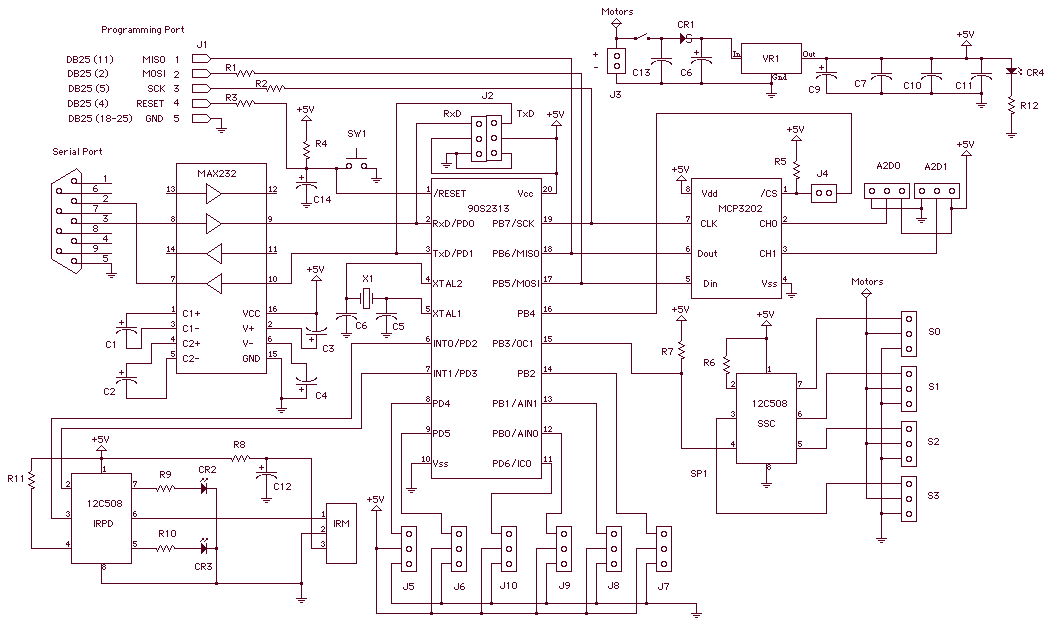
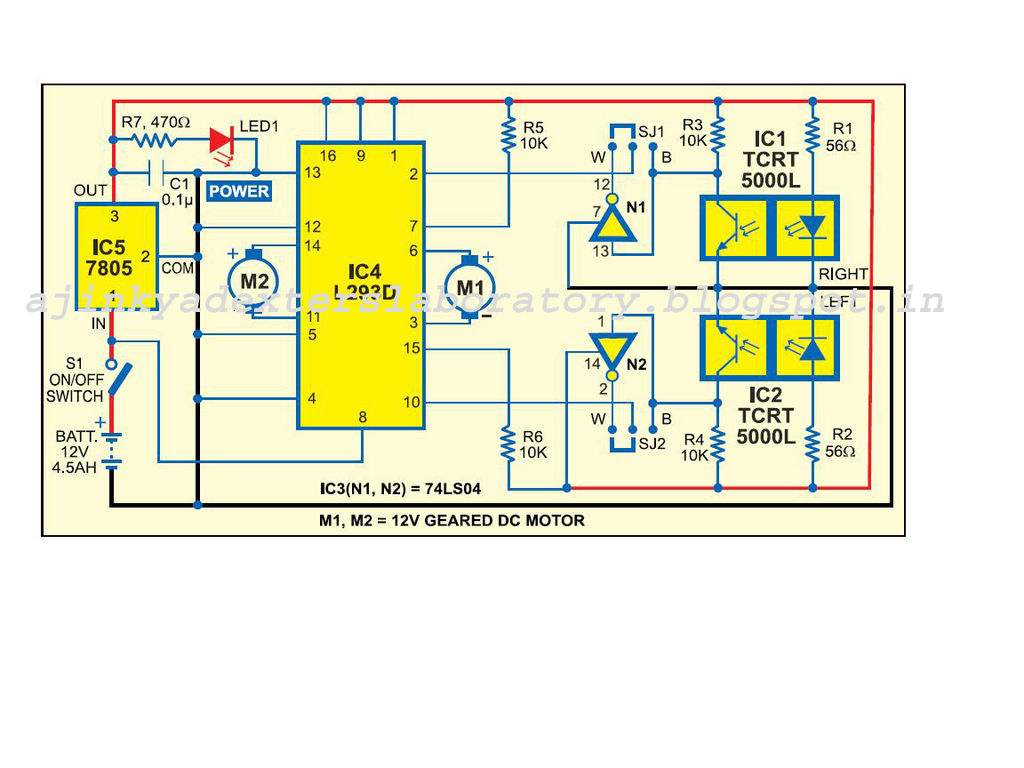
Obstacle Avoiding Robot without microcontroller
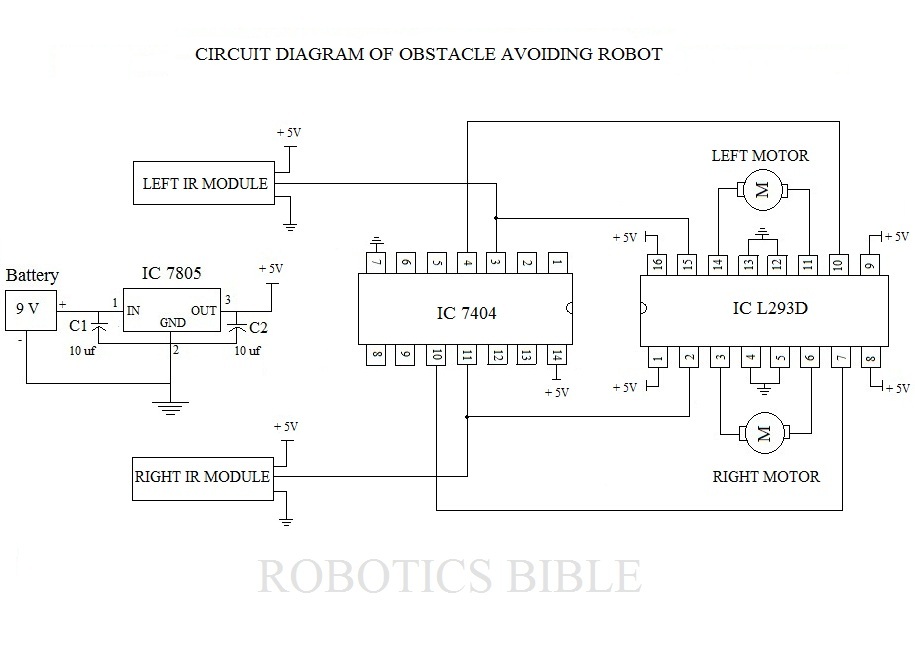
An obstacle-avoiding robot is an intelligent device that can automatically sense and navigate around obstacles in its path. It is designed without a microcontroller to simplify the circuitry and programming requirements. Understanding the circuit diagram is essential for constructing this robot. This straightforward technique can be applied to wheeled robots to prevent damage and accidents. The required components are readily available in electronics markets and are relatively inexpensive. The circuit diagram of the obstacle-avoiding robot is provided for reference. For those new to robotics, step-by-step instructions for making the connections are outlined below. Begin by connecting the positive supply from the battery holder to the IN pin of the IC 7805 and the negative supply to the last row of the breadboard. After completing the assembly, connect a 9V battery using a battery snap and observe the robot in operation. It will automatically navigate an unstructured path without colliding with objects. When the left infrared (IR) module detects an obstacle, the robot will turn right until the obstacle is no longer detected. Conversely, if the right IR module senses an obstacle, the robot will turn left. If both sensors detect obstacles, the robot will stop moving. While the concept of building an obstacle-avoiding robot is straightforward, challenges may arise during implementation. Overall, the provided information is sufficient to construct this intelligent robot, which can be developed for approximately $40 USD. Inquiries related to the project are welcome.
The obstacle-avoiding robot operates using a combination of sensors and simple electronic components. The primary components include infrared (IR) sensors, a motor driver IC, and a power supply. The IR sensors are positioned at the front of the robot to detect obstacles by emitting infrared light and measuring the reflection. When an object is detected, the corresponding sensor sends a signal to the motor driver IC, which controls the direction of the motors connected to the wheels.
The circuit is powered by a 9V battery, which is regulated down to 5V using an IC 7805 voltage regulator to supply the necessary voltage for the sensors and the motor driver. The motor driver IC allows for bidirectional control of the motors, enabling the robot to turn left or right based on sensor input. The assembly of components on a breadboard facilitates easy modifications and troubleshooting.
