nimh charger circuit diagram
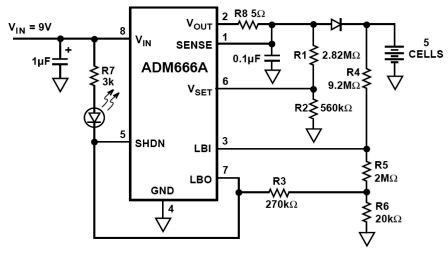
NiMH charger circuit diagram using ADM66A. Related searches include charger circuit, NiMH charger circuit, lead acid battery charger circuit, LiPo charger circuit, automatic battery charger circuit, simple battery charger circuit, lithium battery charger circuit, charger circuit diagram, and 12V charger circuit.
The NiMH charger circuit employing the ADM66A is designed to efficiently charge nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. The ADM66A is a dedicated battery charger IC that offers features such as constant current charging and automatic cut-off when the battery reaches full charge, ensuring safety and longevity of the battery.
The circuit typically consists of an input power supply, which provides the necessary voltage and current to the ADM66A. The input voltage is often regulated to a specific level, ensuring that the IC operates within its optimal range. A rectifier may be included to convert AC voltage to DC if an AC source is used.
The ADM66A controls the charging process by regulating the output current supplied to the battery. It incorporates a feedback mechanism to monitor the battery voltage and adjust the charging current accordingly. This is crucial for preventing overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Additional components in the circuit may include resistors for current sensing, capacitors for stabilizing voltage, and diodes for protecting against reverse polarity. An LED indicator can also be integrated to signal the charging status, providing visual feedback to the user.
For enhanced functionality, the circuit can be designed with additional features such as temperature monitoring to prevent overheating, or a microcontroller interface for programmable charging profiles. This flexibility allows the charger to accommodate various battery chemistries and capacities, making it a versatile solution for battery management.
Overall, the NiMH charger circuit with the ADM66A provides a reliable and efficient means of charging NiMH batteries, suitable for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.NiMH CHARGER Circuit diagram using ADM66A Searches related to CHARGER Circuit, nimh charger circuit, lead acid battery charger circuit, lipo charger circuit, automatic battery charger circuit, simple battery charger circuit, lithium battery charger circuit, charger circuit diagram, charger circuit 12v.. 🔗 External reference
The NiMH charger circuit employing the ADM66A is designed to efficiently charge nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. The ADM66A is a dedicated battery charger IC that offers features such as constant current charging and automatic cut-off when the battery reaches full charge, ensuring safety and longevity of the battery.
The circuit typically consists of an input power supply, which provides the necessary voltage and current to the ADM66A. The input voltage is often regulated to a specific level, ensuring that the IC operates within its optimal range. A rectifier may be included to convert AC voltage to DC if an AC source is used.
The ADM66A controls the charging process by regulating the output current supplied to the battery. It incorporates a feedback mechanism to monitor the battery voltage and adjust the charging current accordingly. This is crucial for preventing overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Additional components in the circuit may include resistors for current sensing, capacitors for stabilizing voltage, and diodes for protecting against reverse polarity. An LED indicator can also be integrated to signal the charging status, providing visual feedback to the user.
For enhanced functionality, the circuit can be designed with additional features such as temperature monitoring to prevent overheating, or a microcontroller interface for programmable charging profiles. This flexibility allows the charger to accommodate various battery chemistries and capacities, making it a versatile solution for battery management.
Overall, the NiMH charger circuit with the ADM66A provides a reliable and efficient means of charging NiMH batteries, suitable for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.NiMH CHARGER Circuit diagram using ADM66A Searches related to CHARGER Circuit, nimh charger circuit, lead acid battery charger circuit, lipo charger circuit, automatic battery charger circuit, simple battery charger circuit, lithium battery charger circuit, charger circuit diagram, charger circuit 12v.. 🔗 External reference