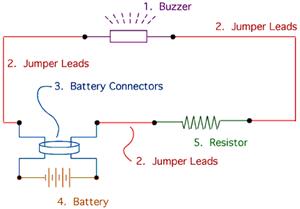
Novel Buzzer
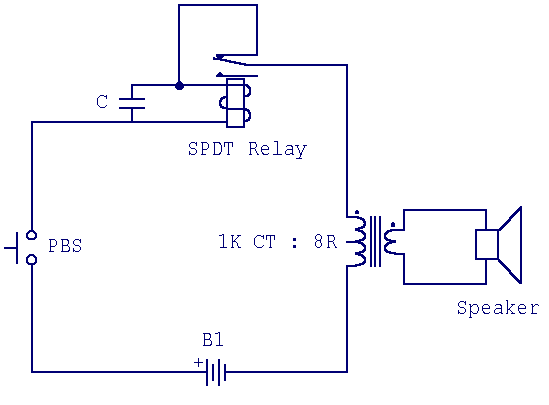
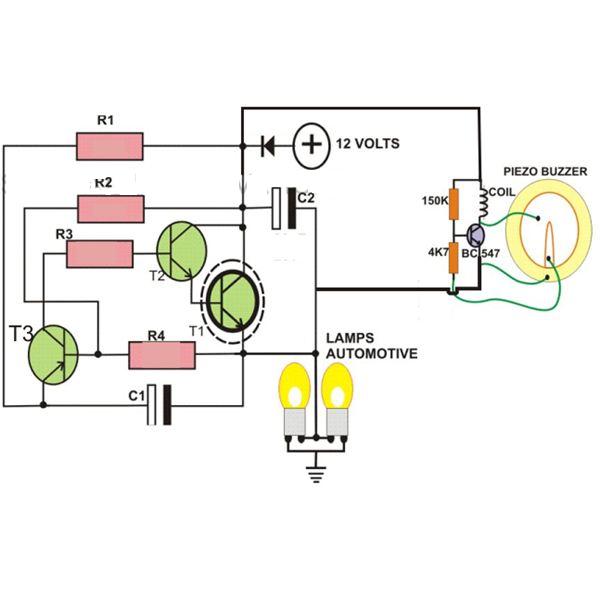
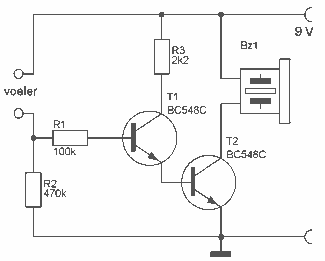
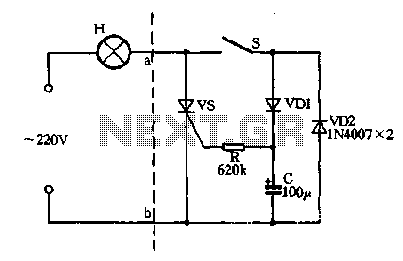
This novel buzzer circuit uses a relay in series with a small audio transformer and speaker. When the switch is pressed, the relay will operate via the transformer primary and closed relay contact. As soon as the relay operates the normally closed contact will open, removing power from the relay, the contacts close and the sequence repeats, all very quickly...so fast that the pulse of current causes fluctuations in the transformer primary, and hence secondary.
The described buzzer circuit operates on a principle of rapid relay actuation to produce sound. The circuit comprises a switch, a relay, an audio transformer, and a speaker. When the switch is engaged, it energizes the relay coil, allowing current to flow through the primary winding of the audio transformer. This action closes the relay's normally closed (NC) contact, which maintains power to the relay.
Once the relay is energized, the NC contact opens, interrupting the power supply to the relay coil. This interruption causes the relay to de-energize, which in turn closes the contact again, reapplying power to the relay. This rapid cycling occurs in quick succession, creating a pulsed output at the transformer secondary. The audio transformer converts these pulses into audible sound waves through the connected speaker.
Key components in this circuit include:
1. **Relay**: Acts as a switch that opens and closes rapidly to create the buzzing sound. The relay should be rated appropriately for the voltage and current requirements of the circuit.
2. **Audio Transformer**: Serves to amplify the voltage and current from the relay to the speaker. The transformer should be selected based on the desired frequency response and power handling capability.
3. **Speaker**: Converts electrical signals into sound. The impedance of the speaker should match the output characteristics of the transformer to ensure optimal performance.
4. **Switch**: Initiates the operation of the circuit. A momentary push button switch is typically used to start the buzzing action.
This circuit design can be utilized in various applications, such as alarms, indicators, or novelty sound effects, where a simple and effective sound generation mechanism is required.This novel buzzer circuit uses a relay in series with a small audio transformer and speaker. When the switch is pressed, the relay will operate via the transformer primary and closed relay contact. As soon as the relay operates the normally closed contact will open, removing power from the relay, the contacts close and the sequence repeats, all very quickly...so fast that the pulse of current causes fluctuations in the transformer primary, and hence secondary.
🔗 External reference
The described buzzer circuit operates on a principle of rapid relay actuation to produce sound. The circuit comprises a switch, a relay, an audio transformer, and a speaker. When the switch is engaged, it energizes the relay coil, allowing current to flow through the primary winding of the audio transformer. This action closes the relay's normally closed (NC) contact, which maintains power to the relay.
Once the relay is energized, the NC contact opens, interrupting the power supply to the relay coil. This interruption causes the relay to de-energize, which in turn closes the contact again, reapplying power to the relay. This rapid cycling occurs in quick succession, creating a pulsed output at the transformer secondary. The audio transformer converts these pulses into audible sound waves through the connected speaker.
Key components in this circuit include:
1. **Relay**: Acts as a switch that opens and closes rapidly to create the buzzing sound. The relay should be rated appropriately for the voltage and current requirements of the circuit.
2. **Audio Transformer**: Serves to amplify the voltage and current from the relay to the speaker. The transformer should be selected based on the desired frequency response and power handling capability.
3. **Speaker**: Converts electrical signals into sound. The impedance of the speaker should match the output characteristics of the transformer to ensure optimal performance.
4. **Switch**: Initiates the operation of the circuit. A momentary push button switch is typically used to start the buzzing action.
This circuit design can be utilized in various applications, such as alarms, indicators, or novelty sound effects, where a simple and effective sound generation mechanism is required.This novel buzzer circuit uses a relay in series with a small audio transformer and speaker. When the switch is pressed, the relay will operate via the transformer primary and closed relay contact. As soon as the relay operates the normally closed contact will open, removing power from the relay, the contacts close and the sequence repeats, all very quickly...so fast that the pulse of current causes fluctuations in the transformer primary, and hence secondary.
🔗 External reference