The robot's functionality can be tested in various environments, including indoor and outdoor settings, to assess its ability to navigate around different types of obstacles. Adjustments to the sensitivity of the IR sensors can be made to improve performance in diverse conditions. The design encourages experimentation, allowing users to explore additional features such as speed control or the addition of more sensors for enhanced obstacle detection.
In summary, the obstacle-avoiding robot serves as an excellent introduction to robotics, combining basic electronic principles with practical application. The project is accessible to beginners and provides a foundation for further exploration in the field of robotics.An obstacle avoiding robot is an intelligent device, which can automatically sense and overcome obstacles on its path. It is developed without micro-controller in order to eliminate critical circuits, difficult programming etc.
All you want to do is to just understand the circuit diagram and start doing this robot. This simple technique can be inc orporated in wheeled robots to keep them away from damages and accidents. This intelligent robot requires several components to bring them alive. Itdoesn`tcost too much, and easily available in all electronics markets as well. Thecircuit diagramof obstacle avoiding robot is shown in the above picture. It could utmost help you to develop this robot with ease. In case, if you are new to robotics, observe the followingstep by step instructionsof all connections given below. Take the positive supply from battery holder via breadboard wire and place it in IN of IC 7805, and also connect its negative supply in last row of breadboard.
After finishing the assembling work, connect the 9V battery via battery snap. Then, see what happens. The robot will automatically start traveling on the unstructured path without hitting any objects. When the left IR module senses any obstacles on its way, it will turn right till it stops sensing. Similarly, it will turn left when the right IR module senses obstacles. If both the sensors sense an obstacle, then the robot will stop moving. The concept of developing an Obstacle Avoiding Robot may be simple, but you may meet some obstacles in implementing it. Overall, I feel the above details are well-enough to complete this intelligent robot. It will cost approximately $40 U S Dollars to develop one. You can try it in your free time, and any quires related to it are most welcomed. 🔗 External reference
The obstacle-avoiding robot operates using a combination of sensors and simple electronic components. The primary components include infrared (IR) sensors, a motor driver IC, and a power supply. The IR sensors are positioned at the front of the robot to detect obstacles by emitting infrared light and measuring the reflection. When an object is detected, the corresponding sensor sends a signal to the motor driver IC, which controls the direction of the motors connected to the wheels.
The circuit is powered by a 9V battery, which is regulated down to 5V using an IC 7805 voltage regulator to supply the necessary voltage for the sensors and the motor driver. The motor driver IC allows for bidirectional control of the motors, enabling the robot to turn left or right based on sensor input. The assembly of components on a breadboard facilitates easy modifications and troubleshooting.
The robot's functionality can be tested in various environments, including indoor and outdoor settings, to assess its ability to navigate around different types of obstacles. Adjustments to the sensitivity of the IR sensors can be made to improve performance in diverse conditions. The design encourages experimentation, allowing users to explore additional features such as speed control or the addition of more sensors for enhanced obstacle detection.
In summary, the obstacle-avoiding robot serves as an excellent introduction to robotics, combining basic electronic principles with practical application. The project is accessible to beginners and provides a foundation for further exploration in the field of robotics.An obstacle avoiding robot is an intelligent device, which can automatically sense and overcome obstacles on its path. It is developed without micro-controller in order to eliminate critical circuits, difficult programming etc.
All you want to do is to just understand the circuit diagram and start doing this robot. This simple technique can be inc orporated in wheeled robots to keep them away from damages and accidents. This intelligent robot requires several components to bring them alive. Itdoesn`tcost too much, and easily available in all electronics markets as well. Thecircuit diagramof obstacle avoiding robot is shown in the above picture. It could utmost help you to develop this robot with ease. In case, if you are new to robotics, observe the followingstep by step instructionsof all connections given below. Take the positive supply from battery holder via breadboard wire and place it in IN of IC 7805, and also connect its negative supply in last row of breadboard.
After finishing the assembling work, connect the 9V battery via battery snap. Then, see what happens. The robot will automatically start traveling on the unstructured path without hitting any objects. When the left IR module senses any obstacles on its way, it will turn right till it stops sensing. Similarly, it will turn left when the right IR module senses obstacles. If both the sensors sense an obstacle, then the robot will stop moving. The concept of developing an Obstacle Avoiding Robot may be simple, but you may meet some obstacles in implementing it. Overall, I feel the above details are well-enough to complete this intelligent robot. It will cost approximately $40 U S Dollars to develop one. You can try it in your free time, and any quires related to it are most welcomed. 🔗 External reference