Undervoltage delay tripping a circuit
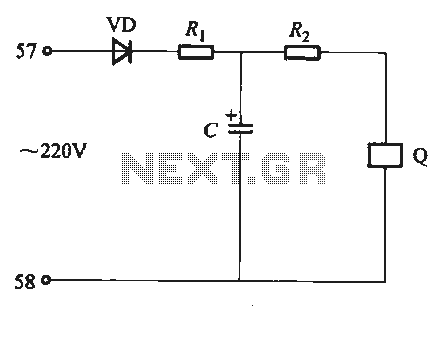
Undervoltage release operates over an extended period. When the power supply voltage drops within the operating voltage range, it triggers the release mechanism, resulting in the rotation of the tripping axle and the disconnection of the circuit breaker. There are two types of undervoltage release: instantaneous tripping and tripping delay. The delay trip can be achieved in two ways: one utilizes an electronic trip unit, while the other employs a resistive-capacitive delay release. In the latter configuration, the undervoltage release coil (denoted as Q) is connected to an adjustable capacitor (C) and a resistor (Ri), where the parameter values of R2 can be modified to alter the delay time.
Undervoltage release mechanisms are essential for protecting electrical circuits from damage caused by prolonged low voltage conditions. The operation principle is based on monitoring the supply voltage and activating a release mechanism when the voltage falls below a predetermined threshold. This is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
In the case of instantaneous tripping, the circuit breaker disconnects immediately upon detection of undervoltage, minimizing the risk of equipment damage. On the other hand, the tripping delay feature allows for temporary voltage fluctuations without immediate disconnection, which can be beneficial in scenarios where brief dips in voltage are common.
The electronic trip unit typically incorporates microcontroller-based technology that continuously monitors the voltage levels and can provide precise control over the tripping characteristics. This allows for programmable settings based on specific application requirements.
In contrast, the resistive-capacitive delay release circuit employs passive components to achieve the desired delay. The resistor (Ri) and capacitor (C) form an RC time constant that determines how quickly the circuit responds to undervoltage conditions. By adjusting the values of these components, the delay time can be fine-tuned to suit the needs of the application. The coil (Q) activates the tripping mechanism when the voltage across the capacitor drops below a certain level, effectively cutting off the breaker and protecting the circuit.
Overall, understanding the functionality and configuration of undervoltage release systems is crucial for electrical engineers and technicians involved in the design and maintenance of reliable power distribution systems.Undervoltage release is long-term work, when the power supply voltage drop in the operating voltage range when the release is released, and directly led to the tripping axle rotation, cut off the breaker. Undervoltage release Instantaneous tripping points and tripping delay two species. Which reached the undervoltage delay trip there two ways kinds: one is the electronic trip unit (see Figure 6-81); the other one is the resistive capacitive delay release, the line shown in Figure 6-84 FIG. FIG, Q is undervoltage release coil. Adjustment capacitor C and a resistor Ri, the parameter value of R2, can change the delay time.
Undervoltage release mechanisms are essential for protecting electrical circuits from damage caused by prolonged low voltage conditions. The operation principle is based on monitoring the supply voltage and activating a release mechanism when the voltage falls below a predetermined threshold. This is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
In the case of instantaneous tripping, the circuit breaker disconnects immediately upon detection of undervoltage, minimizing the risk of equipment damage. On the other hand, the tripping delay feature allows for temporary voltage fluctuations without immediate disconnection, which can be beneficial in scenarios where brief dips in voltage are common.
The electronic trip unit typically incorporates microcontroller-based technology that continuously monitors the voltage levels and can provide precise control over the tripping characteristics. This allows for programmable settings based on specific application requirements.
In contrast, the resistive-capacitive delay release circuit employs passive components to achieve the desired delay. The resistor (Ri) and capacitor (C) form an RC time constant that determines how quickly the circuit responds to undervoltage conditions. By adjusting the values of these components, the delay time can be fine-tuned to suit the needs of the application. The coil (Q) activates the tripping mechanism when the voltage across the capacitor drops below a certain level, effectively cutting off the breaker and protecting the circuit.
Overall, understanding the functionality and configuration of undervoltage release systems is crucial for electrical engineers and technicians involved in the design and maintenance of reliable power distribution systems.Undervoltage release is long-term work, when the power supply voltage drop in the operating voltage range when the release is released, and directly led to the tripping axle rotation, cut off the breaker. Undervoltage release Instantaneous tripping points and tripping delay two species. Which reached the undervoltage delay trip there two ways kinds: one is the electronic trip unit (see Figure 6-81); the other one is the resistive capacitive delay release, the line shown in Figure 6-84 FIG. FIG, Q is undervoltage release coil. Adjustment capacitor C and a resistor Ri, the parameter value of R2, can change the delay time.