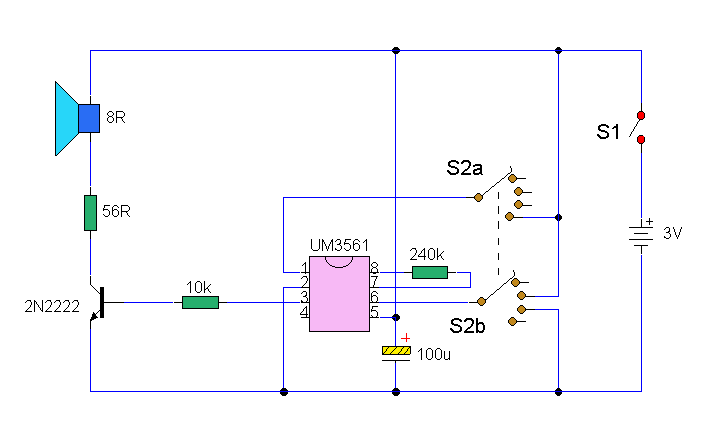
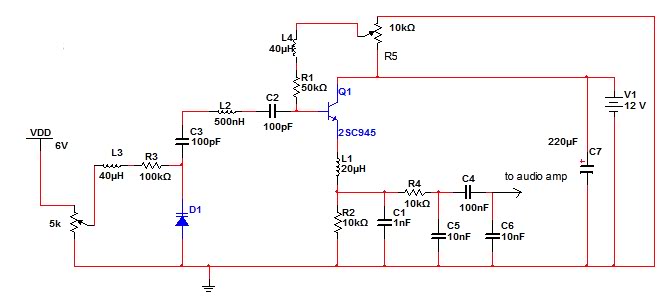
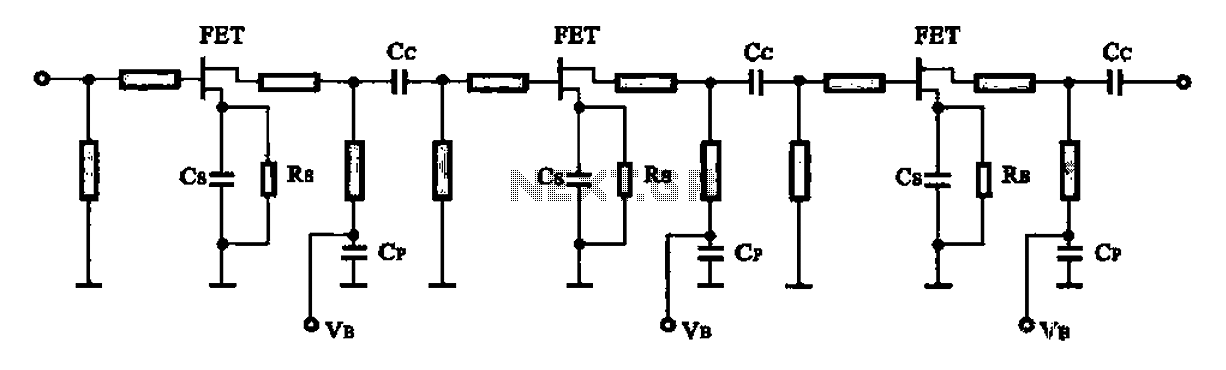
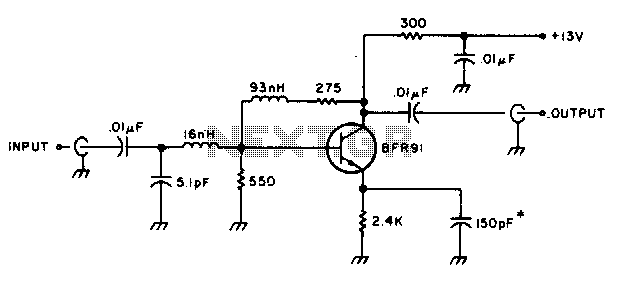
Noise Generators
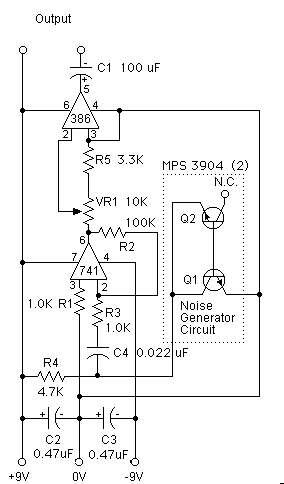
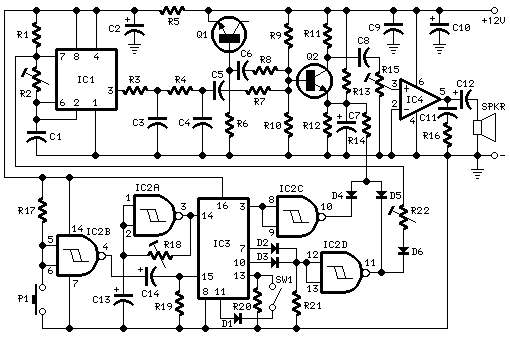
This circuit is effective for testing audio circuits using broadband noise. It employs three inexpensive C-MOS integrated circuits (ICs) that produce a series of output pulses with randomly varying widths. The audio noise generator is designed to drive earphones or a small speaker, generating white noise that is rolled off to suit these applications. The resulting sound resembles a "rushing" noise, akin to air flowing past the ears. While white noise is typically flat across frequencies, this circuit's design incorporates a roll-off within the audio range, hence the term "rolled-off" noise.
