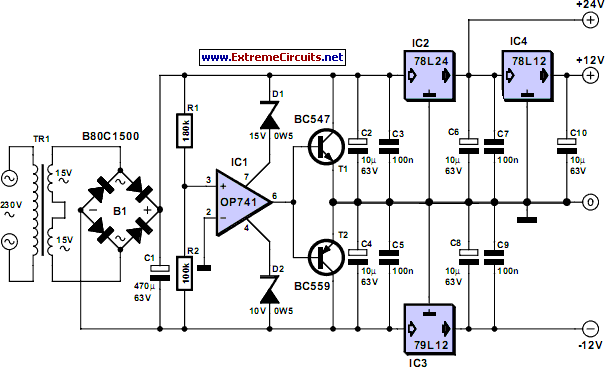
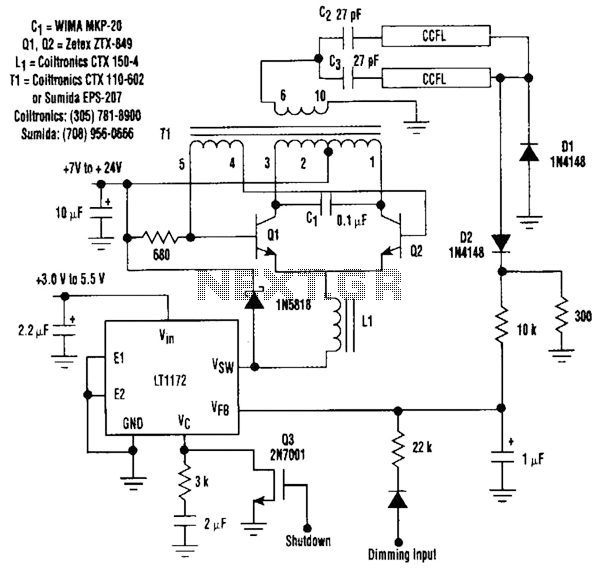
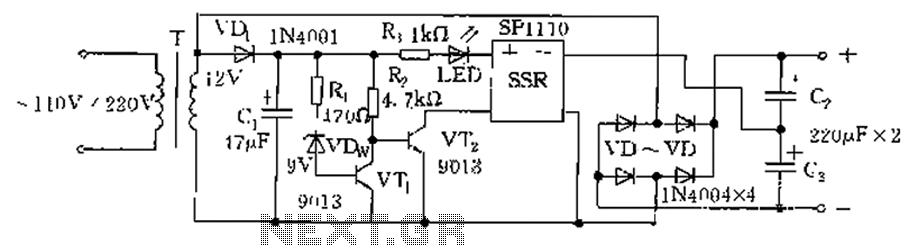
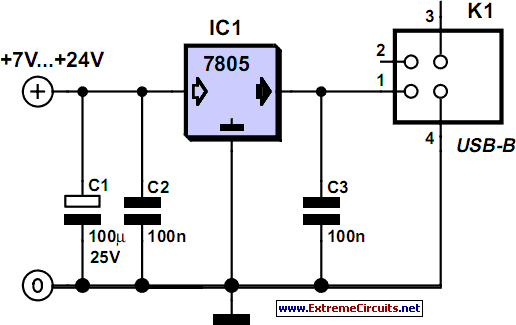
Negative Voltage From A Positive Supply

By utilizing a 555 timer to produce a square wave and employing a voltage-doubling technique on the output, a negative voltage that is nearly equivalent to the positive supply can be achieved. The available current ranges from 20 to 30 mA, depending on the required regulation and voltage specifications.
The circuit employs a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. The frequency of the square wave can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer. The output from the 555 timer is then fed into a voltage-doubling circuit, typically composed of diodes and capacitors arranged in a charge pump configuration.
In the voltage-doubling stage, the positive half of the square wave charges a capacitor through a diode, while during the negative half, the charged capacitor is connected in series with the input voltage, effectively doubling the voltage across the load. This setup allows for the generation of a negative voltage that is close to the magnitude of the positive supply voltage.
The output current capability of the circuit, which can reach between 20 to 30 mA, is influenced by factors such as the load resistance, the efficiency of the voltage-doubling circuit, and the specifications of the components used. Proper selection of the capacitors and diodes is crucial to optimize performance and ensure that the current output meets the desired requirements for the application. Additionally, filtering may be required to reduce ripple voltage and stabilize the output voltage for sensitive applications. By using a 555 timer to generate a square wave and voltage-doubling the output, a negative voltage that is almost equal to the positive supply can be obtained. The current available is up to 20 to 30 mA or so, depending on the regulation and voltage needed. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave output. The frequency of the square wave can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer. The output from the 555 timer is then fed into a voltage-doubling circuit, typically composed of diodes and capacitors arranged in a charge pump configuration.
In the voltage-doubling stage, the positive half of the square wave charges a capacitor through a diode, while during the negative half, the charged capacitor is connected in series with the input voltage, effectively doubling the voltage across the load. This setup allows for the generation of a negative voltage that is close to the magnitude of the positive supply voltage.
The output current capability of the circuit, which can reach between 20 to 30 mA, is influenced by factors such as the load resistance, the efficiency of the voltage-doubling circuit, and the specifications of the components used. Proper selection of the capacitors and diodes is crucial to optimize performance and ensure that the current output meets the desired requirements for the application. Additionally, filtering may be required to reduce ripple voltage and stabilize the output voltage for sensitive applications. By using a 555 timer to generate a square wave and voltage-doubling the output, a negative voltage that is almost equal to the positive supply can be obtained. The current available is up to 20 to 30 mA or so, depending on the regulation and voltage needed. 🔗 External reference