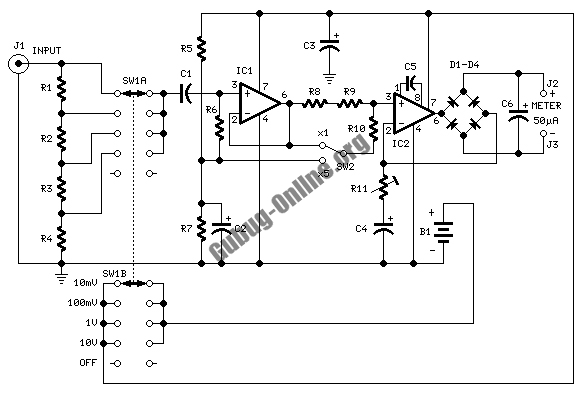
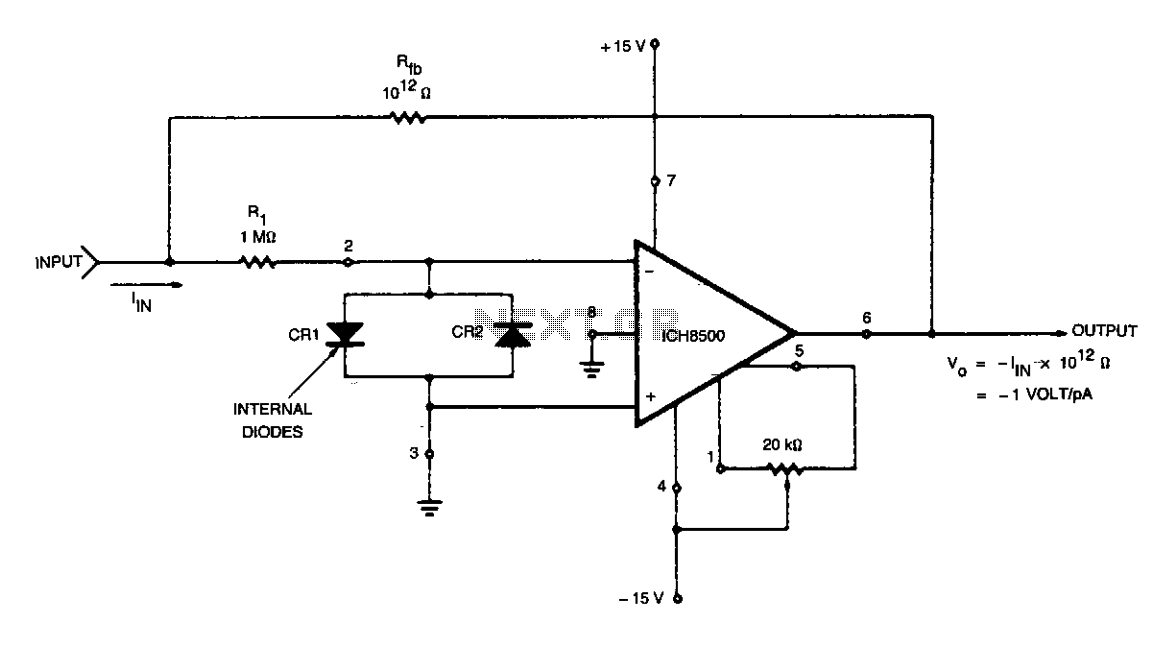
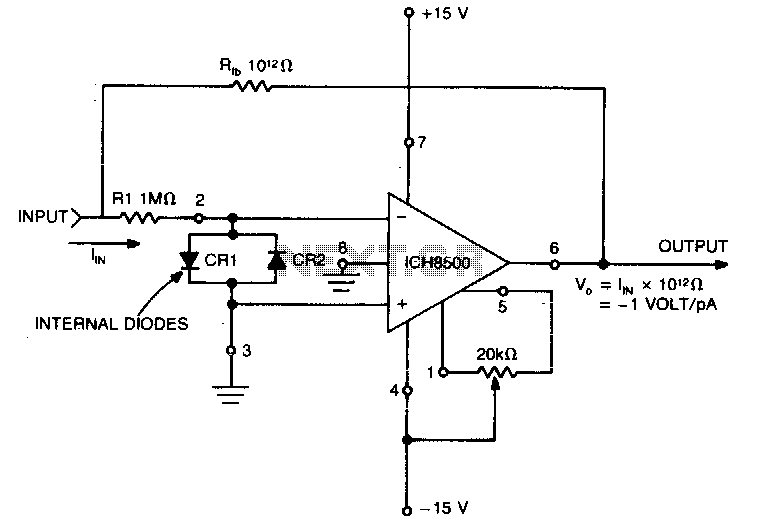
Nano ammeter
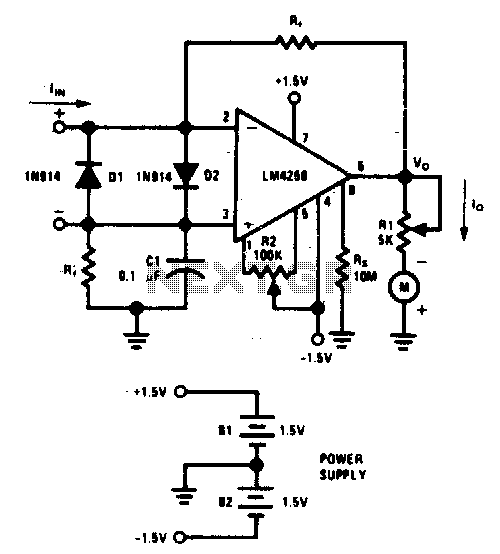
The complete meter amplifier is a differential current-to-voltage converter featuring input protection, zeroing, and full-scale adjustment provisions, along with input resistor balancing to minimize offset voltage.
The complete meter amplifier serves as a crucial component in various electronic measurement applications, functioning as a differential current-to-voltage converter. This device is designed to accurately convert differential input currents into a proportional voltage output, thereby facilitating precise signal processing.
Input protection is a key feature of the meter amplifier, safeguarding the internal circuitry from potential over-voltage or over-current conditions that could lead to damage. This protection ensures the longevity and reliability of the device in diverse operating environments.
The zeroing function allows for the adjustment of the output voltage to zero when no input current is present. This capability is essential for calibrating the meter amplifier, ensuring that any subsequent measurements are accurate and reliable.
Full-scale adjustment provisions enable the user to set the maximum output voltage corresponding to the maximum input current. This flexibility is vital for adapting the amplifier to various measurement ranges, enhancing its versatility in different applications.
Input resistor balancing is implemented to minimize offset voltage, which is the unintended voltage present at the output when the input is zero. By carefully selecting and matching input resistors, the meter amplifier can achieve a significantly reduced offset voltage, improving measurement accuracy and overall performance.
In summary, the complete meter amplifier integrates essential features such as input protection, zeroing, full-scale adjustment, and input resistor balancing, making it an indispensable tool in the realm of electronic measurement and signal processing.The complete meter amplifier is a differential current-to-voltage converter with input protection, zeroing and full scale adjust provisions and input resistor balancing for minimum offset voltage.