The audio noise generator circuit utilizes three C-MOS ICs, which are known for their low power consumption and high noise immunity. The first IC functions as a pulse generator, producing a continuous stream of pulses. The pulse width modulation is achieved through a combination of resistors and capacitors that determine the timing characteristics, resulting in a random variation of pulse widths. This randomness is crucial for simulating white noise, as it mimics the broad frequency spectrum characteristic of such noise.
The second IC serves as an amplifier, boosting the signal generated by the pulse generator to a suitable level for driving output devices. The amplifier stage is designed to ensure that the output maintains fidelity, allowing the generated noise to be accurately reproduced by the earphones or small speaker. Capacitive coupling may be employed at this stage to block any DC offset, ensuring only the AC component of the signal is passed to the output.
The final IC in the circuit may be configured as a low-pass filter, which rolls off the high frequencies above a certain cutoff point. This filtering is essential to tailor the noise output to the desired characteristics, making it suitable for audio testing applications. The roll-off can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the testing scenario.
In summary, this circuit is a practical and effective solution for generating rolled-off white noise, making it an invaluable tool for audio circuit testing and evaluation. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make it an excellent choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.When you need to test an audio circuit with broadband noise, this circuit works great. It uses just three inexpensive C-MOS ICs that generate a series of output pulses whose widths vary randomly. Audio noise generator drives earphones or small speaker - This is a circuit that generates white noise, rolled-
off to drive earphones or a small speaker. White noise creates is a "rushing" sound, which sounds something like air rushing by your ear(s). White noise would be flat with frequency, and since this circuit rolls off within the audio range, I refer to it as "rolled-off" noise. White (or rolled-off) noise. 🔗 External reference
The audio noise generator circuit utilizes three C-MOS ICs, which are known for their low power consumption and high noise immunity. The first IC functions as a pulse generator, producing a continuous stream of pulses. The pulse width modulation is achieved through a combination of resistors and capacitors that determine the timing characteristics, resulting in a random variation of pulse widths. This randomness is crucial for simulating white noise, as it mimics the broad frequency spectrum characteristic of such noise.
The second IC serves as an amplifier, boosting the signal generated by the pulse generator to a suitable level for driving output devices. The amplifier stage is designed to ensure that the output maintains fidelity, allowing the generated noise to be accurately reproduced by the earphones or small speaker. Capacitive coupling may be employed at this stage to block any DC offset, ensuring only the AC component of the signal is passed to the output.
The final IC in the circuit may be configured as a low-pass filter, which rolls off the high frequencies above a certain cutoff point. This filtering is essential to tailor the noise output to the desired characteristics, making it suitable for audio testing applications. The roll-off can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values, allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the testing scenario.
In summary, this circuit is a practical and effective solution for generating rolled-off white noise, making it an invaluable tool for audio circuit testing and evaluation. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make it an excellent choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.When you need to test an audio circuit with broadband noise, this circuit works great. It uses just three inexpensive C-MOS ICs that generate a series of output pulses whose widths vary randomly. Audio noise generator drives earphones or small speaker - This is a circuit that generates white noise, rolled-
off to drive earphones or a small speaker. White noise creates is a "rushing" sound, which sounds something like air rushing by your ear(s). White noise would be flat with frequency, and since this circuit rolls off within the audio range, I refer to it as "rolled-off" noise. White (or rolled-off) noise. 🔗 External reference