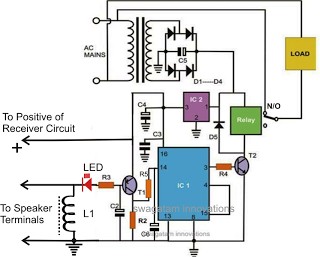
On-off Infrared Remote Control
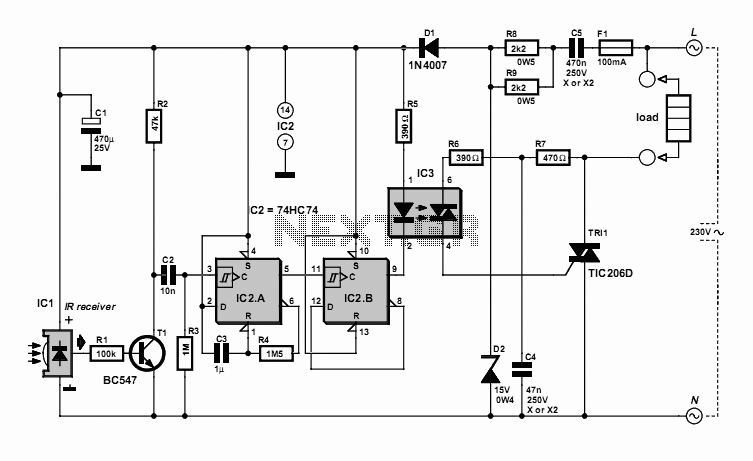
On-off Infrared Remote Control Circuit. Most homes today have at least a few infrared remote controls, whether they are for the television, video recorder, stereo, etc. Despite this, who among us has not cursed the limitations of these devices?
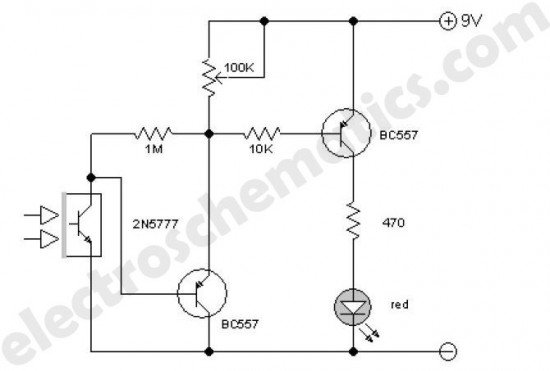
The on-off infrared remote control circuit is designed to allow users to wirelessly control electronic devices from a distance using infrared (IR) signals. This circuit typically consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter includes an infrared LED that emits modulated light signals corresponding to specific commands, while the receiver is equipped with a photodiode or phototransistor that detects these signals.
The circuit operates by converting the user's input commands into a series of binary signals, which are then transmitted as infrared light pulses. The modulation of the IR signals ensures that the receiver can differentiate between different commands, allowing for precise control over the connected devices.
In a typical application, the transmitter circuit may include a microcontroller to process button presses from a keypad or interface. This microcontroller generates the appropriate pulse-width modulation (PWM) output to drive the IR LED. The receiver circuit, on the other hand, is usually connected to a microcontroller or a simple relay driver circuit that interprets the received signals and activates the corresponding output, such as turning a device on or off.
For enhanced functionality, additional components such as capacitors, resistors, and diodes may be integrated into the circuit to filter noise and stabilize the operation. The power supply for both the transmitter and receiver can be provided by batteries or an external power source, depending on the design requirements.
Overall, the on-off infrared remote control circuit exemplifies a practical application of infrared technology in consumer electronics, providing convenience and ease of use in everyday devices.On-off Infrared Remote Control Circuit Most homes today have at least a few infrared remote controls, whether they be for the television, the video recorder, the stereo, etc. Despite that fact, who among us has not cursed the li.. 🔗 External reference
The on-off infrared remote control circuit is designed to allow users to wirelessly control electronic devices from a distance using infrared (IR) signals. This circuit typically consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter includes an infrared LED that emits modulated light signals corresponding to specific commands, while the receiver is equipped with a photodiode or phototransistor that detects these signals.
The circuit operates by converting the user's input commands into a series of binary signals, which are then transmitted as infrared light pulses. The modulation of the IR signals ensures that the receiver can differentiate between different commands, allowing for precise control over the connected devices.
In a typical application, the transmitter circuit may include a microcontroller to process button presses from a keypad or interface. This microcontroller generates the appropriate pulse-width modulation (PWM) output to drive the IR LED. The receiver circuit, on the other hand, is usually connected to a microcontroller or a simple relay driver circuit that interprets the received signals and activates the corresponding output, such as turning a device on or off.
For enhanced functionality, additional components such as capacitors, resistors, and diodes may be integrated into the circuit to filter noise and stabilize the operation. The power supply for both the transmitter and receiver can be provided by batteries or an external power source, depending on the design requirements.
Overall, the on-off infrared remote control circuit exemplifies a practical application of infrared technology in consumer electronics, providing convenience and ease of use in everyday devices.On-off Infrared Remote Control Circuit Most homes today have at least a few infrared remote controls, whether they be for the television, the video recorder, the stereo, etc. Despite that fact, who among us has not cursed the li.. 🔗 External reference