The complete meter amplifier serves as a crucial component in various electronic measurement applications, functioning as a differential current-to-voltage converter. This device is designed to accurately convert differential input currents into a proportional voltage output, thereby facilitating precise signal processing.
Input protection is a key feature of the meter amplifier, safeguarding the internal circuitry from potential over-voltage or over-current conditions that could lead to damage. This protection ensures the longevity and reliability of the device in diverse operating environments.
The zeroing function allows for the adjustment of the output voltage to zero when no input current is present. This capability is essential for calibrating the meter amplifier, ensuring that any subsequent measurements are accurate and reliable.
Full-scale adjustment provisions enable the user to set the maximum output voltage corresponding to the maximum input current. This flexibility is vital for adapting the amplifier to various measurement ranges, enhancing its versatility in different applications.
Input resistor balancing is implemented to minimize offset voltage, which is the unintended voltage present at the output when the input is zero. By carefully selecting and matching input resistors, the meter amplifier can achieve a significantly reduced offset voltage, improving measurement accuracy and overall performance.
In summary, the complete meter amplifier integrates essential features such as input protection, zeroing, full-scale adjustment, and input resistor balancing, making it an indispensable tool in the realm of electronic measurement and signal processing.The complete meter amplifier is a differential current-to-voltage converter with input protection, zeroing and full scale adjust provisions and input resistor balancing for minimum offset voltage.